Private pay daycare offers families flexibility in choosing programs and services tailored to their child's needs, often with smaller class sizes and enhanced amenities. Subsidized payment options provide affordable access to quality childcare for low-income families, ensuring all children receive early learning opportunities regardless of financial status. Comparing both options helps parents balance budget constraints with desired childcare quality and personalized care.
Table of Comparison
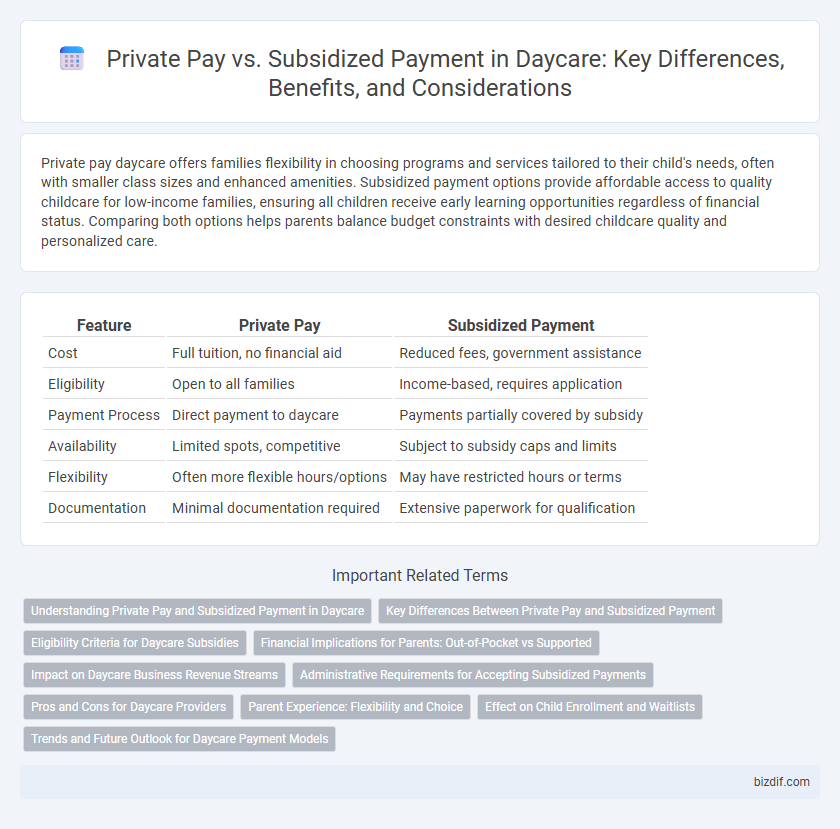
| Feature | Private Pay | Subsidized Payment |
|---|---|---|
| Cost | Full tuition, no financial aid | Reduced fees, government assistance |
| Eligibility | Open to all families | Income-based, requires application |
| Payment Process | Direct payment to daycare | Payments partially covered by subsidy |
| Availability | Limited spots, competitive | Subject to subsidy caps and limits |
| Flexibility | Often more flexible hours/options | May have restricted hours or terms |
| Documentation | Minimal documentation required | Extensive paperwork for qualification |
Understanding Private Pay and Subsidized Payment in Daycare
Private pay in daycare involves families paying the full cost of childcare services directly, offering greater flexibility and choice in provider selection. Subsidized payment programs reduce the financial burden by covering part or all of the childcare fees, typically based on household income and eligibility criteria. Understanding the differences in payment structures helps families make informed decisions about affordable and quality childcare options.
Key Differences Between Private Pay and Subsidized Payment
Private pay daycare requires families to cover the full cost of care, offering greater flexibility in program choice and hours, while subsidized payment programs reduce out-of-pocket expenses by providing government assistance based on income eligibility. Subsidized payment often requires adherence to specific enrollment criteria and may limit available childcare providers, whereas private pay allows unrestricted access to diverse daycare options. Understanding these financial and operational distinctions helps parents select the best childcare solution aligned with their budget and needs.
Eligibility Criteria for Daycare Subsidies
Eligibility criteria for daycare subsidies typically include income limits based on family size, employment or education status of parents, and residency requirements within the service area. Families must provide documentation such as proof of income, work or school enrollment, and legal guardianship to qualify for financial assistance. Meeting these criteria ensures access to subsidized childcare, reducing the overall cost burden compared to private pay options.
Financial Implications for Parents: Out-of-Pocket vs Supported
Private pay daycare requires parents to cover the full cost of childcare, often resulting in significant out-of-pocket expenses that can strain household budgets. Subsidized payment programs reduce financial burdens by providing government assistance, making quality daycare more accessible to families with limited income. Understanding the differences in payment options helps parents plan effectively for childcare costs and maximize available support.
Impact on Daycare Business Revenue Streams
Private pay daycare services generate consistent and often higher revenue per child, directly impacting business profitability through predictable cash flow. Subsidized payment programs, while increasing enrollment rates and accessibility for families, typically involve lower reimbursement rates that can constrain overall revenue growth. Balancing private pay and subsidized enrollments is crucial for optimizing daycare business revenue streams and maintaining financial sustainability.
Administrative Requirements for Accepting Subsidized Payments
Accepting subsidized payments for daycare services entails stringent administrative requirements such as verifying family eligibility, submitting detailed attendance records, and adhering to state-specific reporting guidelines. Providers must maintain accurate documentation to comply with funding regulations and facilitate timely reimbursement from subsidy programs. These administrative duties often demand additional staff training and robust data management systems compared to private pay arrangements.
Pros and Cons for Daycare Providers
Private pay offers daycare providers immediate and full payment, enhancing cash flow and reducing administrative burdens associated with subsidy paperwork and reporting. Subsidized payments guarantee a steady client base and support inclusivity by serving low-income families but often involve delayed reimbursements, lower rates, and increased regulatory compliance. Balancing both payment types allows providers to maintain financial stability while promoting accessibility and community trust.
Parent Experience: Flexibility and Choice
Private pay daycare offers parents greater flexibility in choosing childcare hours and programs tailored to their family's specific needs, enhancing overall satisfaction. Subsidized payment options often come with set schedules and limited provider choices, which may restrict parents' ability to customize care. Many parents prefer private pay for the freedom it provides in aligning care with work commitments and children's unique routines.
Effect on Child Enrollment and Waitlists
Private pay families often face higher costs, which can limit enrollment to those financially able to afford full tuition, resulting in shorter waitlists due to controlled demand. Subsidized payment programs increase accessibility for low-income families, significantly boosting enrollment rates but frequently causing longer waitlists as demand exceeds available spots. Balancing private pay and subsidized slots is essential for managing waitlists while ensuring equitable access to quality daycare services.
Trends and Future Outlook for Daycare Payment Models
Private pay for daycare services remains dominant in urban areas, driven by increasing demand for quality early childhood education. Subsidized payment programs are expanding, supported by government initiatives aimed at improving accessibility and affordability for low-income families. Future trends indicate a hybrid payment model emerging, combining private and public funding to sustain daycare providers and meet diverse family needs.
Private Pay vs Subsidized Payment Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com