Prepress editing involves preparing pet images and layouts for printing, focusing on color correction, resolution, and ensuring print-ready quality. Digital editing emphasizes enhancing pet photos for online use, optimizing for screen display, and applying creative filters or retouching. Both methods ensure the pet's appearance is crisp, clear, and visually appealing, tailored to their respective mediums.
Table of Comparison
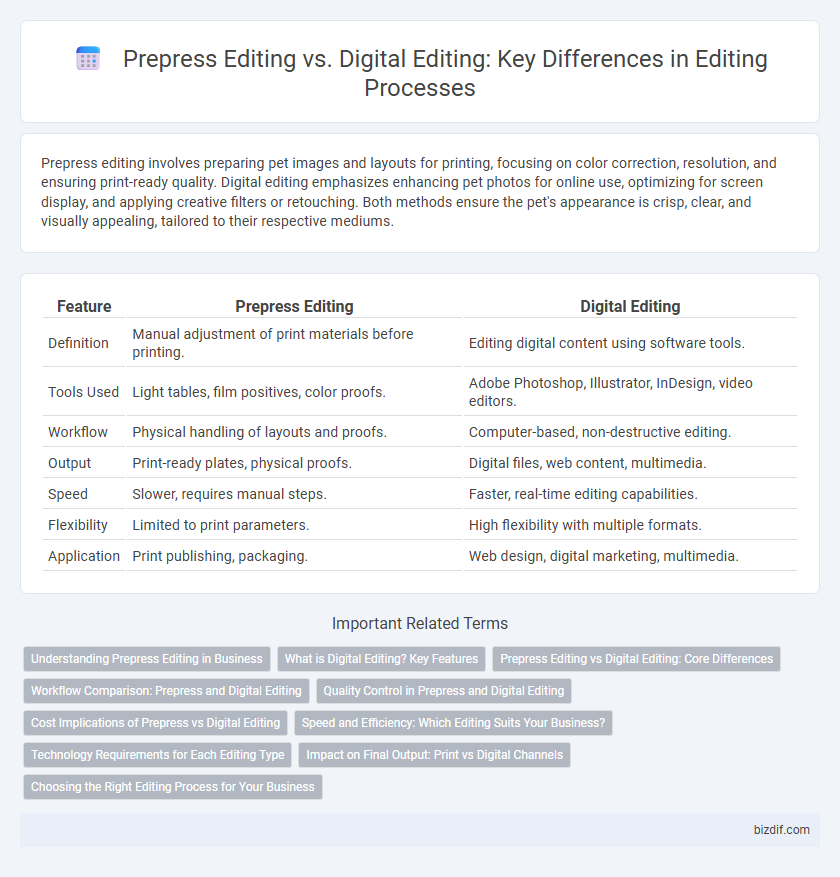
| Feature | Prepress Editing | Digital Editing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Manual adjustment of print materials before printing. | Editing digital content using software tools. |
| Tools Used | Light tables, film positives, color proofs. | Adobe Photoshop, Illustrator, InDesign, video editors. |
| Workflow | Physical handling of layouts and proofs. | Computer-based, non-destructive editing. |
| Output | Print-ready plates, physical proofs. | Digital files, web content, multimedia. |
| Speed | Slower, requires manual steps. | Faster, real-time editing capabilities. |
| Flexibility | Limited to print parameters. | High flexibility with multiple formats. |
| Application | Print publishing, packaging. | Web design, digital marketing, multimedia. |
Understanding Prepress Editing in Business
Prepress editing involves preparing digital files for printing by ensuring color accuracy, layout consistency, and resolution standards essential for high-quality print production. This process includes proofreading, adjusting images, and verifying fonts to prevent costly printing errors and delays, making it crucial for businesses relying on physical marketing materials. Understanding prepress editing enables companies to streamline print workflows, reduce waste, and maintain brand integrity across all printed assets.
What is Digital Editing? Key Features
Digital editing involves modifying text, images, and multimedia in electronic formats using specialized software such as Adobe Photoshop, Illustrator, or InDesign. Key features include non-destructive editing, real-time collaboration, layering, and precise color correction that enhance efficiency and quality in publishing workflows. This contrasts with prepress editing, which focuses primarily on preparing print-ready files and ensuring that designs meet printing specifications and standards.
Prepress Editing vs Digital Editing: Core Differences
Prepress editing involves preparing print materials by refining layouts, color corrections, and ensuring print-ready file formats, whereas digital editing focuses on optimizing content for online platforms, including interactive elements and multimedia integration. Prepress editing demands precision in resolution and color accuracy to meet print standards, while digital editing prioritizes responsive design and fast loading times for various devices. Both processes require distinct skill sets tailored to their specific mediums, highlighting their core differences in workflow and technical requirements.
Workflow Comparison: Prepress and Digital Editing
Prepress editing involves preparing print materials by ensuring color accuracy, layout precision, and compliance with printing standards, often using software like Adobe InDesign and Acrobat. Digital editing workflows emphasize flexibility and speed, focusing on multimedia content adaptation, dynamic formatting, and real-time collaboration tools such as Adobe Photoshop and online platforms. Both workflows require meticulous review processes, but prepress editing prioritizes print-ready outputs while digital editing centers on interactive, screen-optimized content.
Quality Control in Prepress and Digital Editing
Quality control in prepress editing ensures accuracy in color separation, layout consistency, and print readiness, minimizing costly errors before production. Digital editing quality control emphasizes pixel-perfect image adjustments, metadata accuracy, and seamless integration across digital platforms to optimize visual clarity. Both processes require rigorous inspection but target different stages of content refinement for print versus screen.
Cost Implications of Prepress vs Digital Editing
Prepress editing often involves higher upfront costs due to specialized software, hardware, and skilled technicians required to prepare print-ready materials. Digital editing, leveraging advanced cloud-based tools and AI-driven automation, reduces ongoing expenses by enabling faster revisions and minimizing physical proofing. Cost efficiency in digital editing supports scalable workflows, making it a preferred choice for projects with tight budgets and quick turnaround times.
Speed and Efficiency: Which Editing Suits Your Business?
Prepress editing streamlines print production by optimizing files for color accuracy, resolution, and layout consistency, ensuring faster turnaround times for physical media. Digital editing leverages software tools to quickly enhance images, text, and graphics, offering greater flexibility and speed for content intended for online platforms. Businesses prioritizing rapid updates and multimedia versatility typically benefit from digital editing, while those requiring precise print quality may find prepress editing more efficient.
Technology Requirements for Each Editing Type
Prepress editing demands specialized software such as Adobe InDesign, QuarkXPress, and high-resolution PDF proofing tools to ensure print-ready layouts meet strict color and resolution standards. Digital editing relies heavily on cloud-based platforms, real-time collaboration tools, and advanced content management systems to facilitate rapid updates and multi-channel publishing. Each editing type requires distinct hardware capabilities; prepress often needs calibrated monitors and high-performance printers, while digital editing prioritizes robust internet connectivity and versatile devices for seamless content deployment.
Impact on Final Output: Print vs Digital Channels
Prepress editing ensures precise color calibration, resolution, and layout adjustments critical for high-quality print outputs, minimizing errors such as misalignment or color shifts. Digital editing focuses on optimizing images and text for various screen resolutions, load times, and interactive elements essential for digital channels. Both editing types tailor content to their respective mediums, significantly impacting clarity, visual appeal, and user experience in final outputs.
Choosing the Right Editing Process for Your Business
Prepress editing involves preparing print materials by adjusting layouts, colors, and formats to meet publishing standards, ensuring high-quality physical outputs. Digital editing focuses on optimizing content for online platforms, enhancing multimedia integration, and user experience tailored to digital consumption. Choosing the right editing process depends on your business goals, distribution channels, and target audience, as print demands precise color calibration, while digital requires adaptable, interactive content formats.
Prepress Editing vs Digital Editing Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com