Cross-border e-commerce involves selling products across international borders, expanding market reach but facing challenges like customs regulations, currency fluctuations, and longer shipping times. Domestic e-commerce focuses on local markets with faster delivery, lower shipping costs, and simpler legal compliance but has limited growth potential compared to global sales. Businesses must weigh factors such as market demand, logistics, and regulatory environments when choosing between cross-border and domestic e-commerce strategies.
Table of Comparison
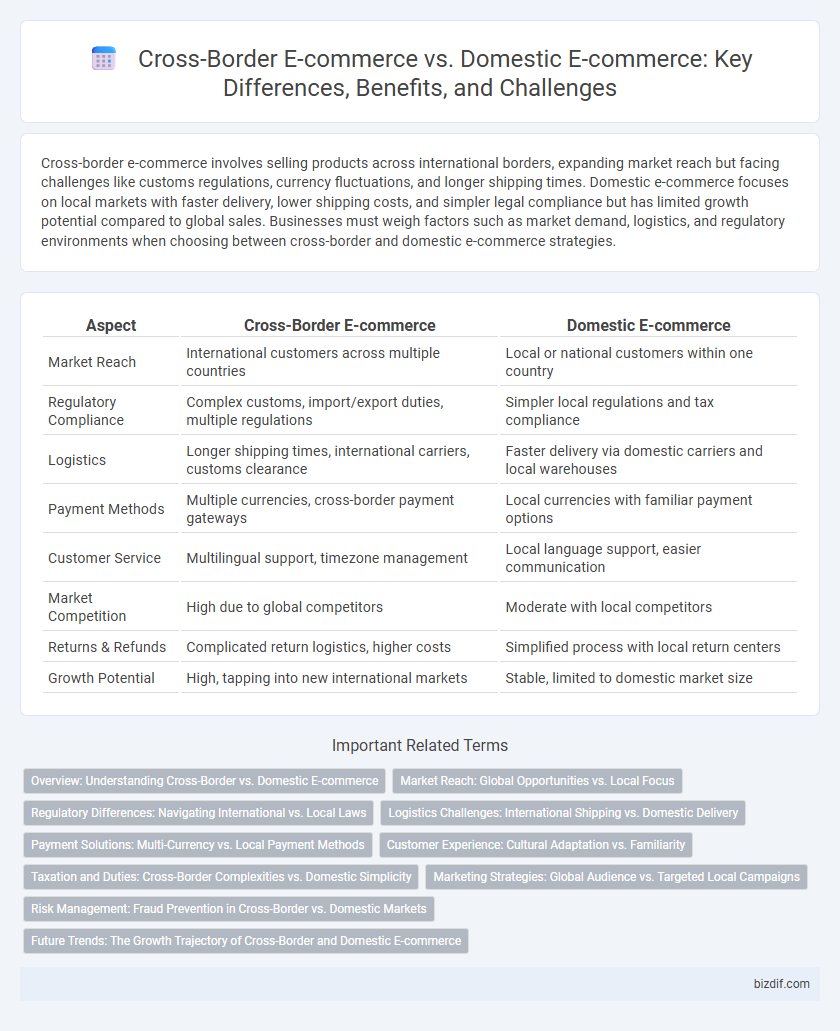
| Aspect | Cross-Border E-commerce | Domestic E-commerce |
|---|---|---|
| Market Reach | International customers across multiple countries | Local or national customers within one country |
| Regulatory Compliance | Complex customs, import/export duties, multiple regulations | Simpler local regulations and tax compliance |
| Logistics | Longer shipping times, international carriers, customs clearance | Faster delivery via domestic carriers and local warehouses |
| Payment Methods | Multiple currencies, cross-border payment gateways | Local currencies with familiar payment options |
| Customer Service | Multilingual support, timezone management | Local language support, easier communication |
| Market Competition | High due to global competitors | Moderate with local competitors |
| Returns & Refunds | Complicated return logistics, higher costs | Simplified process with local return centers |
| Growth Potential | High, tapping into new international markets | Stable, limited to domestic market size |
Overview: Understanding Cross-Border vs. Domestic E-commerce
Cross-border e-commerce involves international transactions where consumers purchase products from sellers in different countries, requiring compliance with customs, taxes, and regulations. Domestic e-commerce operates within a single country, offering faster shipping and easier return processes due to localized supply chains. Understanding these differences is crucial for businesses aiming to optimize logistics, marketing strategies, and customer experience in global versus local markets.
Market Reach: Global Opportunities vs. Local Focus
Cross-border e-commerce enables businesses to access a vast global customer base, expanding market reach far beyond domestic borders and increasing revenue potential. Domestic e-commerce focuses on serving local customers, allowing for tailored marketing strategies and faster delivery times. Leveraging global opportunities requires navigating international regulations, currencies, and logistics, while domestic e-commerce benefits from simplified operations and familiarity with local consumer behavior.
Regulatory Differences: Navigating International vs. Local Laws
Cross-border e-commerce involves complex regulatory frameworks, including customs duties, import/export restrictions, and varying tax policies that differ significantly from domestic e-commerce regulations. Compliance with international trade agreements and data privacy laws such as GDPR is critical for cross-border sellers to avoid legal penalties and ensure smooth transactions. Domestic e-commerce primarily focuses on adhering to local consumer protection laws, sales tax rules, and simpler logistics, making regulatory navigation comparatively more straightforward.
Logistics Challenges: International Shipping vs. Domestic Delivery
Cross-border e-commerce introduces complex logistics challenges such as customs clearance, international shipping regulations, and longer delivery times compared to domestic delivery. Managing international shipping requires advanced tracking systems, coordination with multiple carriers, and compliance with import/export laws. Domestic e-commerce benefits from simpler supply chains, faster last-mile delivery, and lower shipping costs, making it operationally more efficient than cross-border logistics.
Payment Solutions: Multi-Currency vs. Local Payment Methods
Cross-border e-commerce requires seamless multi-currency payment solutions to accommodate international customers and reduce currency conversion barriers. Domestic e-commerce benefits from local payment methods that leverage regional preferences, providing faster transactions and higher trust among consumers. Integrating both multi-currency and localized payment options enhances customer experience and increases conversion rates in global markets.
Customer Experience: Cultural Adaptation vs. Familiarity
Cross-border e-commerce enhances customer experience through cultural adaptation by tailoring language, payment options, and marketing to local preferences, increasing engagement and satisfaction. Domestic e-commerce benefits from customer familiarity with local regulations, shipping speed, and product expectations, resulting in smoother transactions. Brands optimizing customer touchpoints for cultural relevance in international markets see higher conversion rates compared to those relying solely on domestic market strategies.
Taxation and Duties: Cross-Border Complexities vs. Domestic Simplicity
Cross-border e-commerce involves navigating a complex web of international taxation laws, customs duties, and import/export regulations that vary significantly between countries, often leading to delays and increased costs. Domestic e-commerce benefits from simpler tax structures and consistent regulatory frameworks, enabling faster transactions and easier compliance. Effective management of these taxation and duty challenges is crucial for businesses aiming to expand globally while maintaining profitability.
Marketing Strategies: Global Audience vs. Targeted Local Campaigns
Cross-border e-commerce requires marketing strategies that prioritize global audience segmentation, leveraging multilingual content, international SEO, and multicultural social media campaigns to enhance brand visibility and customer engagement worldwide. Domestic e-commerce focuses on targeted local campaigns by utilizing localized keywords, region-specific promotions, and community-based advertising to drive customer loyalty and optimize conversion rates. Understanding the distinct consumer behaviors and preferences in each market allows businesses to tailor their approach for maximum impact in cross-border versus domestic e-commerce environments.
Risk Management: Fraud Prevention in Cross-Border vs. Domestic Markets
Cross-border e-commerce faces higher risks of fraud due to diverse regulations, multiple currencies, and varying authentication standards compared to domestic e-commerce, demanding more advanced fraud prevention systems such as AI-driven transaction monitoring and global identity verification. Domestic e-commerce benefits from more uniform legal frameworks and payment infrastructures, making fraud detection more straightforward and risk management more cost-effective. Effective risk management in cross-border markets requires integrating localized compliance checks and multi-layered security protocols to mitigate chargebacks and phishing attacks.
Future Trends: The Growth Trajectory of Cross-Border and Domestic E-commerce
Cross-border e-commerce is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of over 20% through 2028, driven by increasing internet penetration, global payment innovations, and expanded logistical networks. Domestic e-commerce will continue to strengthen with rising mobile commerce adoption, localized consumer preferences, and enhanced last-mile delivery solutions. The convergence of AI-powered personalized marketing and blockchain-based supply chain transparency will further accelerate growth trajectories in both cross-border and domestic e-commerce markets.
Cross-Border E-commerce vs Domestic E-commerce Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com