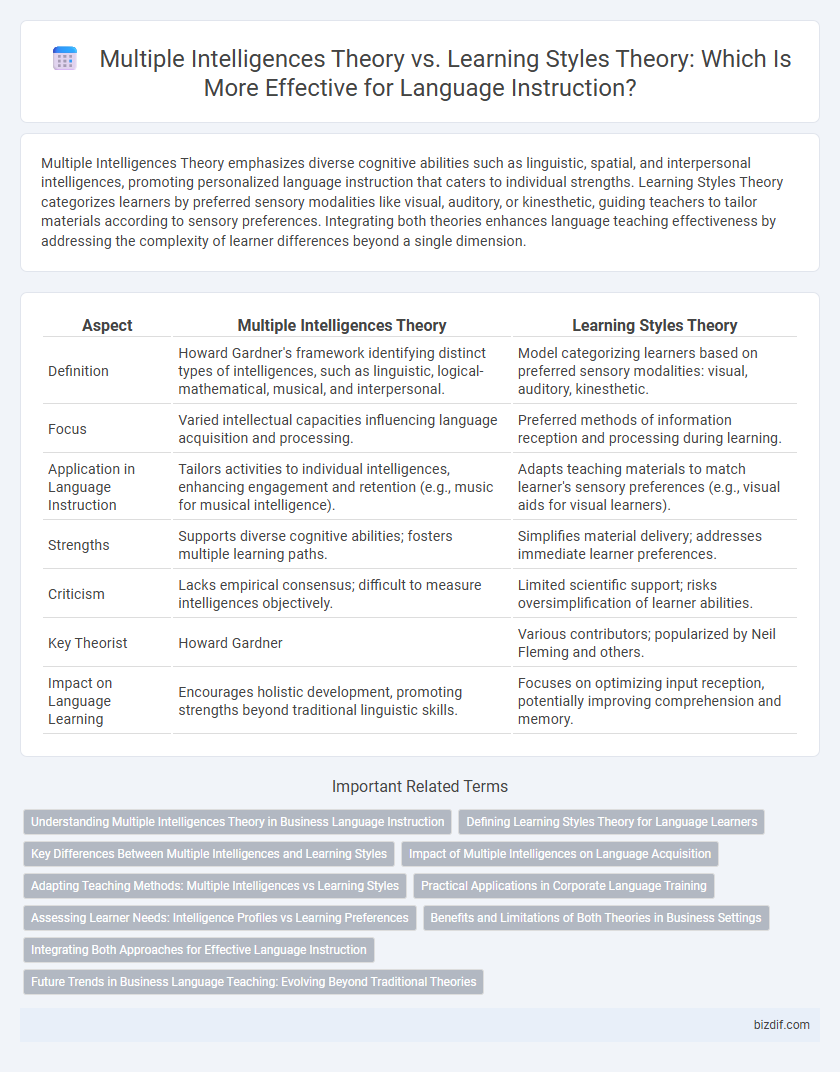
Multiple Intelligences Theory emphasizes diverse cognitive abilities such as linguistic, spatial, and interpersonal intelligences, promoting personalized language instruction that caters to individual strengths. Learning Styles Theory categorizes learners by preferred sensory modalities like visual, auditory, or kinesthetic, guiding teachers to tailor materials according to sensory preferences. Integrating both theories enhances language teaching effectiveness by addressing the complexity of learner differences beyond a single dimension.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Multiple Intelligences Theory | Learning Styles Theory |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Howard Gardner's framework identifying distinct types of intelligences, such as linguistic, logical-mathematical, musical, and interpersonal. | Model categorizing learners based on preferred sensory modalities: visual, auditory, kinesthetic. |
| Focus | Varied intellectual capacities influencing language acquisition and processing. | Preferred methods of information reception and processing during learning. |
| Application in Language Instruction | Tailors activities to individual intelligences, enhancing engagement and retention (e.g., music for musical intelligence). | Adapts teaching materials to match learner's sensory preferences (e.g., visual aids for visual learners). |
| Strengths | Supports diverse cognitive abilities; fosters multiple learning paths. | Simplifies material delivery; addresses immediate learner preferences. |
| Criticism | Lacks empirical consensus; difficult to measure intelligences objectively. | Limited scientific support; risks oversimplification of learner abilities. |
| Key Theorist | Howard Gardner | Various contributors; popularized by Neil Fleming and others. |
| Impact on Language Learning | Encourages holistic development, promoting strengths beyond traditional linguistic skills. | Focuses on optimizing input reception, potentially improving comprehension and memory. |
Understanding Multiple Intelligences Theory in Business Language Instruction
Understanding Multiple Intelligences Theory in business language instruction enhances learner engagement by recognizing diverse cognitive strengths such as linguistic, interpersonal, and logical-mathematical intelligences. This approach allows tailored communication strategies that align with individual intelligence profiles, improving comprehension and retention of business terminology and concepts. Integrating Gardner's Multiple Intelligences promotes dynamic and effective language acquisition compared to the limited scope of traditional learning styles theory.
Defining Learning Styles Theory for Language Learners
Learning Styles Theory categorizes language learners based on their preferred sensory modalities, such as visual, auditory, or kinesthetic, influencing how they best absorb, process, and retain linguistic information. Tailoring instructional methods to these individual learning preferences aims to enhance comprehension and communicative competence. Despite its popularity, conclusive empirical support for the effectiveness of Learning Styles-based approaches in language acquisition remains limited.
Key Differences Between Multiple Intelligences and Learning Styles
Multiple Intelligences Theory, developed by Howard Gardner, identifies distinct types of intelligences such as linguistic, logical-mathematical, and spatial, emphasizing varied ways individuals process information. Learning Styles Theory categorizes preferences in how students absorb material, typically as visual, auditory, or kinesthetic learners. The key difference lies in Multiple Intelligences addressing diverse cognitive strengths, while Learning Styles focus on preferred sensory modalities for receiving information.
Impact of Multiple Intelligences on Language Acquisition
Multiple Intelligences Theory significantly enhances language acquisition by recognizing diverse cognitive strengths such as linguistic, musical, and interpersonal intelligences, allowing tailored instructional strategies that improve comprehension and retention. This approach contrasts with Learning Styles Theory, which often categorizes learners into limited sensory modes but may overlook the complex interplay of intelligences influencing language mastery. Implementing Multiple Intelligences Theory in language instruction fosters a more holistic educational experience, increasing learner engagement and promoting deeper, multifaceted language proficiency.
Adapting Teaching Methods: Multiple Intelligences vs Learning Styles
Adapting teaching methods based on Multiple Intelligences Theory involves recognizing unique cognitive strengths such as linguistic, spatial, or kinesthetic intelligences, allowing educators to diversify instruction techniques to engage different intellectual capacities. In contrast, Learning Styles Theory emphasizes tailoring approaches to preferred sensory modes of information processing, like visual, auditory, or kinesthetic learning styles, to enhance comprehension and retention. Effective language instruction benefits from integrating both frameworks by customizing activities that address varied intelligences and preferred learning styles, thereby optimizing student engagement and achievement.
Practical Applications in Corporate Language Training
Multiple Intelligences Theory enhances corporate language training by tailoring instruction to diverse cognitive strengths such as linguistic, interpersonal, and bodily-kinesthetic intelligences, fostering more effective communication skills development. Learning Styles Theory emphasizes customizing lessons based on individual preferences like visual, auditory, or kinesthetic learning modalities to increase engagement and retention in language acquisition. Integrating both theories allows corporate trainers to design dynamic programs that address varied learner needs, improving overall language proficiency and workplace communication efficiency.
Assessing Learner Needs: Intelligence Profiles vs Learning Preferences
Assessing learner needs through Multiple Intelligences Theory involves identifying diverse intelligence profiles such as linguistic, logical-mathematical, and interpersonal intelligences to tailor instruction methods. In contrast, Learning Styles Theory emphasizes individual learning preferences like visual, auditory, or kinesthetic modalities to customize educational approaches. Integrating intelligence profiles with learning preferences enhances the precision of language instruction by addressing both cognitive capabilities and preferred sensory modalities.
Benefits and Limitations of Both Theories in Business Settings
Multiple Intelligences Theory enhances business training by recognizing diverse cognitive strengths, fostering teamwork through tailored communication strategies, but may require extensive resources for effective implementation. Learning Styles Theory facilitates personalized learning experiences that improve employee engagement and retention, yet its rigid categorization can oversimplify complex learning needs, limiting adaptability. Both theories contribute valuable insights to corporate learning, but their integration demands careful consideration of organizational goals and learner variability.
Integrating Both Approaches for Effective Language Instruction
Integrating Multiple Intelligences Theory and Learning Styles Theory enhances language instruction by addressing diverse learner strengths and preferences, fostering comprehensive language acquisition. Utilizing Gardner's multiple intelligences alongside tailored learning styles allows educators to design activities that engage linguistic, logical-mathematical, spatial, and kinesthetic intelligences while respecting auditory, visual, and kinesthetic learning preferences. This combined approach promotes deeper understanding, increased motivation, and personalized language development outcomes.
Future Trends in Business Language Teaching: Evolving Beyond Traditional Theories
Future trends in business language teaching emphasize integrating Multiple Intelligences Theory to create tailored learning experiences that address diverse cognitive strengths, enhancing communication skills in global markets. Advances in AI and adaptive technology enable dynamic assessment and real-time customization beyond static Learning Styles Theory, promoting practical language proficiency and cultural competence. Embracing this evolution supports holistic learner development and aligns language instruction with the demands of modern international business environments.
Multiple Intelligences Theory vs Learning Styles Theory Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com