Manual testing provides a hands-on approach allowing testers to explore the app's usability and detect unexpected issues through real-time interaction. Automated testing accelerates the development process by executing predefined test scripts, ensuring consistent and repeatable validation of features. Combining both methods enhances app quality by balancing thorough human insight with efficient, scalable test coverage.
Table of Comparison
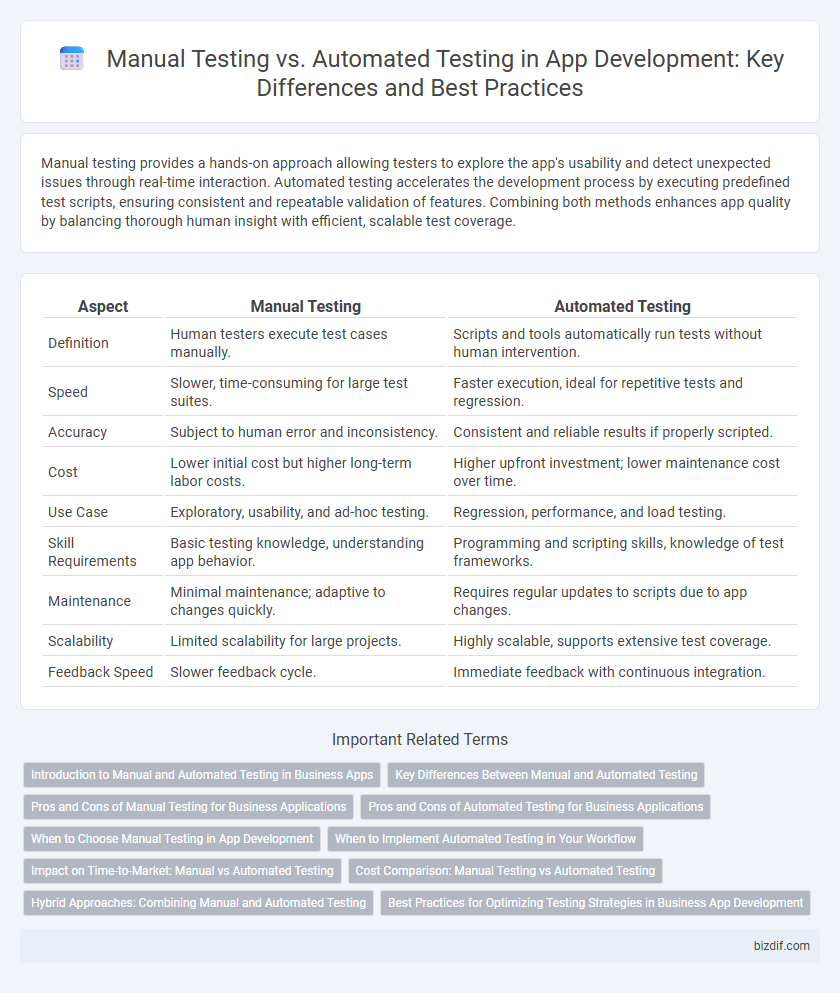
| Aspect | Manual Testing | Automated Testing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Human testers execute test cases manually. | Scripts and tools automatically run tests without human intervention. |
| Speed | Slower, time-consuming for large test suites. | Faster execution, ideal for repetitive tests and regression. |
| Accuracy | Subject to human error and inconsistency. | Consistent and reliable results if properly scripted. |
| Cost | Lower initial cost but higher long-term labor costs. | Higher upfront investment; lower maintenance cost over time. |
| Use Case | Exploratory, usability, and ad-hoc testing. | Regression, performance, and load testing. |
| Skill Requirements | Basic testing knowledge, understanding app behavior. | Programming and scripting skills, knowledge of test frameworks. |
| Maintenance | Minimal maintenance; adaptive to changes quickly. | Requires regular updates to scripts due to app changes. |
| Scalability | Limited scalability for large projects. | Highly scalable, supports extensive test coverage. |
| Feedback Speed | Slower feedback cycle. | Immediate feedback with continuous integration. |
Introduction to Manual and Automated Testing in Business Apps
Manual testing in business apps involves human testers executing test cases without automation tools, ensuring real-time feedback on user experience and functionality. Automated testing uses software scripts and tools to perform repetitive and regression tests efficiently, increasing test coverage and reducing human error. Both methods are critical in app development for identifying defects and ensuring quality, balancing speed with accuracy.
Key Differences Between Manual and Automated Testing
Manual testing requires human involvement to execute test cases and identify software defects, relying heavily on human observation and intuition. Automated testing uses scripts and tools like Selenium or Appium to perform repetitive tasks, ensuring faster execution and higher accuracy in regression testing. Key differences include time efficiency, repeatability, and error detection capabilities, where automated testing excels in large-scale and complex app environments.
Pros and Cons of Manual Testing for Business Applications
Manual testing in business app development offers precise human insight to identify user interface issues and complex usability problems that automated tests might overlook. It demands more time and resources, increasing costs and slowing deployment cycles, especially for extensive or frequently updated applications. However, manual testing excels in exploring unexpected behaviors and providing nuanced feedback crucial for improving user experience.
Pros and Cons of Automated Testing for Business Applications
Automated testing in business applications significantly reduces testing time and increases coverage by executing repetitive test cases efficiently, ensuring faster release cycles. It minimizes human error and provides consistent, repeatable results, enhancing overall software quality and reliability. However, the initial setup cost and maintenance of automated test scripts require substantial investment and technical expertise, potentially limiting flexibility when dealing with dynamic user interfaces or frequent requirement changes.
When to Choose Manual Testing in App Development
Manual testing is essential in app development when evaluating user interfaces, exploratory testing, and usability to catch issues that automated scripts may miss. It is ideal for ad-hoc scenarios and early-stage development where test cases frequently change. Choosing manual testing ensures thorough assessment of user experience and unexpected bugs before automating repetitive tasks.
When to Implement Automated Testing in Your Workflow
Automated testing should be implemented when repetitive test cases need to be executed frequently, enabling faster feedback during continuous integration and deployment. It is most beneficial in regression testing, performance testing, and large-scale projects where manual testing would be time-consuming and error-prone. Integrating automated testing early in the development cycle enhances code quality and accelerates release cycles.
Impact on Time-to-Market: Manual vs Automated Testing
Manual testing requires significant time investment due to repetitive execution and detailed human oversight, often leading to slower feedback and extended time-to-market for apps. Automated testing accelerates release cycles by enabling rapid, consistent, and repeatable test execution, significantly reducing regression testing time and supporting continuous integration workflows. Development teams leveraging automated testing typically achieve faster iterations and higher deployment frequency, directly impacting overall time-to-market efficiency.
Cost Comparison: Manual Testing vs Automated Testing
Manual testing incurs higher long-term costs due to repetitive labor and slower execution, making it less efficient for extensive or frequent test cycles. Automated testing requires an initial investment in tools and script development but reduces costs over time by enabling faster execution and repeatability. Companies often find automated testing more cost-effective for large-scale app development projects with continuous integration and frequent updates.
Hybrid Approaches: Combining Manual and Automated Testing
Hybrid testing in app development integrates manual testing's adaptability with the speed and accuracy of automated testing, enhancing overall test coverage and defect detection. By strategically allocating repetitive tasks to automation and complex scenarios to manual testers, teams achieve efficient resource utilization and faster release cycles. This approach optimizes quality assurance by balancing human insight with technological precision.
Best Practices for Optimizing Testing Strategies in Business App Development
Manual testing in business app development offers detailed user experience insights but requires significant time and human resources. Automated testing enhances efficiency by rapidly executing repetitive test cases and ensuring consistent coverage, especially in regression and load testing. Best practices involve a hybrid approach that leverages automation for routine validations while reserving manual testing for exploratory, usability, and complex scenario assessments to optimize quality and resource allocation.
Manual Testing vs Automated Testing Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com