HIIT training burns more calories in less time by alternating intense bursts of activity with short recovery periods, making it ideal for fat loss and improving cardiovascular fitness. Steady-state cardio involves maintaining a consistent, moderate pace for an extended duration, which builds endurance and supports heart health. Choosing between HIIT and steady-state depends on individual goals, fitness levels, and time availability.
Table of Comparison
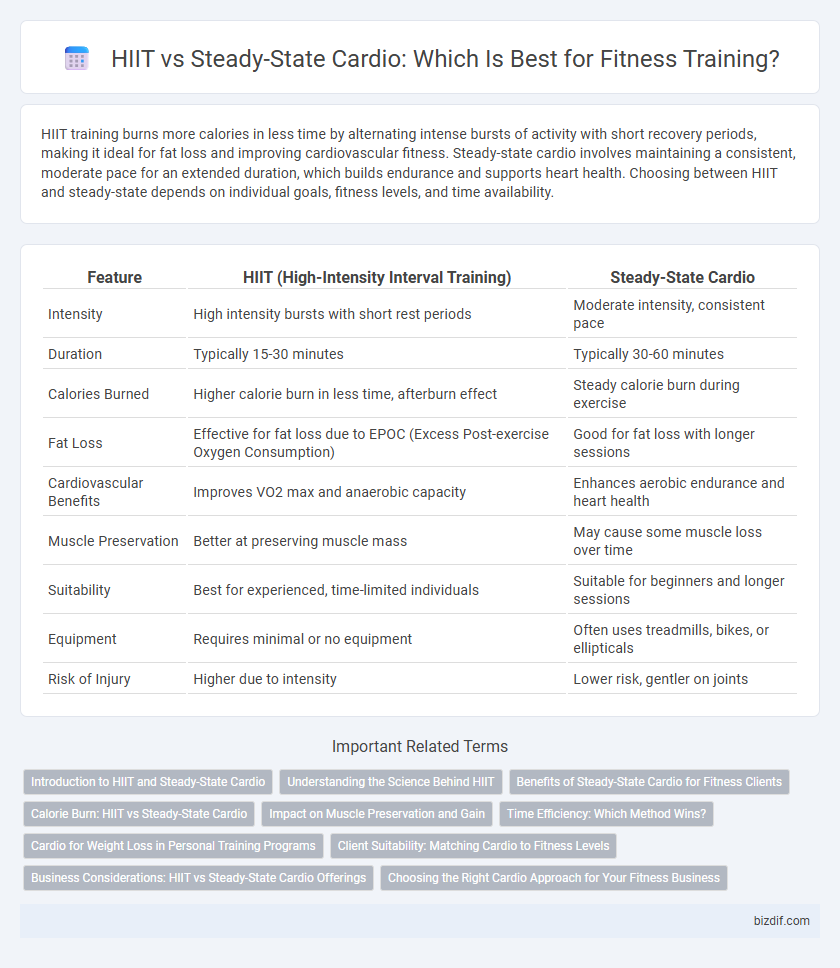
| Feature | HIIT (High-Intensity Interval Training) | Steady-State Cardio |
|---|---|---|
| Intensity | High intensity bursts with short rest periods | Moderate intensity, consistent pace |
| Duration | Typically 15-30 minutes | Typically 30-60 minutes |
| Calories Burned | Higher calorie burn in less time, afterburn effect | Steady calorie burn during exercise |
| Fat Loss | Effective for fat loss due to EPOC (Excess Post-exercise Oxygen Consumption) | Good for fat loss with longer sessions |
| Cardiovascular Benefits | Improves VO2 max and anaerobic capacity | Enhances aerobic endurance and heart health |
| Muscle Preservation | Better at preserving muscle mass | May cause some muscle loss over time |
| Suitability | Best for experienced, time-limited individuals | Suitable for beginners and longer sessions |
| Equipment | Requires minimal or no equipment | Often uses treadmills, bikes, or ellipticals |
| Risk of Injury | Higher due to intensity | Lower risk, gentler on joints |
Introduction to HIIT and Steady-State Cardio
High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT) involves alternating short bursts of intense exercise with recovery periods, maximizing calorie burn and cardiovascular improvement in a shorter time. Steady-State Cardio maintains a consistent, moderate intensity over an extended duration, ideal for endurance building and fat metabolism. Both training methods offer unique cardiovascular benefits, making them valuable for diverse fitness goals and levels.
Understanding the Science Behind HIIT
High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT) enhances cardiovascular fitness and fat loss by alternating short bursts of intense exercise with recovery periods, triggering greater metabolic demands and increased calorie burn post-exercise. Compared to steady-state cardio, HIIT stimulates higher levels of excess post-exercise oxygen consumption (EPOC), which accelerates recovery and improves aerobic and anaerobic capacity more effectively. Research indicates that HIIT induces adaptations in muscle mitochondria and insulin sensitivity, making it a scientifically supported method for optimizing fitness results in less time.
Benefits of Steady-State Cardio for Fitness Clients
Steady-state cardio enhances cardiovascular endurance by maintaining a consistent heart rate, which improves oxygen delivery and overall heart health. This type of training supports fat burning over extended periods, making it effective for weight management and metabolic health. It also promotes joint stability and reduces injury risk through low-impact, continuous movement ideal for diverse fitness levels.
Calorie Burn: HIIT vs Steady-State Cardio
HIIT workouts can burn 25-30% more calories per minute compared to steady-state cardio due to their high intensity and afterburn effect, known as excess post-exercise oxygen consumption (EPOC). Steady-state cardio maintains a consistent heart rate, allowing for longer duration sessions but typically results in lower total calorie expenditure in the same time frame. Research shows HIIT can boost metabolism for hours post-exercise, making it more effective for fat loss and overall calorie burn.
Impact on Muscle Preservation and Gain
High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT) promotes muscle preservation and gain by stimulating fast-twitch muscle fibers through short bursts of intense effort, enhancing strength and hypertrophy alongside cardiovascular benefits. Steady-State Cardio mainly targets slow-twitch muscle fibers, aiding endurance but potentially leading to muscle catabolism if performed excessively without adequate resistance training or nutrition. Integrating HIIT with resistance workouts maximizes muscle growth and retention while using steady-state cardio for active recovery and improved aerobic capacity.
Time Efficiency: Which Method Wins?
High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT) provides superior time efficiency by delivering intense bursts of activity followed by short rest periods, allowing for maximum calorie burn in as little as 20 minutes. Steady-state cardio requires longer durations, typically 30 to 60 minutes, to achieve comparable fat loss and cardiovascular benefits. For individuals with limited time, HIIT offers a more effective workout within a shorter timeframe while still improving aerobic and anaerobic fitness.
Cardio for Weight Loss in Personal Training Programs
HIIT (High-Intensity Interval Training) burns more calories in less time by alternating intense bursts with recovery periods, making it highly effective for weight loss in personal training programs. Steady-state cardio, characterized by prolonged, moderate-intensity exercise, promotes fat oxidation and endurance but generally burns fewer calories per session compared to HIIT. Combining both methods optimizes cardiovascular fitness and maximizes fat loss, tailoring workouts to individual client goals and fitness levels.
Client Suitability: Matching Cardio to Fitness Levels
High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT) suits clients with intermediate to advanced fitness levels due to its demand for intense bursts of effort and shorter recovery periods. Steady-state cardio is ideal for beginners or those with lower cardiovascular endurance, providing a consistent pace that promotes fat burning and improves stamina without overexertion. Matching the cardio modality to individual fitness levels ensures safer workouts and maximizes performance gains.
Business Considerations: HIIT vs Steady-State Cardio Offerings
Fitness businesses should evaluate HIIT and steady-state cardio offerings based on client demand, resource allocation, and session frequency. HIIT classes typically require certified instructors and smaller groups due to their intensity, creating opportunities for premium pricing and shorter, high-impact sessions. Steady-state cardio appeals to a broader audience with lower instructor demand and longer class durations, supporting high-volume, scalable business models.
Choosing the Right Cardio Approach for Your Fitness Business
HIIT (High-Intensity Interval Training) offers efficient calorie burn and boosts metabolic rate, ideal for clients seeking quick, intense workouts. Steady-State Cardio promotes endurance and heart health through consistent, moderate-intensity exercise, appealing to beginners and those focused on long-duration sessions. Tailoring cardio programs by client goals, fitness levels, and class formats optimizes engagement and retention in your fitness business.
HIIT vs Steady-State Cardio Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com