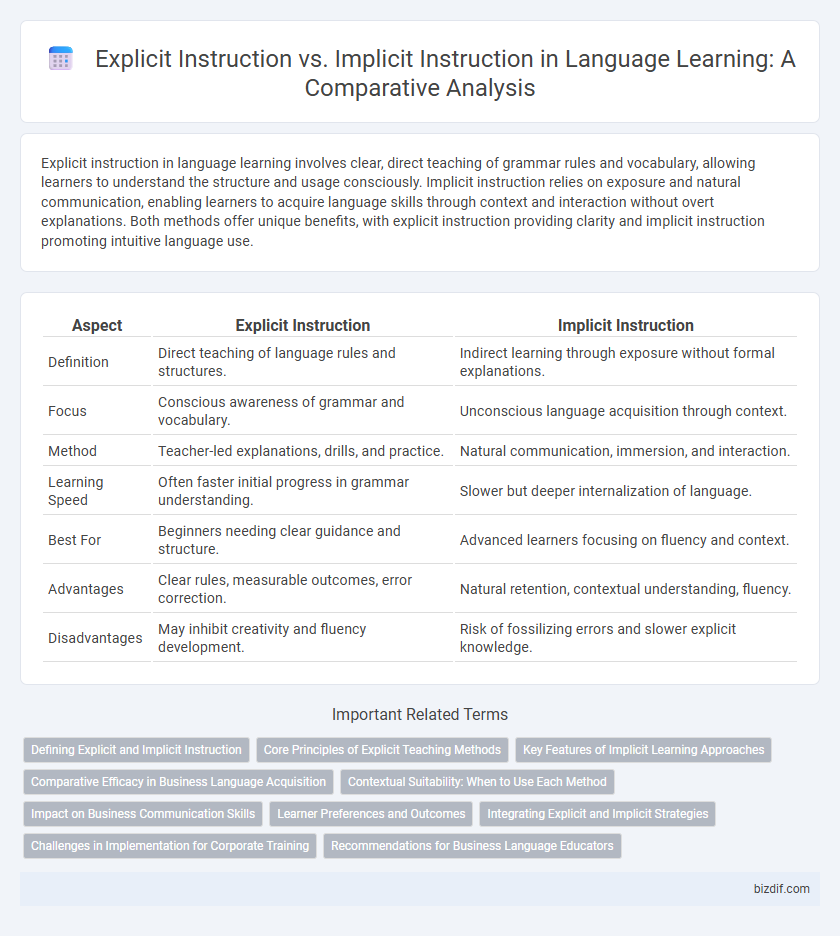
Explicit instruction in language learning involves clear, direct teaching of grammar rules and vocabulary, allowing learners to understand the structure and usage consciously. Implicit instruction relies on exposure and natural communication, enabling learners to acquire language skills through context and interaction without overt explanations. Both methods offer unique benefits, with explicit instruction providing clarity and implicit instruction promoting intuitive language use.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Explicit Instruction | Implicit Instruction |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Direct teaching of language rules and structures. | Indirect learning through exposure without formal explanations. |
| Focus | Conscious awareness of grammar and vocabulary. | Unconscious language acquisition through context. |
| Method | Teacher-led explanations, drills, and practice. | Natural communication, immersion, and interaction. |
| Learning Speed | Often faster initial progress in grammar understanding. | Slower but deeper internalization of language. |
| Best For | Beginners needing clear guidance and structure. | Advanced learners focusing on fluency and context. |
| Advantages | Clear rules, measurable outcomes, error correction. | Natural retention, contextual understanding, fluency. |
| Disadvantages | May inhibit creativity and fluency development. | Risk of fossilizing errors and slower explicit knowledge. |
Defining Explicit and Implicit Instruction
Explicit instruction involves clear, direct teaching where specific language rules and concepts are consciously explained to learners, emphasizing clarity and structured guidance. Implicit instruction relies on natural language exposure and practice without overt explanations, encouraging learners to infer rules through context and usage. Both methods play crucial roles in language acquisition, addressing different learning preferences and goals.
Core Principles of Explicit Teaching Methods
Explicit teaching methods center on clear, structured, and direct language instruction, emphasizing clear learning objectives, systematic skill progression, and immediate feedback to ensure comprehension and mastery. These core principles involve modeling language use, guided practice with corrective feedback, and scaffolded support that gradually shifts responsibility to the learner. Research consistently shows that explicit instruction enhances language acquisition efficiency, particularly for grammar, vocabulary, and reading comprehension skills.
Key Features of Implicit Learning Approaches
Implicit learning approaches in language instruction emphasize natural language acquisition through exposure and meaningful communication rather than direct rule explanations. Key features include subconscious knowledge development, reliance on input-rich environments, and the integration of language use in authentic contexts, promoting fluency and intuitive understanding. This method supports learners in internalizing language patterns without overt analytical effort, enhancing retention and spontaneous language production.
Comparative Efficacy in Business Language Acquisition
Explicit instruction in business language acquisition involves direct teaching of grammar, vocabulary, and usage, which accelerates proficiency by providing clear rules and structured practice. Implicit instruction relies on immersive exposure and contextual learning, fostering natural language development but often requiring more time to achieve fluency. Research shows explicit instruction yields faster results in mastering business terminology and communication skills essential for professional environments.
Contextual Suitability: When to Use Each Method
Explicit instruction is most effective in structured learning environments where clarity and direct guidance are essential, such as teaching grammar rules or vocabulary in a foreign language classroom. Implicit instruction suits immersive contexts like conversational practice or language exposure through media, fostering natural acquisition through context and repetition. Choosing between these methods depends on learners' proficiency levels, goals, and the instructional context to optimize language acquisition outcomes.
Impact on Business Communication Skills
Explicit instruction in business communication prioritizes clear, structured teaching of grammar, vocabulary, and professional writing conventions, leading to improved clarity and effectiveness in workplace interactions. Implicit instruction encourages learning through immersion and context, fostering adaptability and conversational fluency but may result in inconsistent application of formal communication standards. Combining explicit and implicit methods enhances overall business communication competence by balancing accuracy with practical language use.
Learner Preferences and Outcomes
Learners exhibit varied preferences for explicit instruction, which emphasizes clear, direct teaching of language rules, and implicit instruction, which fosters language acquisition through exposure and natural use. Research shows explicit instruction often leads to faster mastery of grammar and vocabulary, while implicit instruction enhances fluency and comprehension by promoting intuitive language use. Optimal language outcomes frequently result from balanced approaches tailored to individual learner needs, combining structured guidance with immersive exposure.
Integrating Explicit and Implicit Strategies
Integrating explicit and implicit instruction strategies enhances language acquisition by balancing clear, structured teaching of grammar rules with natural language exposure through authentic communication. Research highlights that combining direct explanations with immersive, context-rich practice accelerates vocabulary retention and grammatical accuracy. Effective language programs leverage this dual approach to cater to diverse learner needs, promoting both conscious understanding and intuitive language use.
Challenges in Implementation for Corporate Training
Explicit instruction in corporate training often faces challenges such as employee resistance to rigid, teacher-led methods and difficulties in maintaining engagement during structured lessons. Implicit instruction encounters obstacles including assessing learner progress due to its indirect approach and the need for skilled facilitators who can effectively embed language learning within real-world tasks. Both methods require balancing organizational goals with individual learning preferences to ensure successful language acquisition in professional environments.
Recommendations for Business Language Educators
Business language educators should emphasize explicit instruction by providing clear grammar rules, vocabulary definitions, and structured practice to enhance learner comprehension and accuracy. Incorporating contextualized scenarios and role-plays can bridge explicit teaching with practical application, reinforcing language retention in professional settings. Regular formative assessments and targeted feedback help tailor instruction to individual learner needs, maximizing language acquisition efficiency.
Explicit Instruction vs Implicit Instruction Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com