Boutique fashion houses prioritize unique, high-quality designs crafted with meticulous attention to detail, offering exclusive collections that often emphasize sustainability and artisanal techniques. In contrast, fast fashion retailers focus on rapidly producing trendy, affordable clothing in large volumes, frequently sacrificing durability and ethical production standards for speed and cost-efficiency. Choosing a boutique fashion house ensures a personalized shopping experience and investment in timeless, thoughtfully-made garments.
Table of Comparison
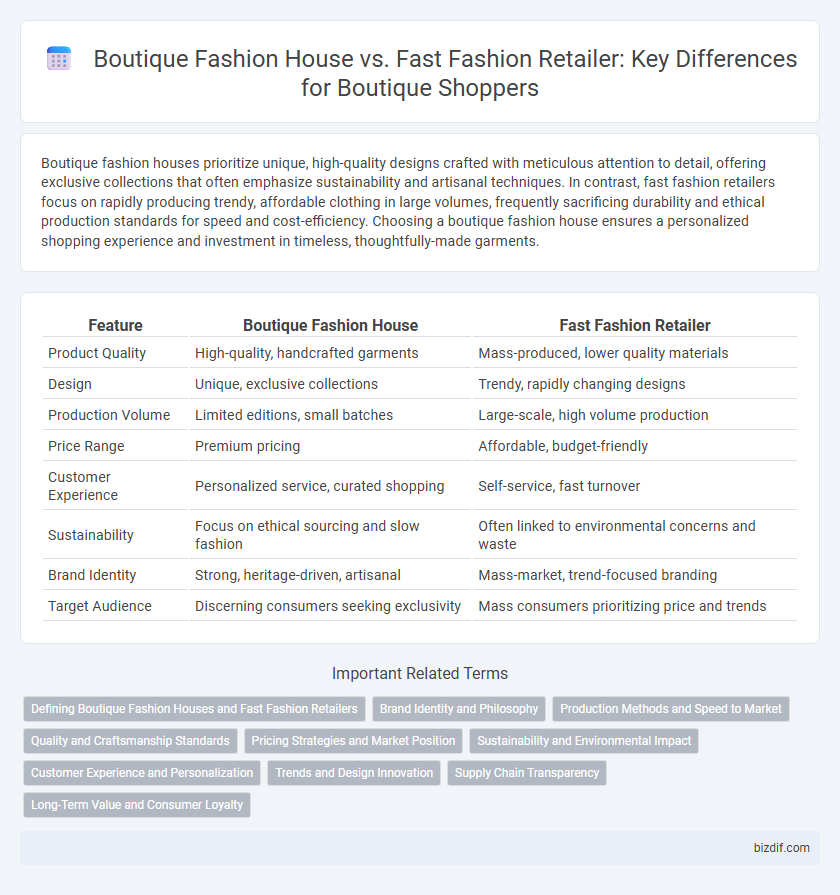
| Feature | Boutique Fashion House | Fast Fashion Retailer |
|---|---|---|
| Product Quality | High-quality, handcrafted garments | Mass-produced, lower quality materials |
| Design | Unique, exclusive collections | Trendy, rapidly changing designs |
| Production Volume | Limited editions, small batches | Large-scale, high volume production |
| Price Range | Premium pricing | Affordable, budget-friendly |
| Customer Experience | Personalized service, curated shopping | Self-service, fast turnover |
| Sustainability | Focus on ethical sourcing and slow fashion | Often linked to environmental concerns and waste |
| Brand Identity | Strong, heritage-driven, artisanal | Mass-market, trend-focused branding |
| Target Audience | Discerning consumers seeking exclusivity | Mass consumers prioritizing price and trends |
Defining Boutique Fashion Houses and Fast Fashion Retailers
Boutique fashion houses specialize in curated, limited-edition collections that emphasize unique design, high-quality craftsmanship, and personalized customer experiences. Fast fashion retailers prioritize mass production, rapid trend replication, and affordability, often sacrificing material durability and exclusivity. Boutique brands typically cater to niche markets seeking exclusivity, whereas fast fashion targets mainstream consumers driven by continuously changing trends.
Brand Identity and Philosophy
Boutique fashion houses emphasize exclusive craftsmanship and a unique brand identity rooted in artistic vision and personalized customer experiences. Fast fashion retailers prioritize mass production, rapid trend replication, and affordability, often sacrificing originality and sustainability. The boutique approach fosters strong emotional connections and brand loyalty, contrasting with fast fashion's focus on volume and trends.
Production Methods and Speed to Market
Boutique fashion houses prioritize artisanal production methods with limited, high-quality runs that emphasize craftsmanship and unique design, contrasting sharply with fast fashion retailers that rely on mass production and automated processes to rapidly replicate trends. The speed to market for boutique fashion is considerably slower, allowing for meticulous attention to detail and exclusivity, whereas fast fashion brands expedite product turnover through streamlined supply chains and rapid inventory replenishment. This divergence affects not only product uniqueness but also sustainability, as boutique fashion often incorporates ethical sourcing while fast fashion faces criticism for wasteful practices.
Quality and Craftsmanship Standards
Boutique fashion houses prioritize exceptional quality and meticulous craftsmanship, often employing skilled artisans and using premium materials to create unique, durable pieces. In contrast, fast fashion retailers focus on rapid production and affordability, resulting in lower-quality garments with less attention to detail and durability. This difference in standards significantly impacts product longevity, customer satisfaction, and sustainability.
Pricing Strategies and Market Position
Boutique fashion houses typically adopt premium pricing strategies, emphasizing exclusivity, craftsmanship, and unique designs to target affluent consumers seeking high-quality, limited-edition pieces. In contrast, fast fashion retailers leverage competitive pricing and rapid product turnover to appeal to price-sensitive customers, prioritizing trends and volume sales over product longevity. The market position of boutique brands centers on brand prestige and niche appeal, while fast fashion occupies the mass market with wide accessibility and affordability.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Boutique fashion houses emphasize sustainable practices by using ethically sourced materials and promoting slow fashion, reducing environmental impact through limited production runs and higher quality garments. Fast fashion retailers prioritize rapid production and low costs, resulting in excessive waste, higher carbon emissions, and significant resource depletion. The boutique model supports circular economy principles and minimizes landfill contributions, contrasting sharply with the fast fashion industry's throwaway culture.
Customer Experience and Personalization
Boutique fashion houses excel in delivering personalized customer experiences by offering curated collections tailored to individual tastes and exclusive styles often unavailable in fast fashion retailers. Their attentive service includes custom fittings, one-on-one consultations, and unique product recommendations that enhance customer loyalty and satisfaction. In contrast, fast fashion retailers prioritize mass production and trend replication, providing limited personalization and a more transactional shopping experience focused on speed and affordability.
Trends and Design Innovation
Boutique fashion houses prioritize exclusive, trend-setting designs with a strong emphasis on craftsmanship and individuality, often producing limited-edition collections that reflect cutting-edge innovation. In contrast, fast fashion retailers focus on rapidly replicating popular trends at mass scale, prioritizing speed and affordability over originality and quality. This fundamental difference drives boutiques to lead in unique stylistic evolution, while fast fashion sustains high-volume access to mainstream styles.
Supply Chain Transparency
Boutique fashion houses prioritize supply chain transparency by sourcing materials ethically from specialized artisans and maintaining detailed provenance records to ensure quality and sustainability. Fast fashion retailers often rely on complex, opaque supply chains with limited visibility, leading to challenges in verifying ethical labor practices and environmental impact. Transparent supply chains in boutique fashion enhance consumer trust and support sustainable production models, contrasting with the high-volume, rapid turnaround strategies of fast fashion.
Long-Term Value and Consumer Loyalty
Boutique fashion houses prioritize craftsmanship, exclusive designs, and personalized customer experiences, fostering long-term value through high-quality products that age well and maintain relevance. Fast fashion retailers emphasize rapid production and low-cost trends, leading to fleeting consumer engagement and limited brand loyalty due to frequent style turnover and lower product durability. Investing in boutique brands often results in stronger customer loyalty and sustainable value appreciation compared to the disposability-driven model of fast fashion.
Boutique fashion house vs Fast fashion retailer Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com