Freemium apps offer users basic features at no cost while charging for premium upgrades, attracting a larger audience and encouraging in-app purchases. Paid apps require an upfront purchase, ensuring immediate revenue but potentially limiting user acquisition due to the initial cost barrier. Choosing between freemium and paid models depends on the target market, app functionality, and long-term monetization goals.
Table of Comparison
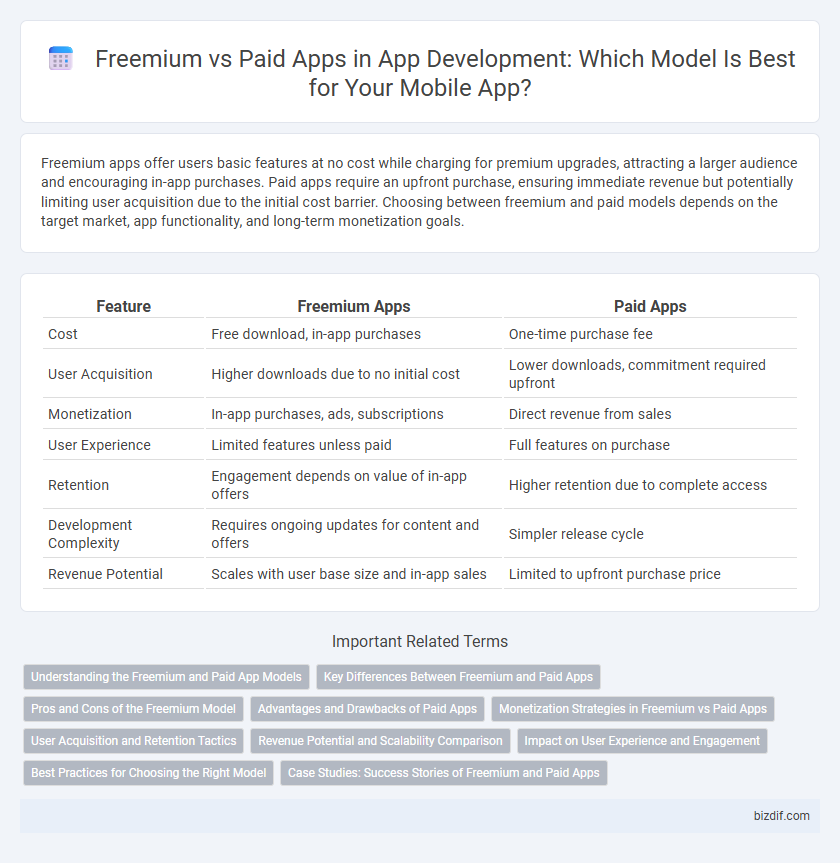
| Feature | Freemium Apps | Paid Apps |
|---|---|---|
| Cost | Free download, in-app purchases | One-time purchase fee |
| User Acquisition | Higher downloads due to no initial cost | Lower downloads, commitment required upfront |
| Monetization | In-app purchases, ads, subscriptions | Direct revenue from sales |
| User Experience | Limited features unless paid | Full features on purchase |
| Retention | Engagement depends on value of in-app offers | Higher retention due to complete access |
| Development Complexity | Requires ongoing updates for content and offers | Simpler release cycle |
| Revenue Potential | Scales with user base size and in-app sales | Limited to upfront purchase price |
Understanding the Freemium and Paid App Models
Freemium app models offer basic features for free while monetizing through in-app purchases or premium upgrades, attracting a larger user base by lowering entry barriers. Paid apps require an upfront purchase, providing immediate revenue and often appealing to users seeking a complete product without ongoing costs. Understanding these models helps developers optimize user acquisition strategies and maximize revenue streams by aligning app features with target audience preferences.
Key Differences Between Freemium and Paid Apps
Freemium apps offer basic features for free with optional in-app purchases or subscriptions to unlock premium content, whereas paid apps require upfront payment for full access. Freemium models often generate revenue through microtransactions and ads, while paid apps rely on initial sales revenue. User acquisition tends to be higher for freemium apps due to zero entry cost, but paid apps may provide a more consistent revenue stream per user.
Pros and Cons of the Freemium Model
The freemium model in app development allows users to access basic features at no cost, significantly increasing initial downloads and user engagement. However, relying on in-app purchases or ads for revenue can limit profitability and frustrate users who desire a seamless experience. Balancing free content with premium features is essential to converting users while maintaining satisfaction and long-term retention.
Advantages and Drawbacks of Paid Apps
Paid apps generate immediate revenue through upfront purchases, ensuring a steady income stream for developers. These apps often provide a higher quality experience with no ads or in-app purchases, enhancing user satisfaction and trust. However, the paywall can significantly limit the user base, reducing exposure and potentially slowing download rates compared to freemium models.
Monetization Strategies in Freemium vs Paid Apps
Freemium apps monetize primarily through in-app purchases, subscriptions, and ads, allowing users to access basic features for free while paying for premium content or enhanced functionality. Paid apps generate revenue upfront through one-time purchases, often relying on delivering a complete experience without additional charges. Monetization strategies in freemium models emphasize user retention and lifetime value, whereas paid apps focus on optimizing initial download conversion and market price positioning.
User Acquisition and Retention Tactics
Freemium apps leverage free access to attract a wider user base, using in-app purchases and premium features to boost revenue while enhancing retention through continuous content updates and personalized user experiences. Paid apps rely on upfront payment which often results in a more committed user base, emphasizing transparent value propositions and exceptional early experiences to maximize acquisition and sustain long-term retention. Optimizing user acquisition for paid apps involves targeted marketing and clear benefits, whereas freemium models focus on funneling free users into paying customers through strategic feature gating and engagement metrics.
Revenue Potential and Scalability Comparison
Freemium apps offer higher scalability by attracting a larger user base through free access with optional in-app purchases, generating diverse revenue streams from ads and premium features. Paid apps rely on upfront payments, limiting user acquisition but ensuring immediate revenue per download. While freemium models maximize lifetime value and scalability, paid apps provide predictable and straightforward revenue, impacting monetization strategies in app development.
Impact on User Experience and Engagement
Freemium apps enhance user experience by offering free access to basic features, encouraging initial downloads and prolonged engagement through optional in-app purchases. Paid apps provide a seamless, ad-free environment from the start, appealing to users seeking premium quality without interruptions. User engagement in freemium models tends to be higher due to continuous feature updates and monetization prompts, whereas paid apps rely on upfront investment to ensure commitment and satisfaction.
Best Practices for Choosing the Right Model
Choosing the right monetization model between freemium and paid apps hinges on understanding user behavior, market demand, and app functionality. Freemium apps excel in attracting a wide user base by offering core features for free while generating revenue through in-app purchases and subscriptions. Paid apps work best for niche markets where users expect full-feature access upfront, emphasizing high-quality, value-driven experiences to justify the initial cost.
Case Studies: Success Stories of Freemium and Paid Apps
Case studies reveal that freemium apps like Spotify and Candy Crush leverage a large user base through free access, converting a portion into paying customers via premium features, driving significant revenue growth. Paid apps such as Calm and Procreate demonstrate sustained income from upfront purchases by targeting niche markets with high-value content and user trust. Data shows freemium models excel in user acquisition and long-term engagement, while paid apps benefit from immediate monetization and reduced churn.
Freemium vs Paid Apps Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com