Age-mixed grouping in daycare environments encourages social development by allowing children to learn from peers of different ages, fostering empathy and leadership skills. Age-segregated grouping, on the other hand, tailors activities to specific developmental stages, ensuring age-appropriate learning and safety. Choosing the right approach depends on balancing social interaction benefits with targeted educational needs.
Table of Comparison
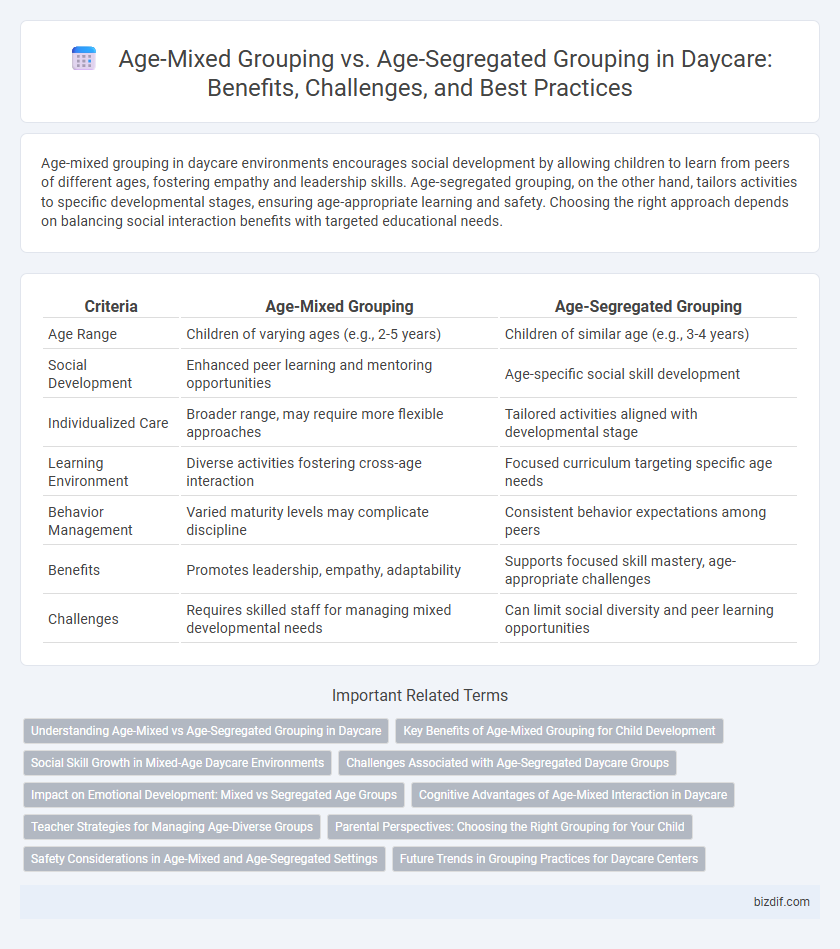
| Criteria | Age-Mixed Grouping | Age-Segregated Grouping |
|---|---|---|
| Age Range | Children of varying ages (e.g., 2-5 years) | Children of similar age (e.g., 3-4 years) |
| Social Development | Enhanced peer learning and mentoring opportunities | Age-specific social skill development |
| Individualized Care | Broader range, may require more flexible approaches | Tailored activities aligned with developmental stage |
| Learning Environment | Diverse activities fostering cross-age interaction | Focused curriculum targeting specific age needs |
| Behavior Management | Varied maturity levels may complicate discipline | Consistent behavior expectations among peers |
| Benefits | Promotes leadership, empathy, adaptability | Supports focused skill mastery, age-appropriate challenges |
| Challenges | Requires skilled staff for managing mixed developmental needs | Can limit social diversity and peer learning opportunities |
Understanding Age-Mixed vs Age-Segregated Grouping in Daycare
Age-mixed grouping in daycare fosters social development by encouraging interactions among children of different ages, promoting empathy, cooperation, and role modeling. In contrast, age-segregated grouping focuses on developmental similarities, allowing targeted activities tailored to specific age ranges that support cognitive and motor skill progression. Understanding the benefits and challenges of both approaches helps caregivers create environments that optimize learning and socialization based on children's developmental needs.
Key Benefits of Age-Mixed Grouping for Child Development
Age-mixed grouping in daycare promotes social-emotional growth by encouraging mentorship and cooperative play among diverse age ranges. Younger children benefit from observing and imitating older peers, accelerating language acquisition and problem-solving skills. This inclusive environment fosters empathy, leadership qualities, and adaptability across developmental stages.
Social Skill Growth in Mixed-Age Daycare Environments
Mixed-age daycare environments significantly enhance social skill development by facilitating peer learning, empathy, and cooperation among children of different ages. Younger children benefit from observing and imitating older peers, while older children develop leadership and nurturing abilities through mentoring. This dynamic interaction fosters communication, problem-solving skills, and emotional intelligence more effectively than age-segregated groupings.
Challenges Associated with Age-Segregated Daycare Groups
Age-segregated daycare groups often face challenges such as limited peer learning opportunities and reduced social skill development because children interact primarily with those at the same developmental stage. This grouping method can lead to increased competition and exclusion among children as age-specific activities may not address individual needs effectively. Furthermore, staff may struggle to provide differentiated instruction and engagement, impacting overall daycare quality and child satisfaction.
Impact on Emotional Development: Mixed vs Segregated Age Groups
Age-mixed grouping in daycare settings fosters emotional development by promoting empathy, patience, and social skills as younger children learn from older peers and older children develop leadership abilities. Age-segregated groups, while providing tailored developmental activities, may limit opportunities for emotional growth through cross-age interactions, potentially reducing children's ability to navigate diverse social dynamics. Research indicates that mixed-age environments enhance emotional resilience and cooperation, contributing to well-rounded social-emotional competence in early childhood.
Cognitive Advantages of Age-Mixed Interaction in Daycare
Age-mixed grouping in daycare promotes cognitive development by encouraging older children to reinforce their knowledge through teaching younger peers, enhancing language and problem-solving skills. Younger children benefit from exposure to advanced social cues and complex vocabulary, accelerating cognitive growth. Studies show that mixed-age interaction fosters empathy and flexible thinking, crucial for overall cognitive advancement in early childhood education.
Teacher Strategies for Managing Age-Diverse Groups
Effective teacher strategies for managing age-mixed daycare groups emphasize differentiated instruction tailored to varied developmental stages, promoting peer learning and social interaction. Implementing flexible routines and personalized activities helps accommodate diverse needs while maintaining group cohesion. Teachers also utilize scaffolding techniques to support younger children's learning while challenging older ones, ensuring engagement across age groups.
Parental Perspectives: Choosing the Right Grouping for Your Child
Parents often weigh the benefits of age-mixed grouping, which fosters social skills and empathy by allowing younger children to learn from older peers, against age-segregated grouping that targets developmentally appropriate activities tailored to specific age ranges. Many caregivers prioritize age-segregated settings for structured learning while appreciating age-mixed environments for promoting natural social interactions and adaptability. Understanding a child's unique temperament and developmental needs guides parents in selecting the most suitable daycare grouping approach.
Safety Considerations in Age-Mixed and Age-Segregated Settings
Age-mixed daycare settings enhance social development but require stringent safety measures to address the physical and emotional differences between age groups, such as closely monitoring activities to prevent accidents among younger children. In age-segregated groupings, tailored safety protocols are easier to implement, as children within similar developmental stages have comparable risk profiles and supervision needs. Facilities must adapt their environment, staffing ratios, and emergency preparedness plans based on age composition to ensure optimal safety across both grouping structures.
Future Trends in Grouping Practices for Daycare Centers
Future trends in daycare grouping practices emphasize a shift towards age-mixed grouping, which fosters social development, empathy, and collaborative learning among children. Research indicates that heterogeneous age groups enhance cognitive skills and peer mentoring compared to age-segregated settings that focus solely on developmental uniformity. As early childhood education evolves, more daycare centers are adopting flexible, mixed-age models to support holistic growth and individualized learning trajectories.
Age-mixed grouping vs age-segregated grouping Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com