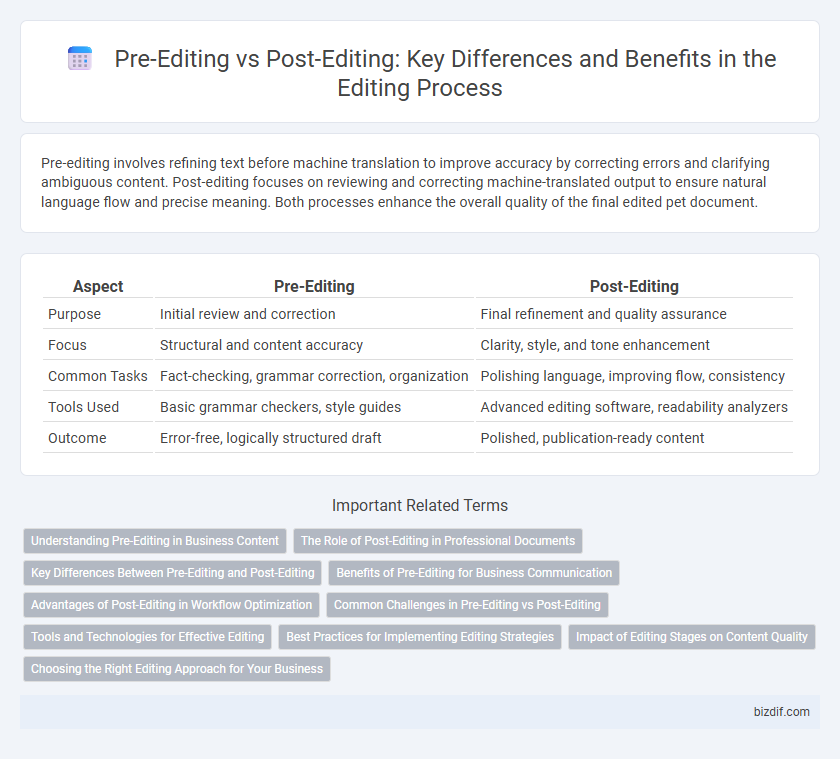
Pre-editing involves refining text before machine translation to improve accuracy by correcting errors and clarifying ambiguous content. Post-editing focuses on reviewing and correcting machine-translated output to ensure natural language flow and precise meaning. Both processes enhance the overall quality of the final edited pet document.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Pre-Editing | Post-Editing |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Initial review and correction | Final refinement and quality assurance |
| Focus | Structural and content accuracy | Clarity, style, and tone enhancement |
| Common Tasks | Fact-checking, grammar correction, organization | Polishing language, improving flow, consistency |
| Tools Used | Basic grammar checkers, style guides | Advanced editing software, readability analyzers |
| Outcome | Error-free, logically structured draft | Polished, publication-ready content |
Understanding Pre-Editing in Business Content
Pre-editing in business content involves reviewing and refining source materials before translation or further processing, ensuring clarity, consistency, and accuracy. This proactive approach reduces errors, enhances translation quality, and minimizes costs associated with extensive post-editing. Implementing structured pre-editing protocols accelerates content workflows and improves overall communication effectiveness in international markets.
The Role of Post-Editing in Professional Documents
Post-editing plays a crucial role in professional documents by enhancing machine-generated content to meet quality standards and ensure accuracy. It involves refining grammar, style, and terminology while aligning the text with brand voice and domain-specific requirements for clarity and consistency. This process optimizes workflow efficiency, reduces manual revision time, and supports scalable content production in industries like legal, medical, and technical fields.
Key Differences Between Pre-Editing and Post-Editing
Pre-editing involves refining the source content before the translation process by simplifying language, correcting errors, and ensuring clarity, which enhances machine translation quality. Post-editing, in contrast, takes place after initial machine translation output, focusing on correcting inaccuracies, improving fluency, and ensuring cultural appropriateness. Key differences center on timing and purpose: pre-editing prepares text to reduce errors beforehand, while post-editing cleans up and perfects machine-generated translations.
Benefits of Pre-Editing for Business Communication
Pre-editing enhances clarity and consistency in business communication by addressing errors and ambiguities before the content reaches translation or publication stages. This process reduces turnaround time and lowers costs associated with extensive post-editing by minimizing the need for significant revisions. Improving source text quality through pre-editing ensures more accurate, coherent translations, which strengthens professional credibility and client trust.
Advantages of Post-Editing in Workflow Optimization
Post-editing enhances workflow optimization by allowing initial machine translation to handle bulk content quickly, significantly reducing turnaround time. It enables human editors to focus on improving accuracy, tone, and context, ensuring higher quality output with less repetitive effort. This approach also offers scalability and cost-efficiency, making it ideal for managing large volumes of text in fast-paced environments.
Common Challenges in Pre-Editing vs Post-Editing
Common challenges in pre-editing include identifying inconsistent style, reducing errors in the source text, and ensuring clarity before translation or further processing. Post-editing difficulties often involve correcting machine translation errors, improving fluency, and maintaining the original meaning while adjusting for natural language flow. Both stages require balancing accuracy and efficiency to optimize the overall editing workflow.
Tools and Technologies for Effective Editing
Pre-editing tools enhance text quality by integrating grammar checkers, style analyzers, and AI-driven content suggestions to reduce errors before initial editing. Post-editing technologies utilize machine learning algorithms and automated feedback systems to refine translations, correct inconsistencies, and improve readability after the first draft. Combining advanced software such as Natural Language Processing (NLP) platforms and cloud-based collaboration tools streamlines both pre-editing and post-editing processes for efficient, accurate results.
Best Practices for Implementing Editing Strategies
Pre-editing involves refining the source text to reduce errors and improve clarity before translation or further processing, enhancing machine translation quality and reducing post-editing effort. Post-editing focuses on correcting and enhancing translated content to meet accuracy and style standards, often requiring a balance between fluency and adherence to the original text. Best practices for implementing editing strategies include comprehensive error analysis, clear style guides, leveraging technology for consistency, and continuous training to optimize workflow efficiency and output quality.
Impact of Editing Stages on Content Quality
Pre-editing enhances content quality by addressing structural and clarity issues before the initial draft is finalized, reducing errors and improving coherence. Post-editing refines language, style, and accuracy after the draft is complete, ensuring polished and consistent output. Effective editing strategies that combine both stages result in higher overall content quality and increased audience engagement.
Choosing the Right Editing Approach for Your Business
Choosing the right editing approach depends on your business goals, workflow, and resource availability, with pre-editing ensuring text clarity before translation, and post-editing refining machine-translated content for accuracy. Pre-editing minimizes errors early, reducing costly revisions later, while post-editing leverages AI efficiency balanced by human expertise to maintain quality. Assessing content complexity, deadlines, and budget will guide whether pre-editing, post-editing, or a hybrid method best suits your operational needs.
Pre-Editing vs Post-Editing Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com