Native apps deliver superior performance and seamless user experience by utilizing platform-specific languages and tools, ensuring full access to device features. Hybrid apps allow faster development and cross-platform compatibility by combining web technologies within a native container, but may face limitations in speed and UI consistency. Choosing between native and hybrid app development depends on project requirements, budget, and desired user experience.
Table of Comparison
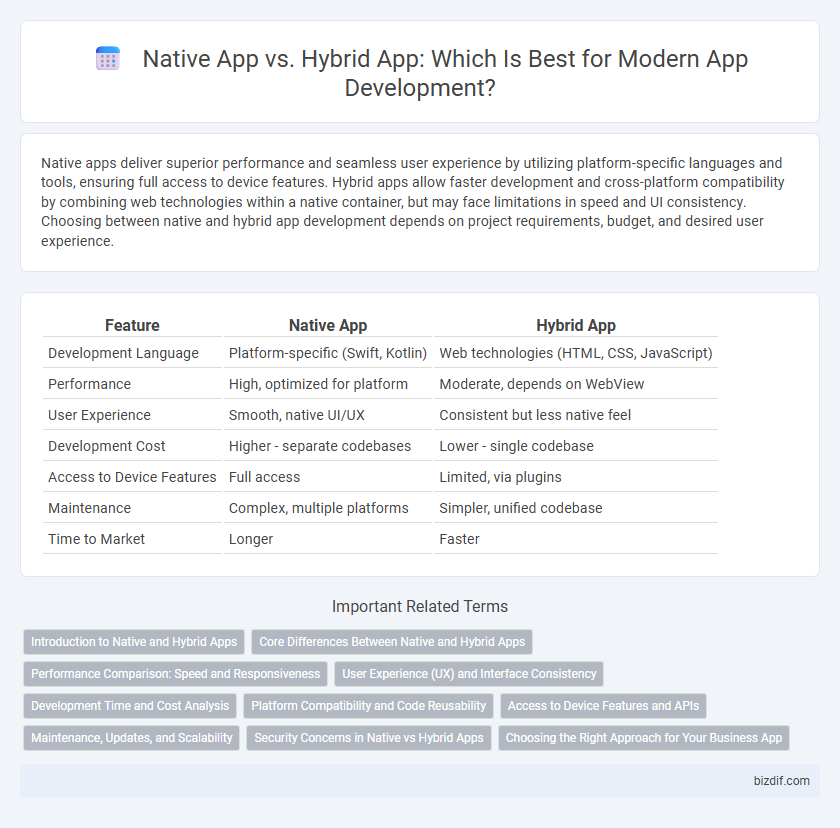
| Feature | Native App | Hybrid App |
|---|---|---|
| Development Language | Platform-specific (Swift, Kotlin) | Web technologies (HTML, CSS, JavaScript) |
| Performance | High, optimized for platform | Moderate, depends on WebView |
| User Experience | Smooth, native UI/UX | Consistent but less native feel |
| Development Cost | Higher - separate codebases | Lower - single codebase |
| Access to Device Features | Full access | Limited, via plugins |
| Maintenance | Complex, multiple platforms | Simpler, unified codebase |
| Time to Market | Longer | Faster |
Introduction to Native and Hybrid Apps
Native apps are developed specifically for a single platform using platform-specific languages like Swift for iOS or Kotlin for Android, offering high performance and seamless integration with device features. Hybrid apps combine web technologies such as HTML, CSS, and JavaScript within a native container, enabling cross-platform compatibility and faster development cycles. Choosing between native and hybrid approaches depends on factors like performance requirements, development budget, and target audience.
Core Differences Between Native and Hybrid Apps
Native apps are developed specifically for a single platform using platform-specific programming languages like Swift for iOS and Kotlin for Android, offering superior performance and seamless access to device features. Hybrid apps leverage web technologies such as HTML, CSS, and JavaScript wrapped in a native container, allowing cross-platform compatibility but often resulting in slower performance and limited access to device-specific functionalities. Core differences include development costs, user experience, performance optimization, and maintainability, with native apps excelling in speed and integration while hybrid apps provide faster deployment across multiple platforms.
Performance Comparison: Speed and Responsiveness
Native apps deliver superior speed and responsiveness by leveraging platform-specific APIs and optimized code, resulting in smooth animations and faster load times. Hybrid apps, relying on web technologies and an additional abstraction layer, often experience latency and less fluid user interactions. Performance discrepancies become more noticeable in graphics-intensive or real-time applications where native development excels.
User Experience (UX) and Interface Consistency
Native app development offers superior user experience (UX) due to optimized performance and seamless integration with device-specific features, ensuring smooth animations and faster load times. Hybrid apps, while cost-effective and easier to maintain across multiple platforms, often struggle with interface consistency, as they rely on web technologies that can cause variations in UI elements across different devices. Prioritizing UX in native apps results in more intuitive navigation and a cohesive interface that aligns perfectly with the operating system's design standards.
Development Time and Cost Analysis
Native app development requires separate coding for iOS and Android platforms, increasing both development time and costs, while hybrid apps use a single codebase for multiple platforms, significantly reducing these factors. The use of frameworks like React Native and Flutter allows hybrid apps to accelerate deployment and minimize resource allocation without sacrificing substantial performance. Budget-conscious projects prioritize hybrid app development for faster turnaround, whereas native apps are often reserved for high-performance requirements despite increased investment.
Platform Compatibility and Code Reusability
Native app development offers superior platform compatibility by leveraging specific operating system features, resulting in optimized performance and seamless user experience on iOS or Android devices. Hybrid apps enable extensive code reusability across multiple platforms by utilizing web technologies like HTML, CSS, and JavaScript, which reduces development time and costs. However, hybrid frameworks may face limitations in accessing native device capabilities and can sometimes compromise app responsiveness compared to native solutions.
Access to Device Features and APIs
Native apps provide direct access to device features and APIs, enabling seamless integration with hardware components like GPS, camera, and sensors for optimal performance. Hybrid apps rely on plugins and third-party frameworks to access device capabilities, which can introduce latency and limit the range of supported features. Native development ensures faster, more reliable interactions with device functionalities, crucial for performance-intensive applications.
Maintenance, Updates, and Scalability
Native apps offer streamlined maintenance and updates through platform-specific tools, ensuring optimal performance and faster issue resolution. Hybrid apps require managing multiple frameworks and plugins, potentially increasing complexity and slower update cycles. Scalability is more efficient in native apps due to direct access to device features and optimized resource management, while hybrid apps may face limitations in performance as the application grows.
Security Concerns in Native vs Hybrid Apps
Native apps provide enhanced security by leveraging platform-specific security features such as biometric authentication, secure storage, and sandboxing, reducing vulnerabilities compared to hybrid apps. Hybrid apps face increased security risks due to their reliance on web technologies, making them more susceptible to code injection and man-in-the-middle attacks. Developers must implement robust encryption, secure APIs, and frequent security audits to mitigate hybrid app vulnerabilities effectively.
Choosing the Right Approach for Your Business App
Native apps offer superior performance and seamless integration with device features, making them ideal for businesses requiring high responsiveness and user experience. Hybrid apps provide cost-effective development across multiple platforms with shared codebases, suitable for startups and businesses needing faster market entry. Evaluating your target audience, budget, and required functionality is crucial when choosing between native and hybrid app development approaches.
Native app vs Hybrid app Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com