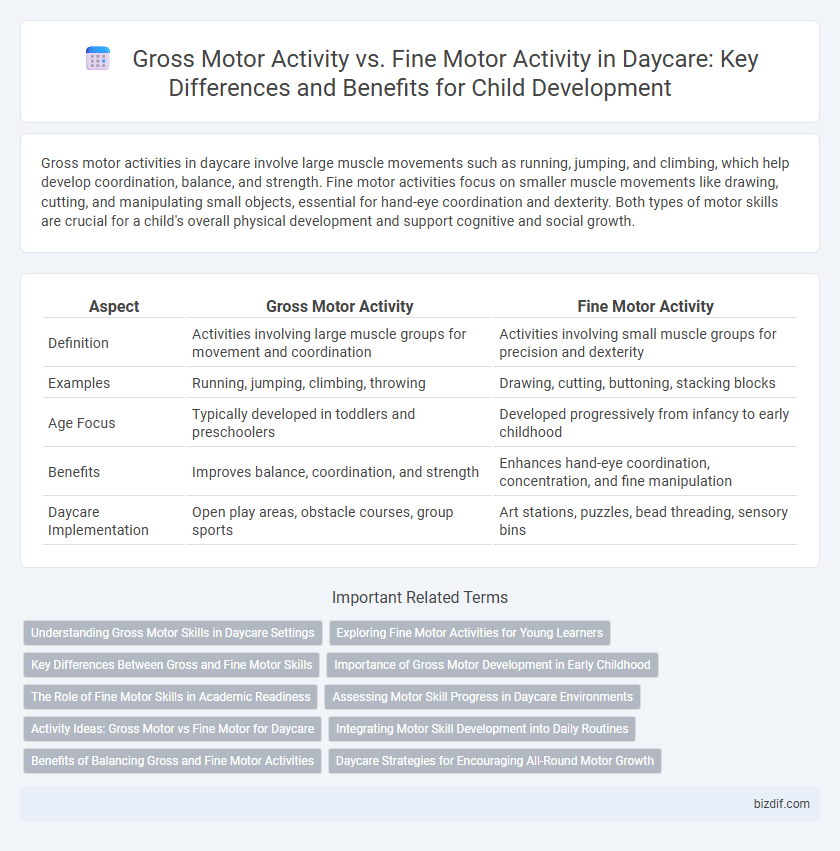
Gross motor activities in daycare involve large muscle movements such as running, jumping, and climbing, which help develop coordination, balance, and strength. Fine motor activities focus on smaller muscle movements like drawing, cutting, and manipulating small objects, essential for hand-eye coordination and dexterity. Both types of motor skills are crucial for a child's overall physical development and support cognitive and social growth.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Gross Motor Activity | Fine Motor Activity |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Activities involving large muscle groups for movement and coordination | Activities involving small muscle groups for precision and dexterity |
| Examples | Running, jumping, climbing, throwing | Drawing, cutting, buttoning, stacking blocks |
| Age Focus | Typically developed in toddlers and preschoolers | Developed progressively from infancy to early childhood |
| Benefits | Improves balance, coordination, and strength | Enhances hand-eye coordination, concentration, and fine manipulation |
| Daycare Implementation | Open play areas, obstacle courses, group sports | Art stations, puzzles, bead threading, sensory bins |
Understanding Gross Motor Skills in Daycare Settings
Gross motor activities in daycare settings involve large muscle movements such as running, jumping, and climbing, essential for developing balance, coordination, and overall physical strength in young children. These activities support neurological growth and provide foundational skills that influence fine motor development by enhancing body awareness and spatial orientation. Structured playtimes that emphasize gross motor skills contribute to better posture, endurance, and confidence, crucial for early childhood development milestones.
Exploring Fine Motor Activities for Young Learners
Engaging young learners in fine motor activities such as threading beads, cutting with safety scissors, and manipulating playdough enhances hand-eye coordination and dexterity crucial for writing skills development. These activities stimulate small muscle groups in the fingers and hands, supporting brain development and improving concentration and patience. Prioritizing fine motor play in daycare settings fosters independence and prepares children for academic tasks requiring precision and control.
Key Differences Between Gross and Fine Motor Skills
Gross motor skills involve large muscle groups used for actions like walking, jumping, and climbing, essential for overall body coordination and balance in daycare activities. Fine motor skills focus on smaller muscle movements in the hands and fingers, crucial for tasks such as drawing, cutting, and buttoning clothes, supporting children's hand-eye coordination and dexterity. Understanding these key differences helps caregivers design age-appropriate activities that promote both gross and fine motor development effectively.
Importance of Gross Motor Development in Early Childhood
Gross motor development in early childhood is crucial for building foundational skills like balance, coordination, and strength, which support overall physical health and daily functional activities. Activities such as running, jumping, and climbing enhance gross motor skills by engaging large muscle groups essential for movement and spatial awareness. Prioritizing gross motor development in daycare settings fosters confidence, independence, and social interaction among young children.
The Role of Fine Motor Skills in Academic Readiness
Fine motor skills involve the coordination of small muscles in the hands and fingers, crucial for tasks like writing, cutting, and manipulating classroom tools. Developing these skills in daycare settings supports academic readiness by enhancing children's ability to perform essential school activities, such as holding a pencil and using scissors accurately. Research indicates that fine motor proficiency strongly correlates with early literacy and numeracy success, making it a vital focus in early childhood education programs.
Assessing Motor Skill Progress in Daycare Environments
Assessing motor skill progress in daycare environments involves distinguishing between gross motor activities, which develop large muscle groups through actions like running, climbing, and jumping, and fine motor activities that enhance hand-eye coordination and dexterity through tasks such as drawing, buttoning, and manipulating small objects. Effective evaluation methods include standardized checklists, observational assessments, and age-appropriate milestone tracking that reflect children's abilities in both skill areas. Monitoring these developmental domains supports tailored interventions, promotes age-appropriate physical growth, and ensures comprehensive motor development in early childhood settings.
Activity Ideas: Gross Motor vs Fine Motor for Daycare
Gross motor activities in daycare, such as jumping, climbing, and running, promote large muscle development and coordination, essential for overall physical growth and balance. Fine motor activities like threading beads, using scissors, and drawing enhance hand-eye coordination, dexterity, and precision necessary for writing and self-care skills. Incorporating a balanced mix of gross and fine motor activities supports comprehensive motor development and prepares children for academic and daily life challenges.
Integrating Motor Skill Development into Daily Routines
Integrating gross motor activities such as running, jumping, and climbing with fine motor tasks like drawing, buttoning, and manipulating small objects supports comprehensive motor skill development in daycare settings. Daily routines that combine active play and precise hand movements enhance children's coordination, balance, and dexterity while promoting cognitive and social growth. Structured integration of these motor skills during snack time, playtime, and clean-up activities optimizes physical development and reinforces practical, functional abilities.
Benefits of Balancing Gross and Fine Motor Activities
Balancing gross motor activities, such as running and jumping, with fine motor activities like drawing and buttoning enhances overall child development by improving coordination, strength, and dexterity. This balance supports cognitive growth, promotes better hand-eye coordination, and encourages social interaction in a daycare setting. Integrating both types of activities helps children build foundational skills essential for daily tasks and future learning.
Daycare Strategies for Encouraging All-Round Motor Growth
Daycare strategies for promoting all-round motor growth emphasize a balanced mix of gross motor activities, such as climbing, running, and jumping, with fine motor activities like drawing, buttoning, and using utensils. Incorporating structured playtime with equipment like climbing frames and puzzles encourages physical strength alongside hand-eye coordination and dexterity. Providing diverse, age-appropriate motor challenges fosters comprehensive motor skill development, essential for children's overall growth and daily functional independence.
Gross motor activity vs Fine motor activity Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com