DEI programs prioritize creating inclusive work environments by promoting diversity, equity, and belonging, extending beyond the legal requirements of affirmative action. Affirmative action focuses primarily on compliance with regulations designed to ensure representation of underrepresented groups in hiring and promotion. Effective HR consulting integrates DEI strategies with affirmative action to drive sustainable organizational change and foster a culture of equity.
Table of Comparison
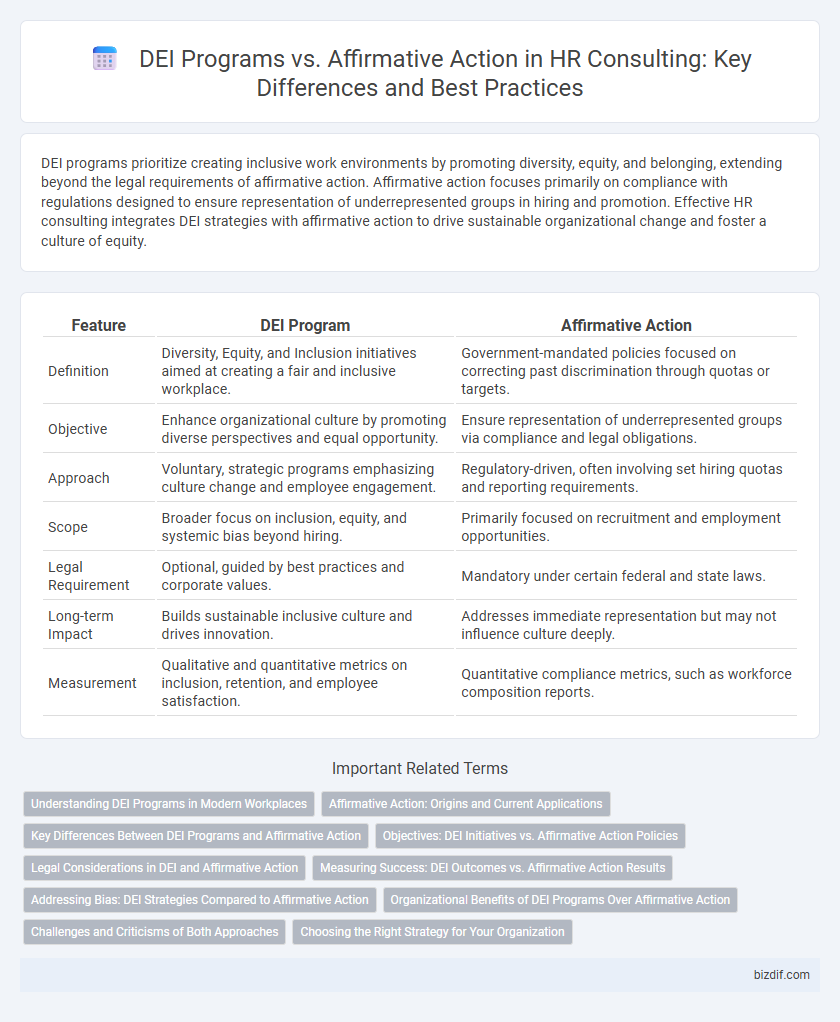
| Feature | DEI Program | Affirmative Action |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion initiatives aimed at creating a fair and inclusive workplace. | Government-mandated policies focused on correcting past discrimination through quotas or targets. |
| Objective | Enhance organizational culture by promoting diverse perspectives and equal opportunity. | Ensure representation of underrepresented groups via compliance and legal obligations. |
| Approach | Voluntary, strategic programs emphasizing culture change and employee engagement. | Regulatory-driven, often involving set hiring quotas and reporting requirements. |
| Scope | Broader focus on inclusion, equity, and systemic bias beyond hiring. | Primarily focused on recruitment and employment opportunities. |
| Legal Requirement | Optional, guided by best practices and corporate values. | Mandatory under certain federal and state laws. |
| Long-term Impact | Builds sustainable inclusive culture and drives innovation. | Addresses immediate representation but may not influence culture deeply. |
| Measurement | Qualitative and quantitative metrics on inclusion, retention, and employee satisfaction. | Quantitative compliance metrics, such as workforce composition reports. |
Understanding DEI Programs in Modern Workplaces
DEI programs in modern workplaces emphasize diversity, equity, and inclusion by fostering a culture of belonging and addressing systemic barriers beyond compliance requirements. Unlike affirmative action, which primarily focuses on meeting legal quotas for underrepresented groups, DEI initiatives integrate ongoing education, policy reforms, and employee engagement to create sustainable organizational change. Effective DEI strategies lead to increased innovation, improved employee satisfaction, and enhanced business performance by valuing diverse perspectives and equitable opportunities.
Affirmative Action: Origins and Current Applications
Affirmative Action, rooted in the Civil Rights Movement of the 1960s, originated as a legal mandate to address historical discrimination against marginalized groups in employment and education. Current applications of Affirmative Action focus on implementing controlled hiring quotas and compliance reporting to ensure diversity among underrepresented populations within organizations. Unlike broader DEI programs that foster inclusive workplace cultures, Affirmative Action stresses measurable outcomes and regulatory adherence in recruitment and retention processes.
Key Differences Between DEI Programs and Affirmative Action
DEI programs focus on fostering an inclusive workplace culture that values diversity across all dimensions, promoting equity and belonging beyond compliance requirements. Affirmative action mandates specific hiring or promotion goals to address historical discrimination, often driven by legal obligations and government policies. Key differences lie in DEI's voluntary, holistic approach to culture change versus affirmative action's targeted, compliance-driven framework.
Objectives: DEI Initiatives vs. Affirmative Action Policies
DEI initiatives prioritize fostering an inclusive workplace culture that values diversity across all dimensions, aiming to enhance employee engagement, innovation, and equity. Affirmative action policies focus on compliance-driven goals to increase representation of historically marginalized groups through targeted recruitment and hiring practices. Both approaches seek to improve workforce diversity but differ in their scope; DEI emphasizes long-term cultural change while affirmative action concentrates on specific demographic outcomes.
Legal Considerations in DEI and Affirmative Action
Legal considerations in DEI programs emphasize proactive cultural transformation and voluntary inclusion efforts beyond compliance, while affirmative action mandates specific hiring or promotion quotas to address historical discrimination under federal guidelines such as Executive Order 11246. DEI initiatives must navigate evolving anti-discrimination laws and Supreme Court rulings that impact race-conscious practices, ensuring policies foster equity without violating equal protection clauses. Employers benefit from integrating legal expertise to balance proactive diversity goals with affirmative action requirements, mitigating risks of litigation and regulatory audits.
Measuring Success: DEI Outcomes vs. Affirmative Action Results
Measuring success in DEI programs involves assessing qualitative outcomes such as employee engagement, inclusion perception, and cultural shifts, whereas affirmative action focuses on quantifiable results like representation metrics and compliance with legal benchmarks. DEI outcome evaluation utilizes tools like employee surveys, retention rates, and promotion equity analyses to gauge long-term organizational impact. Affirmative action results are primarily tracked through demographic data, hiring statistics, and adherence to mandated diversity targets.
Addressing Bias: DEI Strategies Compared to Affirmative Action
DEI programs emphasize creating inclusive workplace cultures by addressing unconscious bias through continuous education, employee resource groups, and systemic policy changes. Affirmative action primarily focuses on meeting legal requirements to increase representation of underrepresented groups through targeted hiring and promotion practices. DEI strategies foster long-term behavioral change and equity, whereas affirmative action mainly targets demographic outcomes.
Organizational Benefits of DEI Programs Over Affirmative Action
DEI programs foster inclusive workplace cultures that drive innovation, employee engagement, and retention, surpassing the compliance-focused scope of affirmative action. Organizations implementing DEI initiatives report improvements in team collaboration and decision-making diversity, leading to enhanced business performance. Emphasizing equity and belonging, DEI strategies contribute to sustained competitive advantage beyond the legal mandates of affirmative action.
Challenges and Criticisms of Both Approaches
DEI programs often face challenges related to measuring impact and ensuring genuine cultural transformation beyond compliance, while affirmative action is criticized for potential reverse discrimination and legal complexities. Both approaches encounter resistance from employees perceiving unfair advantages or tokenism, complicating workplace dynamics and trust. Navigating these challenges requires transparent communication, ongoing education, and the integration of inclusive practices into organizational policies to achieve sustainable diversity outcomes.
Choosing the Right Strategy for Your Organization
Selecting between a DEI program and affirmative action requires evaluating your organization's long-term diversity goals and compliance needs. DEI programs emphasize inclusive culture and equitable opportunities beyond legal mandates, fostering innovation and employee engagement. Affirmative action focuses on meeting regulatory requirements by addressing demographic disparities through targeted hiring practices.
DEI program vs affirmative action Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com