The gig economy offers freelancers flexibility and autonomy, allowing them to choose projects and set their schedules, unlike traditional employment which typically involves fixed hours and defined roles. Gig workers often experience variable income and lack benefits such as health insurance and retirement plans that are commonly provided in conventional jobs. This shift in work dynamics challenges traditional employment structures by prioritizing independence and adaptability in the modern workforce.
Table of Comparison
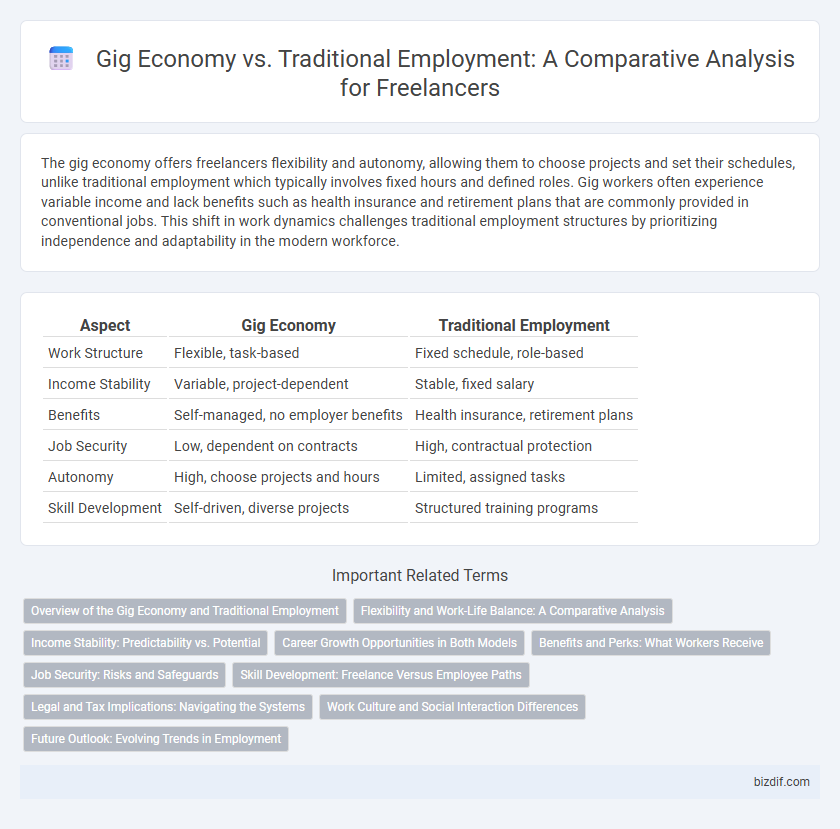
| Aspect | Gig Economy | Traditional Employment |
|---|---|---|
| Work Structure | Flexible, task-based | Fixed schedule, role-based |
| Income Stability | Variable, project-dependent | Stable, fixed salary |
| Benefits | Self-managed, no employer benefits | Health insurance, retirement plans |
| Job Security | Low, dependent on contracts | High, contractual protection |
| Autonomy | High, choose projects and hours | Limited, assigned tasks |
| Skill Development | Self-driven, diverse projects | Structured training programs |
Overview of the Gig Economy and Traditional Employment
The gig economy consists of flexible, short-term contracts or freelance work, often facilitated by digital platforms, allowing workers to manage their own schedules and choose diverse projects. Traditional employment typically involves long-term contracts with fixed salaries, structured job roles, and benefits such as health insurance and retirement plans. While gig work offers autonomy and variety, traditional employment provides stability and consistent income.
Flexibility and Work-Life Balance: A Comparative Analysis
Freelancing in the gig economy offers unparalleled flexibility, allowing workers to set their own hours and choose projects that align with personal preferences, significantly enhancing work-life balance. Traditional employment typically involves fixed schedules and limited autonomy, which can restrict individuals' ability to manage personal commitments effectively. Studies indicate gig workers report higher satisfaction with work-life integration, though they often face income variability and lack of benefits compared to salaried employees.
Income Stability: Predictability vs. Potential
In the gig economy, income varies significantly based on project availability, client demand, and seasonal trends, leading to less predictable earnings but potential for higher pay during peak periods. Traditional employment offers a steady paycheck with fixed salary or hourly wages, providing reliable income stability and benefits such as health insurance and retirement plans. Freelancers prioritize flexibility and earning potential, whereas traditional employees value consistency and financial security.
Career Growth Opportunities in Both Models
Freelancing within the gig economy offers flexible career growth opportunities through diverse project experiences and skill expansion across various industries. Traditional employment provides structured advancement paths, job stability, and professional development programs that support long-term career progression. Balancing gig economy agility with the stability of traditional roles enables individuals to customize their career trajectories according to personal growth goals and market demands.
Benefits and Perks: What Workers Receive
Freelancers in the gig economy often enjoy flexibility, diverse income streams, and control over their workload, while traditional employees typically receive consistent wages, healthcare benefits, retirement plans, and paid leave. Gig workers face challenges like income variability and lack of employer-sponsored benefits but gain opportunities for skill growth and autonomy. Traditional employment provides stability and social security but limits flexibility and entrepreneurial freedom.
Job Security: Risks and Safeguards
Gig economy workers face job security risks due to irregular income and lack of benefits like health insurance and retirement plans, unlike traditional employees who have stable salaries and employer-provided safeguards. Freelancers often mitigate risks by diversifying clients, maintaining emergency savings, and securing private insurance. Understanding and implementing strategic safeguards is crucial for sustaining financial stability amid the inherent uncertainties of gig work.
Skill Development: Freelance Versus Employee Paths
Freelancers continuously adapt to evolving market demands by acquiring diverse skills through varied projects, fostering rapid and versatile skill development. Traditional employees often gain depth in specific roles with structured training programs and career progression plans that emphasize specialization and company expertise. The gig economy promotes self-driven, broad skill acquisition, while traditional employment supports focused, long-term professional growth within established organizational frameworks.
Legal and Tax Implications: Navigating the Systems
Freelancers operating within the gig economy face distinct legal and tax challenges compared to traditional employees, including self-employment tax liabilities and the need for personal liability management. Unlike salaried workers with employer-covered benefits and tax withholdings, gig workers must navigate complex reporting requirements and may lack protections such as unemployment insurance and workers' compensation. Understanding the regulatory frameworks governing independent contractors versus employees is crucial for compliance and optimizing financial outcomes in freelance work.
Work Culture and Social Interaction Differences
Freelancers in the gig economy often experience flexible work hours and project-based tasks, fostering autonomy but limited team collaboration compared to traditional employment. Traditional jobs emphasize structured schedules, stable roles, and frequent face-to-face interactions, which enhance social connections and workplace camaraderie. The gig economy's decentralized work culture can challenge consistent social engagement, while traditional employment supports sustained professional relationships and collective company culture.
Future Outlook: Evolving Trends in Employment
The gig economy is projected to grow significantly, driven by advancements in technology and increasing demand for flexible work arrangements, with forecasts estimating a 17% annual growth rate through 2030. Traditional employment faces challenges adapting to remote work preferences and digital transformation, pushing companies to integrate hybrid models for talent retention. Emerging trends highlight a hybrid workforce, where freelancers and full-time employees collaborate, reshaping job roles and benefits structures to meet future labor market demands.
Gig Economy vs Traditional Employment Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com