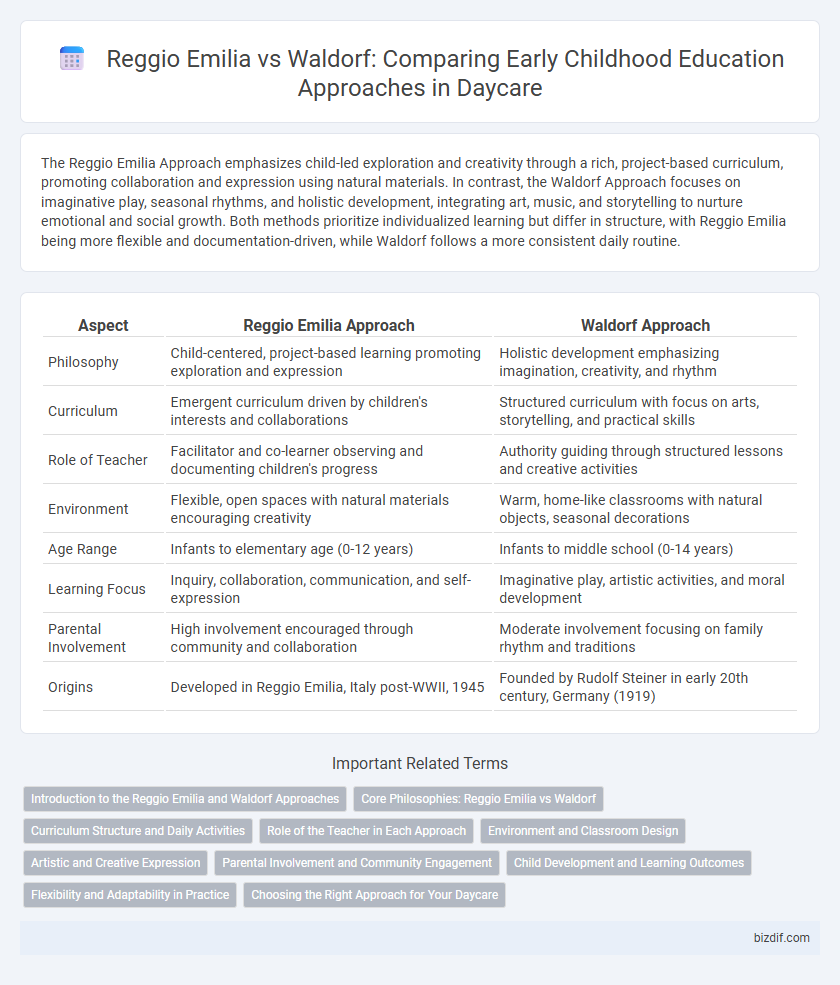
The Reggio Emilia Approach emphasizes child-led exploration and creativity through a rich, project-based curriculum, promoting collaboration and expression using natural materials. In contrast, the Waldorf Approach focuses on imaginative play, seasonal rhythms, and holistic development, integrating art, music, and storytelling to nurture emotional and social growth. Both methods prioritize individualized learning but differ in structure, with Reggio Emilia being more flexible and documentation-driven, while Waldorf follows a more consistent daily routine.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Reggio Emilia Approach | Waldorf Approach |
|---|---|---|
| Philosophy | Child-centered, project-based learning promoting exploration and expression | Holistic development emphasizing imagination, creativity, and rhythm |
| Curriculum | Emergent curriculum driven by children's interests and collaborations | Structured curriculum with focus on arts, storytelling, and practical skills |
| Role of Teacher | Facilitator and co-learner observing and documenting children's progress | Authority guiding through structured lessons and creative activities |
| Environment | Flexible, open spaces with natural materials encouraging creativity | Warm, home-like classrooms with natural objects, seasonal decorations |
| Age Range | Infants to elementary age (0-12 years) | Infants to middle school (0-14 years) |
| Learning Focus | Inquiry, collaboration, communication, and self-expression | Imaginative play, artistic activities, and moral development |
| Parental Involvement | High involvement encouraged through community and collaboration | Moderate involvement focusing on family rhythm and traditions |
| Origins | Developed in Reggio Emilia, Italy post-WWII, 1945 | Founded by Rudolf Steiner in early 20th century, Germany (1919) |
Introduction to the Reggio Emilia and Waldorf Approaches
The Reggio Emilia Approach emphasizes child-led exploration, creativity, and collaboration in a nurturing environment inspired by the Italian town of Reggio Emilia, fostering strong relationships between children, educators, and families. Waldorf Approach, founded by Rudolf Steiner, centers on imaginative play, artistic expression, and holistic development, integrating rhythm and nature to support emotional and intellectual growth. Both methods prioritize experiential learning but differ in their educational philosophy and classroom structure.
Core Philosophies: Reggio Emilia vs Waldorf
The Reggio Emilia approach centers on child-led learning, emphasizing exploration, creativity, and collaboration through a rich, responsive environment that views children as competent and resourceful individuals. In contrast, the Waldorf approach prioritizes imaginative play, artistic expression, and holistic development grounded in Rudolf Steiner's anthroposophical philosophy, fostering a balanced growth of body, mind, and spirit. Both methodologies value nurturing individuality and creativity, but Reggio Emilia emphasizes documentation and community engagement, while Waldorf focuses on rhythm, storytelling, and natural materials in early childhood education.
Curriculum Structure and Daily Activities
The Reggio Emilia Approach emphasizes a child-led curriculum with project-based learning, encouraging exploration and creativity through hands-on activities and collaboration in a flexible environment. The Waldorf Approach follows a structured, rhythm-based curriculum that integrates arts, storytelling, and practical tasks to foster imagination and holistic development, maintaining consistent daily routines. Both curricula prioritize developmental milestones but differ in flexibility, with Reggio Emilia adapting to children's interests and Waldorf adhering to predetermined thematic sequences.
Role of the Teacher in Each Approach
The Reggio Emilia Approach positions the teacher as a co-learner and collaborator, guiding children's exploration through observation and documentation, which fosters creativity and critical thinking. In contrast, the Waldorf Approach views the teacher as a nurturing role model who carefully follows a structured curriculum designed to support holistic development, blending academic, artistic, and practical activities. Both approaches emphasize the teacher's influence but differ in methods: Reggio Emilia prioritizes child-led discovery, whereas Waldorf emphasizes guided learning through rhythm and story.
Environment and Classroom Design
The Reggio Emilia approach emphasizes a flexible, child-centered environment with natural materials, open spaces, and areas designed to promote exploration and creativity, reflecting the belief that the classroom is the "third teacher." In contrast, the Waldorf approach features a warm, home-like atmosphere with soft colors, natural woods, and handmade objects to create a nurturing space that supports imaginative play and rhythm-based learning. Both approaches prioritize nature and aesthetics but differ in their philosophies on structure and sensory experiences within classroom design.
Artistic and Creative Expression
The Reggio Emilia Approach emphasizes child-led, open-ended artistic exploration through diverse mediums that encourage creativity and self-expression within a collaborative environment. The Waldorf Approach integrates art deeply into daily activities, fostering creativity through storytelling, music, and hands-on crafts aligned with developmental stages and rhythms. Both approaches nurture artistic expression but differ in structure, with Reggio Emilia promoting spontaneous creation and Waldorf emphasizing guided, holistic artistic experiences.
Parental Involvement and Community Engagement
The Reggio Emilia Approach emphasizes strong parental involvement, inviting parents to collaborate as partners in their child's education and encouraging regular communication and participation in classroom activities. The Waldorf Approach fosters community engagement by promoting a holistic family experience, with parents actively participating in school festivals, crafts, and celebrations to build a close-knit school community. Both approaches value parental input but differ in their framework: Reggio Emilia prioritizes educational co-creation, while Waldorf centers on cultural and artistic community integration.
Child Development and Learning Outcomes
The Reggio Emilia Approach emphasizes child-led exploration, fostering creativity and critical thinking through project-based learning, which enhances problem-solving skills and social collaboration. The Waldorf Approach prioritizes imaginative play and artistic expression, supporting holistic development by integrating cognitive, emotional, and physical growth within a structured routine. Both methods promote developmentally appropriate learning outcomes but differ in their focus on autonomy versus guided rhythm and creativity.
Flexibility and Adaptability in Practice
The Reggio Emilia Approach emphasizes flexibility by promoting child-led projects that adapt to each child's interests and developmental pace, fostering creativity and exploration. In contrast, the Waldorf Approach follows a more structured daily rhythm with a focus on consistency and predictable routines, which supports emotional stability but offers less spontaneous adaptability. Both methods prioritize responsiveness to children's needs, but Reggio Emilia allows greater fluidity in adapting activities and learning environments.
Choosing the Right Approach for Your Daycare
Selecting the right educational philosophy for your daycare involves evaluating the core principles of the Reggio Emilia Approach and the Waldorf Approach. The Reggio Emilia model emphasizes child-led exploration, collaborative learning, and the environment as the "third teacher," fostering creativity through project-based activities and strong parental involvement. In contrast, the Waldorf Approach focuses on holistic development through rhythmic routines, imaginative play, and artistic expression, aiming to nurture a child's emotional and spiritual growth alongside cognitive skills.
Reggio Emilia Approach vs Waldorf Approach Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com