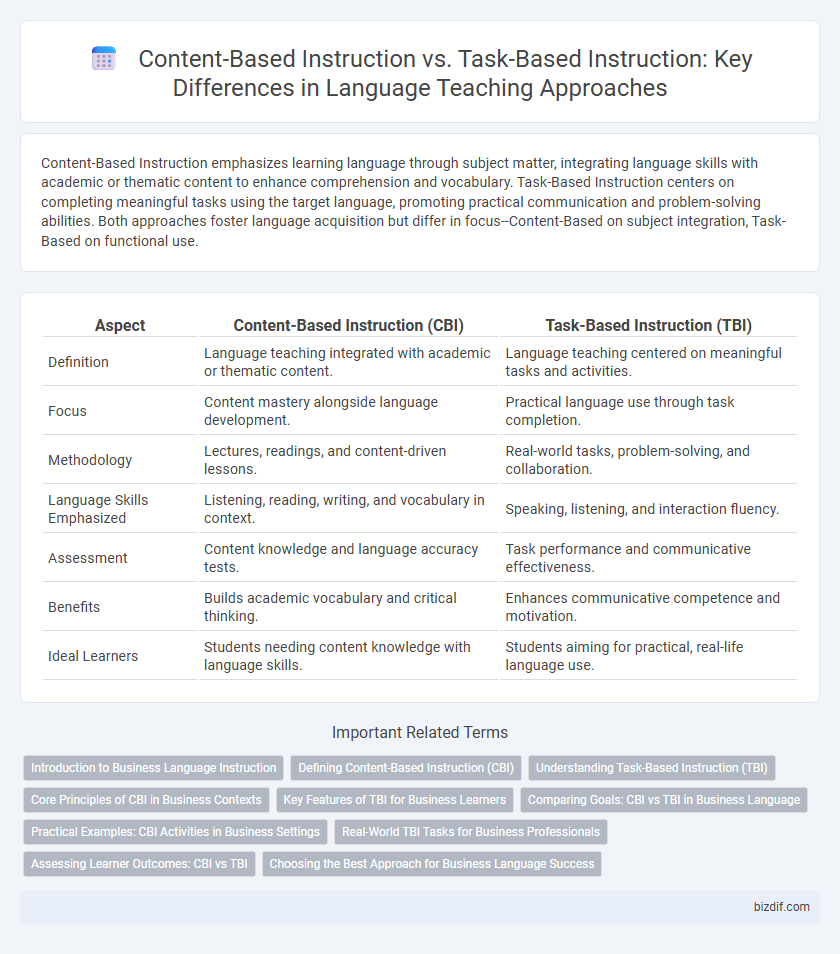
Content-Based Instruction emphasizes learning language through subject matter, integrating language skills with academic or thematic content to enhance comprehension and vocabulary. Task-Based Instruction centers on completing meaningful tasks using the target language, promoting practical communication and problem-solving abilities. Both approaches foster language acquisition but differ in focus--Content-Based on subject integration, Task-Based on functional use.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Content-Based Instruction (CBI) | Task-Based Instruction (TBI) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Language teaching integrated with academic or thematic content. | Language teaching centered on meaningful tasks and activities. |
| Focus | Content mastery alongside language development. | Practical language use through task completion. |
| Methodology | Lectures, readings, and content-driven lessons. | Real-world tasks, problem-solving, and collaboration. |
| Language Skills Emphasized | Listening, reading, writing, and vocabulary in context. | Speaking, listening, and interaction fluency. |
| Assessment | Content knowledge and language accuracy tests. | Task performance and communicative effectiveness. |
| Benefits | Builds academic vocabulary and critical thinking. | Enhances communicative competence and motivation. |
| Ideal Learners | Students needing content knowledge with language skills. | Students aiming for practical, real-life language use. |
Introduction to Business Language Instruction
Content-Based Instruction (CBI) in business language focuses on integrating language learning with subject matter, enabling students to acquire relevant vocabulary and communication skills essential for real-world business contexts. Task-Based Instruction (TBI) emphasizes practical tasks such as writing emails, conducting meetings, or negotiating deals, promoting active language use through meaningful business activities. Both approaches enhance proficiency but differ in emphasis: CBI centers on content integration, while TBI prioritizes task completion in business language education.
Defining Content-Based Instruction (CBI)
Content-Based Instruction (CBI) centers on teaching language through subject matter that is meaningful and relevant to learners, integrating language learning with content mastery. It emphasizes the use of authentic materials and promotes cognitive engagement by linking language skills to academic or professional topics. This approach fosters deeper understanding and retention by aligning linguistic goals with real-world content.
Understanding Task-Based Instruction (TBI)
Task-Based Instruction (TBI) centers on using meaningful tasks to promote practical language use, enhancing learners' real-world communication skills through interactive activities like problem-solving or role-playing. Unlike Content-Based Instruction, which integrates language learning with subject matter content, TBI prioritizes accomplishing specific tasks that require authentic language application. Research indicates TBI effectively improves learner engagement and language retention by focusing on purpose-driven communication rather than abstract language rules.
Core Principles of CBI in Business Contexts
Content-Based Instruction (CBI) in business contexts centers on integrating language learning with subject matter relevant to the corporate environment, emphasizing authentic materials and industry-specific terminology. Core principles include contextualized learning, where language skills develop through meaningful business content, and learner-centered approaches that tailor instruction to professional goals. This approach enhances communication proficiency by aligning language acquisition with real-world business tasks and scenarios.
Key Features of TBI for Business Learners
Task-Based Instruction (TBI) emphasizes practical language use through real-world business scenarios, promoting communication skills essential for professional interactions. Key features include learner-centered tasks, authentic materials reflecting workplace contexts, and a focus on achieving specific business outcomes. TBI enhances problem-solving, collaboration, and language fluency by engaging learners in meaningful, goal-oriented activities tailored to business environments.
Comparing Goals: CBI vs TBI in Business Language
Content-Based Instruction (CBI) in business language aims to develop language proficiency by integrating specific subject matter knowledge, enhancing learners' industry-related vocabulary and concepts. Task-Based Instruction (TBI) focuses on practical communication skills through real-world business tasks, such as negotiating contracts or conducting meetings, promoting functional language use. While CBI emphasizes content mastery for professional expertise, TBI prioritizes the completion of meaningful business activities to improve pragmatic language application.
Practical Examples: CBI Activities in Business Settings
Content-Based Instruction (CBI) in business settings often includes activities like analyzing market reports or conducting industry-specific case studies to enhance language acquisition through relevant content. Task-Based Instruction (TBI) emphasizes practical tasks such as role-playing client meetings or drafting business emails, which simulate real workplace communication. Both approaches integrate language learning with professional skills, boosting vocabulary and fluency in context-specific scenarios.
Real-World TBI Tasks for Business Professionals
Content-Based Instruction integrates language learning with subject matter expertise, enhancing business professionals' understanding of industry-specific terminology and concepts. Task-Based Instruction emphasizes completing authentic tasks such as writing reports, conducting meetings, or negotiating deals, directly simulating real-world business scenarios. Real-world TBI tasks improve practical communication skills by prioritizing meaningful interaction and problem-solving relevant to professional environments.
Assessing Learner Outcomes: CBI vs TBI
Assessing learner outcomes in Content-Based Instruction (CBI) primarily emphasizes subject-matter mastery alongside language proficiency, using assessments such as thematic projects and content quizzes that measure both academic knowledge and language application. Task-Based Instruction (TBI) evaluates learners based on their ability to complete real-world communicative tasks, with assessments like role-plays and problem-solving activities that reflect practical language use in authentic contexts. While CBI outcomes focus on integrated content and language growth, TBI prioritizes functional language competence and task completion effectiveness.
Choosing the Best Approach for Business Language Success
Content-Based Instruction (CBI) integrates language learning with subject matter relevant to business contexts, enhancing vocabulary and industry-specific communication skills. Task-Based Instruction (TBI) emphasizes practical language use through real-world business tasks, promoting fluency and problem-solving abilities. Selecting between CBI and TBI depends on learners' goals: CBI suits those needing in-depth sector knowledge, while TBI benefits learners focusing on dynamic interaction and task completion in professional settings.
Content-Based Instruction vs Task-Based Instruction Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com