Physical goods require inventory management, shipping logistics, and handling returns, which can increase operational costs for e-commerce businesses. Digital goods offer instant delivery, lower overhead expenses, and ease of scalability, making them attractive for online retailers focusing on efficiency. Choosing between these goods depends on product type, target audience, and business goals within the e-commerce landscape.
Table of Comparison
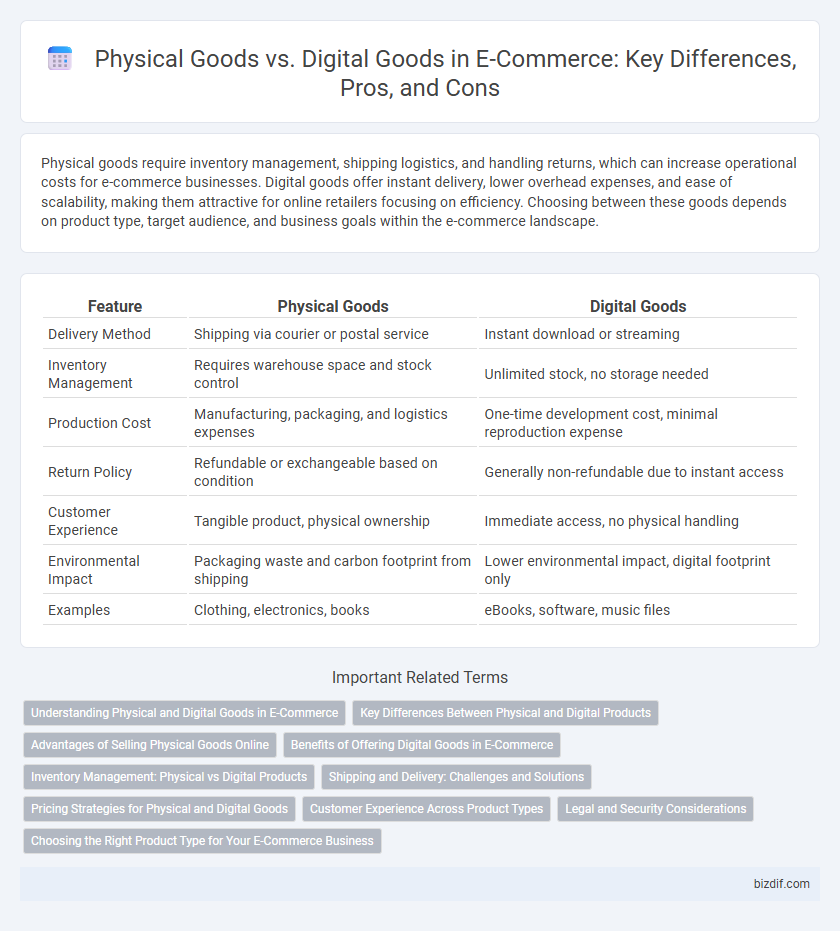
| Feature | Physical Goods | Digital Goods |
|---|---|---|
| Delivery Method | Shipping via courier or postal service | Instant download or streaming |
| Inventory Management | Requires warehouse space and stock control | Unlimited stock, no storage needed |
| Production Cost | Manufacturing, packaging, and logistics expenses | One-time development cost, minimal reproduction expense |
| Return Policy | Refundable or exchangeable based on condition | Generally non-refundable due to instant access |
| Customer Experience | Tangible product, physical ownership | Immediate access, no physical handling |
| Environmental Impact | Packaging waste and carbon footprint from shipping | Lower environmental impact, digital footprint only |
| Examples | Clothing, electronics, books | eBooks, software, music files |
Understanding Physical and Digital Goods in E-Commerce
Physical goods in e-commerce refer to tangible products such as clothing, electronics, and home appliances that require inventory, shipping, and handling. Digital goods encompass non-physical products like software, eBooks, and online courses, delivered instantly via downloads or streaming. Understanding the distinctions between physical and digital goods enables e-commerce businesses to optimize logistics, pricing strategies, and customer experience effectively.
Key Differences Between Physical and Digital Products
Physical goods require inventory management, shipping logistics, and storage space, whereas digital goods offer instant delivery and unlimited replicability without physical constraints. Physical products often involve manufacturing costs, packaging, and returns processing, while digital products benefit from lower marginal costs and easy scalability. Customer experience also varies, as physical goods provide tactile satisfaction whereas digital goods emphasize accessibility and immediate consumption.
Advantages of Selling Physical Goods Online
Selling physical goods online offers tangible products that customers can see, touch, and use, increasing trust and satisfaction. Physical products often have higher perceived value, driving higher sales and brand loyalty. Inventory management and shipping logistics enable businesses to provide personalized packaging and memorable unboxing experiences, enhancing customer retention.
Benefits of Offering Digital Goods in E-Commerce
Offering digital goods in e-commerce reduces inventory costs and eliminates shipping delays, enabling instant delivery to customers worldwide. Digital goods provide scalable revenue opportunities with low overhead, making it easier to update or customize products quickly. This enhances customer satisfaction and retention through seamless access and ongoing product improvements.
Inventory Management: Physical vs Digital Products
Inventory management for physical goods involves tracking stock levels, storage conditions, and supply chain logistics to prevent overstocking or stockouts. Digital goods eliminate traditional inventory concerns, as they require no physical storage and can be distributed instantly with zero depletion. This difference simplifies operational complexity for digital products, enabling scalable sales without inventory risk.
Shipping and Delivery: Challenges and Solutions
Shipping physical goods involves logistical challenges such as packaging, shipping costs, and delivery time that can affect customer satisfaction and require inventory management and reliable carriers. Digital goods eliminate physical shipping barriers, enabling instant delivery and reducing overhead, but they face challenges in secure file transfer, digital rights management (DRM), and preventing unauthorized distribution. Solutions for physical goods include real-time tracking systems and optimized supply chain management, while digital goods benefit from secure cloud delivery platforms and encryption technologies to ensure safe and efficient distribution.
Pricing Strategies for Physical and Digital Goods
Pricing strategies for physical goods often involve considerations such as manufacturing costs, inventory management, shipping expenses, and supplier markups, leading to a cost-plus or competitive pricing approach. In contrast, digital goods benefit from low marginal costs and scalability, allowing for flexible pricing models like freemium, subscription, or dynamic pricing based on user engagement and demand. Understanding these distinctions enables e-commerce businesses to optimize revenue by tailoring pricing tactics to the unique cost structures and value perceptions of physical versus digital products.
Customer Experience Across Product Types
Customer experience varies significantly between physical goods and digital goods in e-commerce, with tangible products requiring efficient shipping, packaging, and return processes to meet expectations. Digital goods offer instant delivery and easy access, enhancing convenience but demanding robust digital rights management and seamless download experiences to ensure satisfaction. Personalization, clear product descriptions, and responsive customer support remain critical across both product types to foster trust and repeat purchases.
Legal and Security Considerations
Legal considerations for physical goods include compliance with product safety standards, import/export regulations, and warranty obligations, while digital goods require adherence to copyright laws, digital rights management (DRM), and licensing agreements. Security concerns for physical products primarily involve inventory theft prevention and secure shipping methods, whereas digital goods necessitate robust cybersecurity measures to protect against piracy, data breaches, and unauthorized access. Both types demand clear terms of service and privacy policies to ensure consumer protection and regulatory compliance in e-commerce transactions.
Choosing the Right Product Type for Your E-Commerce Business
Selecting the right product type for your e-commerce business hinges on factors such as inventory management, shipping logistics, and customer preferences. Physical goods require efficient warehouse operations and shipping solutions, impacting costs and delivery times, whereas digital goods eliminate shipping, offering instant access and scalability with minimal overhead. Analyzing target market demand, profit margins, and operational capacity ensures alignment with business goals and enhances customer satisfaction.
Physical Goods vs Digital Goods Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com