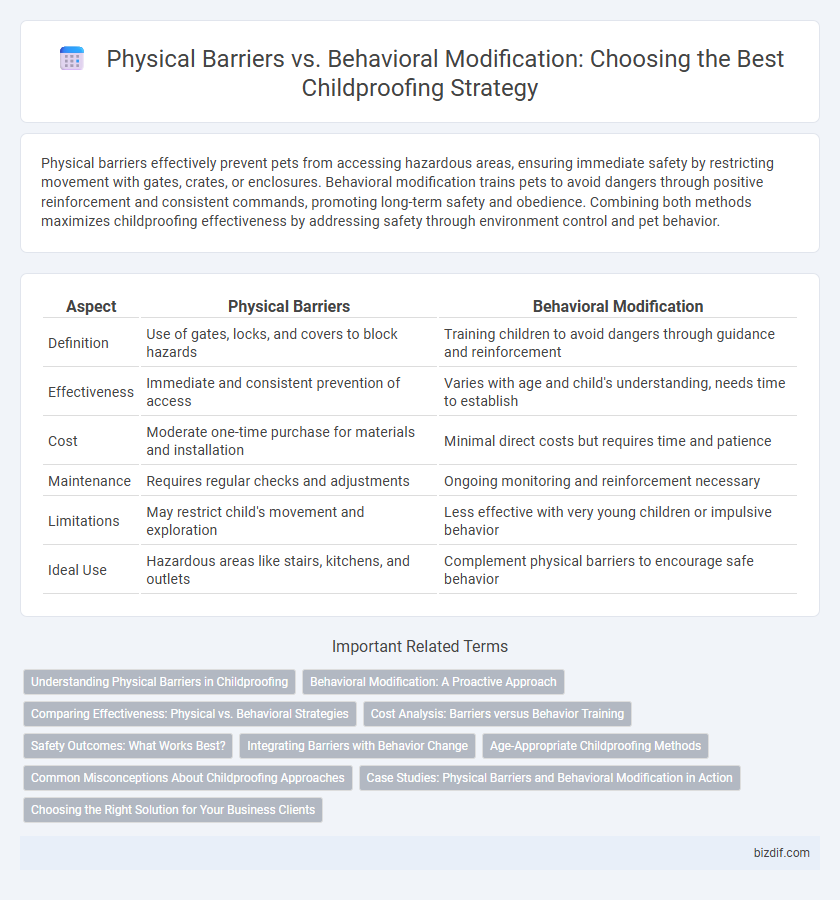
Physical barriers effectively prevent pets from accessing hazardous areas, ensuring immediate safety by restricting movement with gates, crates, or enclosures. Behavioral modification trains pets to avoid dangers through positive reinforcement and consistent commands, promoting long-term safety and obedience. Combining both methods maximizes childproofing effectiveness by addressing safety through environment control and pet behavior.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Physical Barriers | Behavioral Modification |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Use of gates, locks, and covers to block hazards | Training children to avoid dangers through guidance and reinforcement |
| Effectiveness | Immediate and consistent prevention of access | Varies with age and child's understanding, needs time to establish |
| Cost | Moderate one-time purchase for materials and installation | Minimal direct costs but requires time and patience |
| Maintenance | Requires regular checks and adjustments | Ongoing monitoring and reinforcement necessary |
| Limitations | May restrict child's movement and exploration | Less effective with very young children or impulsive behavior |
| Ideal Use | Hazardous areas like stairs, kitchens, and outlets | Complement physical barriers to encourage safe behavior |
Understanding Physical Barriers in Childproofing
Physical barriers in childproofing provide a tangible, effective means of preventing access to hazardous areas such as staircases, kitchens, and electrical outlets, ensuring children's safety by limiting their physical reach. These barriers include safety gates, outlet covers, and cabinet locks, which create secure boundaries that do not rely on a child's compliance or understanding. Understanding the strategic placement and durability of physical barriers is crucial for maximizing protection and minimizing potential risks within the home environment.
Behavioral Modification: A Proactive Approach
Behavioral modification in childproofing emphasizes teaching children safe habits to reduce risks, promoting long-term safety through consistent reinforcement rather than solely relying on physical barriers. This proactive approach encourages awareness and responsibility, gradually decreasing dependence on external safety measures. Evidence shows that combining behavioral strategies with selective physical barriers maximizes effectiveness in preventing accidents.
Comparing Effectiveness: Physical vs. Behavioral Strategies
Physical barriers provide immediate, tangible protection by restricting access to hazardous areas, ensuring child safety through environmental control. Behavioral modification focuses on teaching children safe habits and awareness, fostering long-term risk recognition and self-regulation. Studies indicate a combined approach, integrating both physical barriers and behavioral strategies, delivers the most comprehensive effectiveness in childproofing.
Cost Analysis: Barriers versus Behavior Training
Physical barriers for childproofing, such as safety gates and cabinet locks, typically involve a one-time purchase cost ranging from $20 to $150, offering immediate protection with minimal maintenance. Behavioral modification training, involving techniques to teach children safety awareness, may require multiple sessions with costs averaging $50 to $100 per hour and relies on consistent reinforcement over time. Cost analysis shows physical barriers provide a more cost-effective and reliable solution for immediate risk reduction, while behavior training can complement barriers but entails higher long-term expenses.
Safety Outcomes: What Works Best?
Physical barriers such as safety gates, cabinet locks, and window guards provide immediate and reliable protection by restricting access to hazardous areas, significantly reducing injury risks in children. Behavioral modification techniques, including teaching children about dangers and reinforcing safe behaviors, contribute to long-term safety awareness but often require consistent supervision and reinforcement to be effective. Combining physical barriers with behavioral strategies yields the best safety outcomes, ensuring both environmental control and cognitive understanding of risks.
Integrating Barriers with Behavior Change
Integrating physical barriers with behavioral modification enhances childproofing effectiveness by combining tangible safety measures with proactive parenting strategies. Physical barriers such as safety gates and cabinet locks prevent immediate hazards, while behavioral modification encourages children to understand and respect safety rules, fostering long-term cautious habits. This dual approach reduces risks more comprehensively than relying solely on barriers or behavior change.
Age-Appropriate Childproofing Methods
Age-appropriate childproofing methods emphasize both physical barriers, such as safety gates and cabinet locks, and behavioral modification techniques tailored to the developmental stage of the child. Physical barriers provide immediate protection by restricting access to hazards, while behavioral modification focuses on teaching children safe habits and awareness over time. Combining these approaches ensures a comprehensive safety strategy that adapts as the child's abilities and understanding evolve.
Common Misconceptions About Childproofing Approaches
Physical barriers and behavioral modification are often misunderstood as interchangeable solutions in childproofing, yet they serve distinct roles in safety strategies. Many believe physical barriers alone guarantee child safety, overlooking the critical role of behavioral modification in teaching children safe habits and awareness. Effective childproofing combines robust physical barriers with consistent behavioral reinforcement to address both environmental dangers and the child's growing understanding of risks.
Case Studies: Physical Barriers and Behavioral Modification in Action
Case studies demonstrate that physical barriers, such as safety gates and cabinet locks, effectively prevent access to hazardous areas, reducing injury rates by up to 45%. Behavioral modification techniques, including consistent supervision and teaching children safety rules, complement these barriers by promoting long-term awareness and compliance. Combining both approaches results in a significant decrease in accidents, highlighting the synergy between environment control and child behavior management.
Choosing the Right Solution for Your Business Clients
Physical barriers provide immediate, tangible protection by restricting access to hazardous areas, making them essential for environments with high-risk elements. Behavioral modification involves training and education to encourage safe practices, ideal for fostering long-term awareness among employees and clients. Combining both strategies ensures comprehensive childproofing solutions tailored to meet specific business needs and compliance requirements.
Physical barriers vs Behavioral modification Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com