Certified kitchens meet strict health and safety standards set by local authorities, ensuring legal compliance for food preparation and service. Commissary kitchens provide shared commercial kitchen spaces that cater to small food businesses needing professional-grade facilities without the overhead of owning a dedicated kitchen. Choosing between a certified kitchen and a commissary kitchen depends on regulatory requirements, budget constraints, and the scale of the catering operation.
Table of Comparison
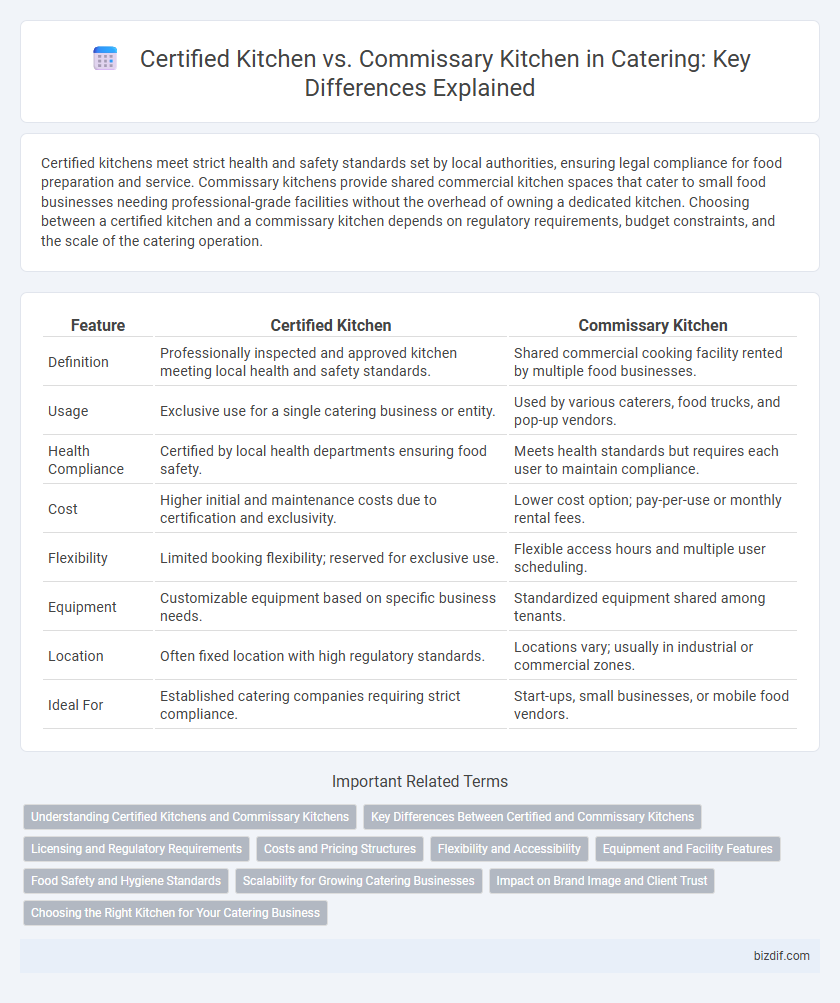
| Feature | Certified Kitchen | Commissary Kitchen |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Professionally inspected and approved kitchen meeting local health and safety standards. | Shared commercial cooking facility rented by multiple food businesses. |
| Usage | Exclusive use for a single catering business or entity. | Used by various caterers, food trucks, and pop-up vendors. |
| Health Compliance | Certified by local health departments ensuring food safety. | Meets health standards but requires each user to maintain compliance. |
| Cost | Higher initial and maintenance costs due to certification and exclusivity. | Lower cost option; pay-per-use or monthly rental fees. |
| Flexibility | Limited booking flexibility; reserved for exclusive use. | Flexible access hours and multiple user scheduling. |
| Equipment | Customizable equipment based on specific business needs. | Standardized equipment shared among tenants. |
| Location | Often fixed location with high regulatory standards. | Locations vary; usually in industrial or commercial zones. |
| Ideal For | Established catering companies requiring strict compliance. | Start-ups, small businesses, or mobile food vendors. |
Understanding Certified Kitchens and Commissary Kitchens
Certified kitchens comply with local health regulations and possess official permits to prepare and serve food commercially, ensuring safety and hygiene standards are met. Commissary kitchens provide shared cooking spaces for multiple food businesses, equipped with professional-grade appliances, and typically undergo regular inspections to maintain compliance. Understanding the distinctions between these two is essential for food entrepreneurs seeking legal operation and efficient resource use in the catering industry.
Key Differences Between Certified and Commissary Kitchens
Certified kitchens undergo official inspections to meet health and safety regulations, ensuring compliance with local public health standards, while commissary kitchens serve as shared commercial spaces providing licensed facilities for multiple food businesses. Certified kitchens offer a guaranteed sanitized environment with certified food handling processes, whereas commissary kitchens emphasize resource-sharing like equipment, storage, and prep areas without inherently assuring individual certifications. Key differences include regulatory certification status, ownership and access, liability responsibilities, and specific suitability for catering operations or food truck preparation.
Licensing and Regulatory Requirements
Certified kitchens comply with stringent health and safety regulations enforced by local health departments, ensuring proper licensing for food preparation and handling. Commissary kitchens, often used by mobile or pop-up catering operations, must meet specific regulatory requirements, including sanitation standards and waste management protocols, to maintain their licensed status. Both types of kitchens require continuous inspections and certification updates to adhere to evolving food safety laws and licensing mandates.
Costs and Pricing Structures
Certified kitchens typically involve higher upfront costs due to necessary health inspections, licensing fees, and maintaining compliance with food safety regulations, making them more expensive for small-scale caterers. Commissary kitchens offer a cost-effective alternative by providing shared commercial kitchen space with flexible rental pricing, reducing overhead and allowing caterers to pay only for the time and resources they use. Understanding the pricing structures and regulatory requirements of certified kitchens versus commissary kitchens is crucial for catering businesses aiming to optimize operational costs.
Flexibility and Accessibility
Certified kitchens offer greater flexibility by meeting strict health and safety regulations, allowing caterers to operate in various locations without compromising food quality. Commissary kitchens provide accessibility through shared, fully equipped spaces that reduce startup costs and enable caterers to scale operations efficiently. Both options support diverse catering needs, but certified kitchens cater to stringent compliance requirements while commissary kitchens emphasize communal resource sharing.
Equipment and Facility Features
Certified kitchens comply with strict health and safety regulations, featuring commercial-grade equipment, approved ventilation systems, and sanitation stations essential for food safety certification. Commissary kitchens provide a shared facility with industrial appliances, ample storage, and prep areas designed to accommodate multiple food businesses under one roof. Both kitchen types offer professional-grade equipment but differ in exclusivity and regulatory inspection frequency, impacting client trust and operational efficiency.
Food Safety and Hygiene Standards
Certified kitchens adhere to strict food safety and hygiene standards regulated by health authorities, ensuring proper sanitation, temperature control, and allergen management. Commissary kitchens often provide shared commercial cooking spaces that meet basic regulatory requirements but may vary in oversight and cleanliness protocols depending on location and management. Businesses prioritizing food safety typically select certified kitchens for consistent compliance with rigorous health inspections and certifications.
Scalability for Growing Catering Businesses
Certified kitchens provide stringent health and safety compliance, essential for scaling catering businesses seeking trust and regulatory approval. Commissary kitchens offer flexible, shared spaces with access to professional-grade equipment, allowing growing caterers to expand operations without heavy capital investment. Choosing between them depends on the business's growth stage, budget, and demand for scalable, compliant kitchen infrastructure.
Impact on Brand Image and Client Trust
Certified kitchens adhere to stringent health and safety regulations, enhancing brand credibility and fostering client trust through verified compliance. Commissary kitchens provide shared culinary spaces that may lack formal certification, potentially raising concerns about food safety and consistency in clients' perceptions. Utilizing a certified kitchen reinforces professionalism and commitment to quality, directly impacting positive brand image and client confidence in catering services.
Choosing the Right Kitchen for Your Catering Business
Selecting between a certified kitchen and a commissary kitchen significantly impacts your catering business's operational efficiency and compliance with health regulations. Certified kitchens meet stringent local health codes and offer reliability for food safety, while commissary kitchens provide shared, fully equipped spaces that reduce overhead costs and allow flexibility for small to medium catering operations. Evaluating your business size, budget, and growth plans ensures you choose a kitchen environment that supports quality service and scalable food production.
Certified kitchen vs Commissary kitchen Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com