Cart abandonment occurs when customers add products to their shopping cart but leave the e-commerce site before initiating the checkout process. Checkout abandonment happens when shoppers begin the checkout process but exit before completing the purchase. Understanding the distinction between these behaviors helps pet e-commerce businesses implement targeted strategies to reduce drop-offs and increase conversion rates.
Table of Comparison
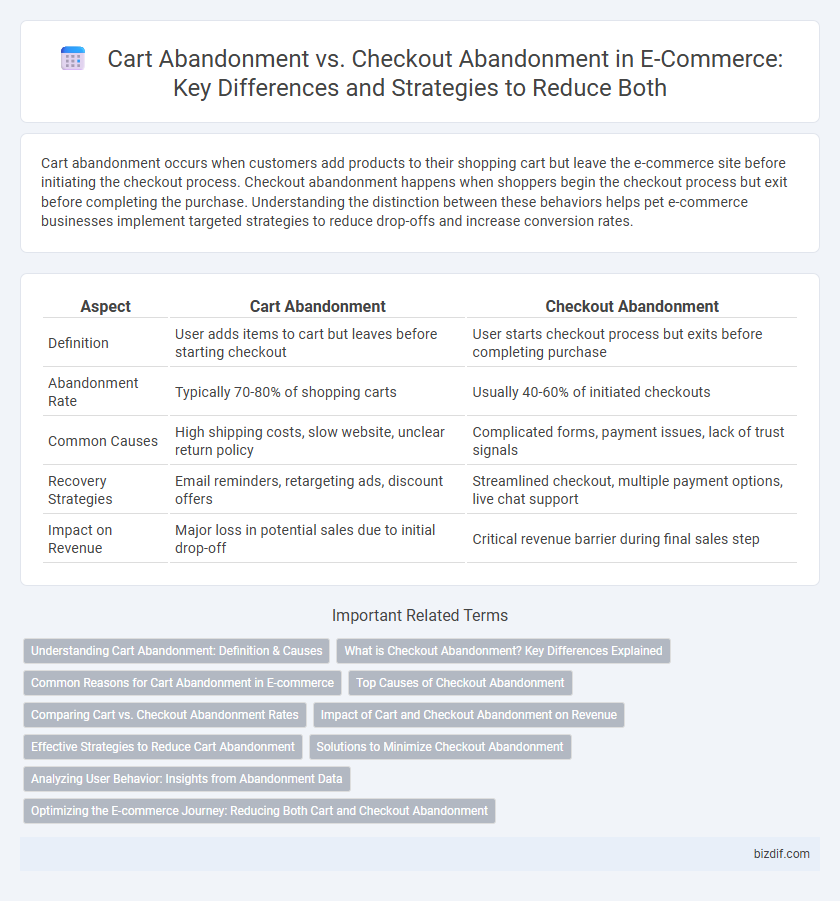
| Aspect | Cart Abandonment | Checkout Abandonment |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | User adds items to cart but leaves before starting checkout | User starts checkout process but exits before completing purchase |
| Abandonment Rate | Typically 70-80% of shopping carts | Usually 40-60% of initiated checkouts |
| Common Causes | High shipping costs, slow website, unclear return policy | Complicated forms, payment issues, lack of trust signals |
| Recovery Strategies | Email reminders, retargeting ads, discount offers | Streamlined checkout, multiple payment options, live chat support |
| Impact on Revenue | Major loss in potential sales due to initial drop-off | Critical revenue barrier during final sales step |
Understanding Cart Abandonment: Definition & Causes
Cart abandonment occurs when shoppers add products to their online shopping cart but leave the site before completing the purchase, resulting in lost sales opportunities for e-commerce businesses. Common causes include unexpected costs such as shipping fees, complicated checkout processes, lack of payment options, slow website performance, and concerns about security or privacy. Understanding these factors allows retailers to optimize the user experience by streamlining checkout flows, providing transparent pricing, and offering trust-building assurances to reduce abandonment rates.
What is Checkout Abandonment? Key Differences Explained
Checkout abandonment occurs when customers add products to their cart but leave during the final steps of the purchase process without completing payment. Unlike cart abandonment, which happens anytime before entering checkout, checkout abandonment specifically disrupts the payment stage, revealing potential issues with payment options or checkout complexity. Understanding these key differences helps e-commerce businesses optimize the checkout flow and reduce revenue loss by targeting specific drop-off points.
Common Reasons for Cart Abandonment in E-commerce
High shipping costs, complicated checkout processes, and unexpected fees are among the most common reasons for cart abandonment in e-commerce. Lack of trust, limited payment options, and slow website performance also significantly contribute to customers leaving their carts without completing purchases. Addressing these factors can reduce abandonment rates and improve overall conversion.
Top Causes of Checkout Abandonment
Checkout abandonment occurs when customers initiate the payment process but fail to complete the purchase, often due to unexpected costs, complicated checkout forms, or limited payment options. High shipping fees, mandatory account creation, and lack of trust signals also significantly contribute to abandonment rates during checkout. Reducing friction at this stage, such as offering guest checkout and transparent pricing, can drastically improve conversion rates and reduce lost revenue.
Comparing Cart vs. Checkout Abandonment Rates
Cart abandonment rates typically range between 60% and 80%, reflecting shoppers who add items but leave before initiating checkout. Checkout abandonment rates are generally lower, averaging around 40% to 60%, as users have already begun the purchase process but drop out before completion. Understanding the discrepancy in rates helps e-commerce businesses identify friction points in the checkout flow and optimize conversion strategies.
Impact of Cart and Checkout Abandonment on Revenue
Cart abandonment, occurring when customers add items but leave before initiating checkout, significantly reduces potential sales opportunities, with rates often exceeding 70%, leading to substantial revenue loss. Checkout abandonment, where users abandon the process after starting checkout, though less frequent, impacts conversion rates more directly and often reflects friction in payment or shipping options. Both behaviors critically affect e-commerce revenue streams, highlighting the importance of optimizing cart recovery strategies and streamlining the checkout experience to minimize lost transactions.
Effective Strategies to Reduce Cart Abandonment
Cart abandonment occurs when shoppers add items to their cart but leave without initiating checkout, while checkout abandonment happens during the payment process. Implementing strategies like streamlined checkout processes, real-time cart reminders, and personalized offers can significantly reduce cart abandonment rates. Leveraging data analytics to identify drop-off points allows e-commerce businesses to optimize user experience and increase conversion rates.
Solutions to Minimize Checkout Abandonment
Reducing checkout abandonment requires streamlining the payment process by offering multiple secure payment options and ensuring fast load times on checkout pages to prevent user frustration. Implementing persistent cart features and personalized reminder emails can re-engage customers who leave before completing their purchase. Transparent pricing, including clear shipping costs and return policies, builds trust and encourages users to finalize their transactions.
Analyzing User Behavior: Insights from Abandonment Data
Cart abandonment occurs when users add items to their shopping cart but leave before initiating checkout, while checkout abandonment happens during the final steps of the purchase process. Analyzing abandonment data reveals patterns such as unexpected shipping costs, complicated checkout forms, and lack of payment options as primary causes for drop-off. By understanding these user behaviors, e-commerce businesses can optimize their funnels, reduce friction, and increase conversion rates effectively.
Optimizing the E-commerce Journey: Reducing Both Cart and Checkout Abandonment
Reducing cart abandonment requires streamlining the browsing experience with clear product information and easy add-to-cart options, while checkout abandonment focuses on simplifying payment processes and minimizing unexpected costs. Implementing features like persistent shopping carts, guest checkout, and multiple secure payment methods significantly improves conversion rates. Leveraging data analytics to identify drop-off points enables targeted interventions that optimize each stage of the e-commerce journey, driving higher customer retention and sales.
Cart Abandonment vs Checkout Abandonment Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com