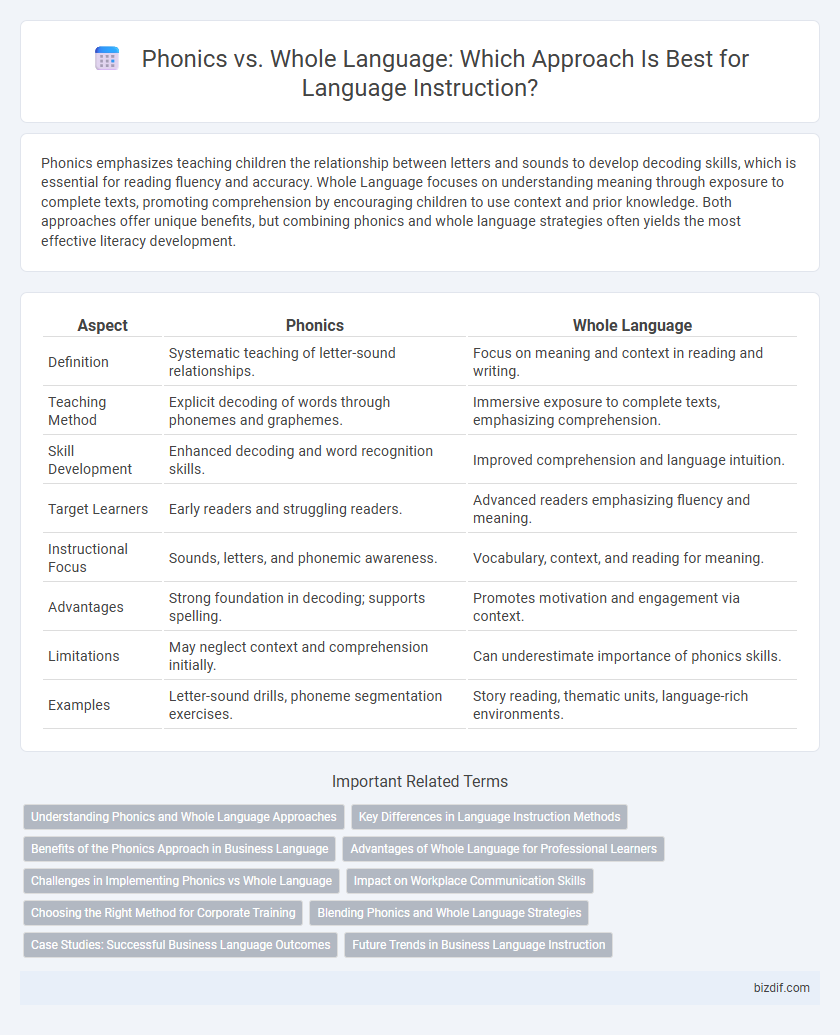
Phonics emphasizes teaching children the relationship between letters and sounds to develop decoding skills, which is essential for reading fluency and accuracy. Whole Language focuses on understanding meaning through exposure to complete texts, promoting comprehension by encouraging children to use context and prior knowledge. Both approaches offer unique benefits, but combining phonics and whole language strategies often yields the most effective literacy development.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Phonics | Whole Language |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Systematic teaching of letter-sound relationships. | Focus on meaning and context in reading and writing. |
| Teaching Method | Explicit decoding of words through phonemes and graphemes. | Immersive exposure to complete texts, emphasizing comprehension. |
| Skill Development | Enhanced decoding and word recognition skills. | Improved comprehension and language intuition. |
| Target Learners | Early readers and struggling readers. | Advanced readers emphasizing fluency and meaning. |
| Instructional Focus | Sounds, letters, and phonemic awareness. | Vocabulary, context, and reading for meaning. |
| Advantages | Strong foundation in decoding; supports spelling. | Promotes motivation and engagement via context. |
| Limitations | May neglect context and comprehension initially. | Can underestimate importance of phonics skills. |
| Examples | Letter-sound drills, phoneme segmentation exercises. | Story reading, thematic units, language-rich environments. |
Understanding Phonics and Whole Language Approaches
Phonics instruction emphasizes decoding skills by teaching the relationships between letters and sounds to enable accurate word recognition. Whole Language approach prioritizes meaning and context, encouraging learners to engage with text as a whole to develop comprehension and fluency. Research indicates a balanced literacy program integrating systematic phonics with rich language experiences supports effective reading development.
Key Differences in Language Instruction Methods
Phonics instruction emphasizes decoding skills by teaching the relationship between letters and sounds, promoting systematic reading development. Whole Language focuses on meaning and context, encouraging learners to recognize words as whole pieces within authentic texts. The key difference lies in phonics' bottom-up approach versus whole language's top-down strategy in fostering reading proficiency.
Benefits of the Phonics Approach in Business Language
The phonics approach in business language instruction enhances clarity by teaching learners to decode and pronounce industry-specific terminology accurately, leading to improved communication with clients and colleagues. This method fosters stronger reading comprehension skills essential for understanding complex business documents and contracts. Mastery of phonics contributes to increased confidence and professionalism in verbal presentations and negotiations.
Advantages of Whole Language for Professional Learners
Whole Language empowers professional learners by emphasizing context and meaning, fostering deeper comprehension and practical language application. This approach leverages authentic texts and real-world communication, enhancing vocabulary retention and critical thinking skills. Professional learners benefit from the integrative, learner-centered nature of Whole Language, which supports advanced language proficiency and adaptable communication strategies.
Challenges in Implementing Phonics vs Whole Language
Implementing phonics often faces challenges such as the need for systematic teacher training and resistance from educators accustomed to whole language approaches. Whole language instruction encounters difficulties in ensuring students acquire foundational decoding skills, leading to variances in reading proficiency. Both methods require careful integration to address diverse learner needs and instructional consistency.
Impact on Workplace Communication Skills
Phonics instruction improves workplace communication skills by enhancing employees' ability to decode and comprehend complex vocabulary, resulting in clearer written and verbal expression. Whole language approaches foster contextual understanding and inferencing, which supports interpreting nuanced messages and adapting communication style to diverse professional audiences. Combining phonics and whole language methods develops balanced literacy skills that enhance clarity, comprehension, and effectiveness in workplace communication.
Choosing the Right Method for Corporate Training
Phonics emphasizes systematic instruction in letter-sound relationships, fostering strong decoding skills essential for clear communication in corporate training environments. Whole Language prioritizes contextual understanding and meaning-making, supporting employee engagement through real-world text applications. Selecting the right method involves assessing workforce literacy levels and training goals to enhance comprehension and retention effectively.
Blending Phonics and Whole Language Strategies
Blending phonics emphasizes decoding words by correlating letters with sounds, enhancing reading fluency through systematic instruction. Whole language strategies focus on meaning-making and context, encouraging learners to recognize words as whole units within authentic text. Integrating blending phonics with whole language techniques fosters balanced literacy by combining phonemic awareness and comprehension skills.
Case Studies: Successful Business Language Outcomes
Case studies in language instruction reveal that phonics-based approaches significantly improve decoding and pronunciation skills, leading to enhanced business communication proficiency. Whole language methods foster contextual understanding and fluency, which contribute to better comprehension and application in real-world business scenarios. Combining phonics and whole language strategies often results in superior outcomes for effective business language acquisition and usage.
Future Trends in Business Language Instruction
Future trends in business language instruction emphasize an integration of phonics and whole language approaches to enhance communicative competence and literacy. Advances in AI-driven language learning platforms customize phonics-based exercises with context-rich, whole language content to improve practical business communication skills. This blended method supports efficient vocabulary acquisition and fluency, meeting evolving corporate demands for multilingual professionals.
Phonics vs Whole Language Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com