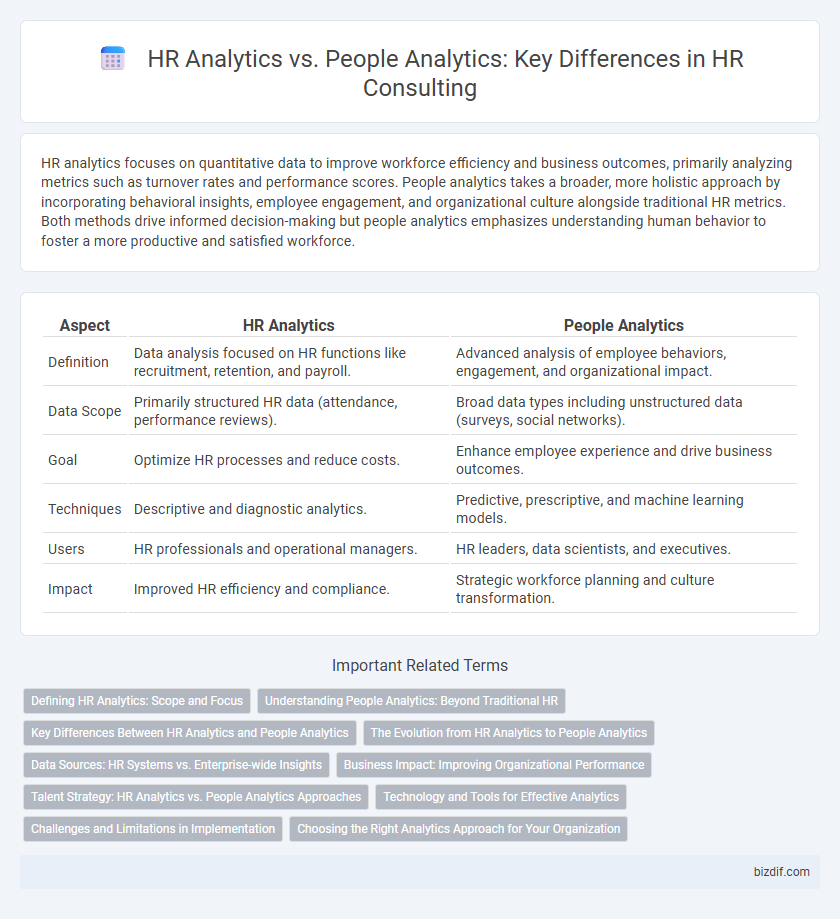
HR analytics focuses on quantitative data to improve workforce efficiency and business outcomes, primarily analyzing metrics such as turnover rates and performance scores. People analytics takes a broader, more holistic approach by incorporating behavioral insights, employee engagement, and organizational culture alongside traditional HR metrics. Both methods drive informed decision-making but people analytics emphasizes understanding human behavior to foster a more productive and satisfied workforce.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | HR Analytics | People Analytics |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Data analysis focused on HR functions like recruitment, retention, and payroll. | Advanced analysis of employee behaviors, engagement, and organizational impact. |
| Data Scope | Primarily structured HR data (attendance, performance reviews). | Broad data types including unstructured data (surveys, social networks). |
| Goal | Optimize HR processes and reduce costs. | Enhance employee experience and drive business outcomes. |
| Techniques | Descriptive and diagnostic analytics. | Predictive, prescriptive, and machine learning models. |
| Users | HR professionals and operational managers. | HR leaders, data scientists, and executives. |
| Impact | Improved HR efficiency and compliance. | Strategic workforce planning and culture transformation. |
Defining HR Analytics: Scope and Focus
HR analytics involves measuring, analyzing, and reporting workforce data to improve HR strategies, focusing primarily on employee performance, recruitment, and retention metrics. People analytics extends beyond traditional HR data by integrating behavioral, social, and organizational network analysis to optimize overall workforce effectiveness and business outcomes. The scope of HR analytics is more operational, while people analytics encompasses a broader and deeper analysis of human behavior and interactions within the workplace.
Understanding People Analytics: Beyond Traditional HR
People analytics delves deeper than traditional HR analytics by leveraging advanced data science techniques to analyze employee behavior, performance, and engagement patterns across the organization. This approach integrates diverse data sources such as social interactions, sentiment analysis, and real-time feedback, enabling predictive insights that drive strategic workforce decisions. Organizations adopting people analytics benefit from improved talent management, enhanced employee experience, and stronger alignment with business objectives.
Key Differences Between HR Analytics and People Analytics
HR analytics primarily focuses on quantifying workforce metrics such as employee turnover rates, recruitment efficiency, and performance evaluation to optimize organizational HR processes. People analytics expands beyond traditional HR data by integrating behavioral, social, and cultural insights to understand employee experience, engagement, and organizational dynamics. The key differences lie in HR analytics' concentration on administrative metrics versus people analytics' broader approach incorporating predictive models and employee-centric data to drive strategic decision-making.
The Evolution from HR Analytics to People Analytics
The evolution from HR analytics to people analytics represents a shift from traditional workforce data analysis to a more holistic approach encompassing employee experience, engagement, and organizational culture. While HR analytics primarily focuses on metrics such as turnover rates and recruitment efficiency, people analytics integrates behavioral data and predictive modeling to drive strategic workforce decisions. This transition enables companies to enhance talent management, boost employee productivity, and foster a data-driven organizational culture.
Data Sources: HR Systems vs. Enterprise-wide Insights
HR analytics primarily relies on data from HR systems such as payroll, recruitment, and performance management platforms to analyze workforce metrics. People analytics integrates enterprise-wide data sources, including finance, marketing, and operations, providing a holistic view of employee impact on organizational performance. Combining these data sets enables more strategic decision-making by linking HR outcomes to broader business objectives.
Business Impact: Improving Organizational Performance
HR analytics focuses on collecting and analyzing employee data to enhance workforce planning, talent acquisition, and employee retention, directly improving organizational performance. People analytics extends this by integrating behavioral, social, and operational data to provide deeper insights into employee engagement, leadership effectiveness, and team dynamics. By leveraging advanced analytics techniques, organizations can make data-driven decisions that boost productivity, reduce turnover, and align human capital strategies with business goals.
Talent Strategy: HR Analytics vs. People Analytics Approaches
Talent strategy leverages HR analytics to analyze workforce metrics such as turnover rates, recruitment efficiency, and employee performance data, providing insight into operational HR functions. People analytics goes deeper by integrating behavioral data, employee engagement levels, and cultural dynamics to predict talent trends and inform strategic decision-making. Combining both approaches enhances workforce planning, optimizing talent acquisition and retention aligned with business objectives.
Technology and Tools for Effective Analytics
HR analytics leverages advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence, machine learning, and big data platforms to process and interpret employee data, enabling strategic decision-making. People analytics integrates these tools with behavioral and performance metrics through specialized software like Visier, Workday, and SAP SuccessFactors, enhancing insights into workforce dynamics. Utilizing cloud-based analytics dashboards and predictive modeling tools accelerates the identification of talent trends and optimizes human capital management outcomes.
Challenges and Limitations in Implementation
HR analytics and people analytics both face significant challenges in implementation, including data quality issues, integration difficulties across disparate systems, and privacy concerns related to employee information. Accurately interpreting complex data requires advanced analytical skills and a clear alignment with organizational goals, while resistance from employees and management can hinder adoption. Limited standardization in metrics and tools further complicates consistent application, reducing the overall effectiveness of these analytics initiatives.
Choosing the Right Analytics Approach for Your Organization
Choosing the right analytics approach requires understanding the nuanced differences between HR analytics, which focuses on workforce metrics like turnover and performance, and people analytics, which delves deeper into behavioral patterns and employee experience. Organizations aiming to improve talent management and strategic decision-making should evaluate their specific goals, data maturity, and available technology to select the method that best aligns with their business objectives. Integrating predictive modeling and real-time insights from people analytics often drives more impactful outcomes than traditional HR analytics alone.
HR analytics vs people analytics Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com