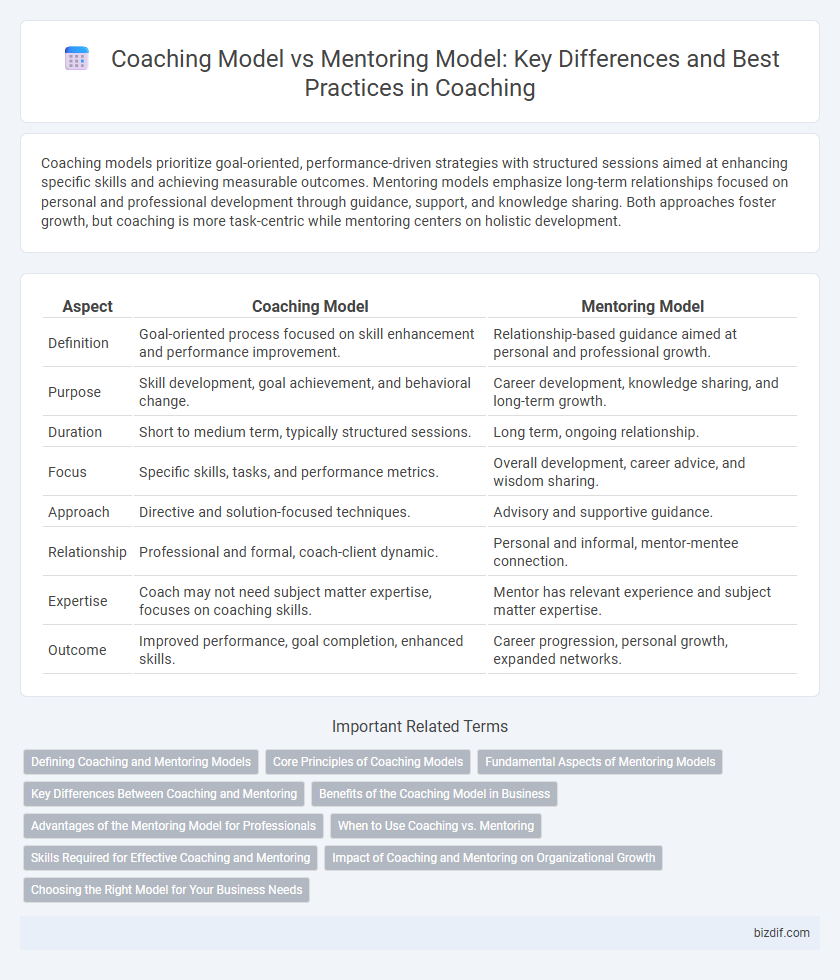
Coaching models prioritize goal-oriented, performance-driven strategies with structured sessions aimed at enhancing specific skills and achieving measurable outcomes. Mentoring models emphasize long-term relationships focused on personal and professional development through guidance, support, and knowledge sharing. Both approaches foster growth, but coaching is more task-centric while mentoring centers on holistic development.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Coaching Model | Mentoring Model |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Goal-oriented process focused on skill enhancement and performance improvement. | Relationship-based guidance aimed at personal and professional growth. |
| Purpose | Skill development, goal achievement, and behavioral change. | Career development, knowledge sharing, and long-term growth. |
| Duration | Short to medium term, typically structured sessions. | Long term, ongoing relationship. |
| Focus | Specific skills, tasks, and performance metrics. | Overall development, career advice, and wisdom sharing. |
| Approach | Directive and solution-focused techniques. | Advisory and supportive guidance. |
| Relationship | Professional and formal, coach-client dynamic. | Personal and informal, mentor-mentee connection. |
| Expertise | Coach may not need subject matter expertise, focuses on coaching skills. | Mentor has relevant experience and subject matter expertise. |
| Outcome | Improved performance, goal completion, enhanced skills. | Career progression, personal growth, expanded networks. |
Defining Coaching and Mentoring Models
Coaching models emphasize goal-oriented, performance-driven processes where the coach facilitates self-discovery and skill development through structured techniques like GROW and STAR. Mentoring models focus on long-term relationship-building, knowledge transfer, and career guidance typically provided by an experienced mentor sharing insights and expertise. Defining these models highlights coaching's emphasis on empowering individuals to unlock potential versus mentoring's role in personalized support and professional growth.
Core Principles of Coaching Models
Coaching models prioritize active listening, goal-setting, and empowering clients to unlock their own potential through reflective questioning and accountability. They emphasize self-discovery and behavioral change by fostering awareness, responsibility, and forward-thinking strategies. Unlike mentoring models, which often rely on expert advice and experience-sharing, coaching models center on facilitating clients' intrinsic growth and solution-focused mindset.
Fundamental Aspects of Mentoring Models
Mentoring models emphasize long-term relationships centered on personal and professional growth, fostering trust, guidance, and knowledge transfer from experienced mentors to mentees. These models prioritize holistic development, including emotional support, career advice, and skill enhancement within an evolving dialogue. Unlike coaching models that often target performance improvement with structured goals, mentoring models focus on building a nurturing connection that facilitates continuous learning and mutual respect.
Key Differences Between Coaching and Mentoring
Coaching models focus on specific skill development and goal achievement through structured sessions with measurable outcomes, while mentoring models emphasize long-term personal and professional growth via relationship-building and guidance. Coaching typically involves a performance-driven approach with a formal framework, whereas mentoring is more informal, centered on sharing experiences and wisdom. The key difference lies in coaching's task-oriented methodology versus mentoring's holistic support and development.
Benefits of the Coaching Model in Business
The coaching model in business fosters employee development by promoting self-awareness, accountability, and goal-setting, leading to enhanced performance and innovation. Unlike mentoring, coaching offers structured, goal-oriented sessions that empower individuals to unlock their potential through targeted feedback and personalized strategies. Organizations leveraging coaching models report increased employee engagement, improved leadership skills, and measurable productivity gains.
Advantages of the Mentoring Model for Professionals
The mentoring model offers professionals personalized guidance tailored to their career development, fostering long-term growth through knowledge transfer from experienced mentors. It enhances networking opportunities and builds strong professional relationships that support skill advancement and confidence building. This model prioritizes holistic development, addressing both technical skills and emotional intelligence for sustained success.
When to Use Coaching vs. Mentoring
Coaching is most effective when specific skills, performance goals, or behavioral changes need to be developed within a set timeframe, often structured around measurable outcomes. Mentoring is better suited for long-term professional growth, career development, and personal guidance, fostering a deeper relationship based on experience sharing and support. Choose coaching for targeted improvement and short-term objectives, while mentoring aligns with broader growth and ongoing development.
Skills Required for Effective Coaching and Mentoring
Effective coaching requires strong active listening, powerful questioning, and goal-setting skills to facilitate self-discovery and personal growth. In contrast, mentoring demands deep industry knowledge, experience sharing, and relationship-building skills to guide mentees through career development. Both models benefit from empathy, clear communication, and continuous feedback, but coaching leans more on fostering autonomy, while mentoring emphasizes transfer of wisdom.
Impact of Coaching and Mentoring on Organizational Growth
Coaching models emphasize skill development and performance enhancement through structured goal-setting and feedback, driving measurable improvements in employee productivity and engagement. Mentoring models foster long-term professional growth by facilitating knowledge transfer, career guidance, and leadership development, which strengthens organizational culture and talent retention. Organizations leveraging both coaching and mentoring benefit from accelerated innovation, improved workforce capabilities, and sustainable growth trajectories.
Choosing the Right Model for Your Business Needs
Choosing the right model for your business needs involves understanding that the coaching model focuses on unlocking an individual's potential through goal-oriented strategies and skill development. In contrast, the mentoring model emphasizes knowledge transfer and long-term relationship building between an experienced mentor and a mentee. Evaluating your organizational goals, employee development stage, and desired outcomes helps determine whether coaching's performance-driven approach or mentoring's experiential guidance aligns best with your business objectives.
Coaching model vs mentoring model Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com