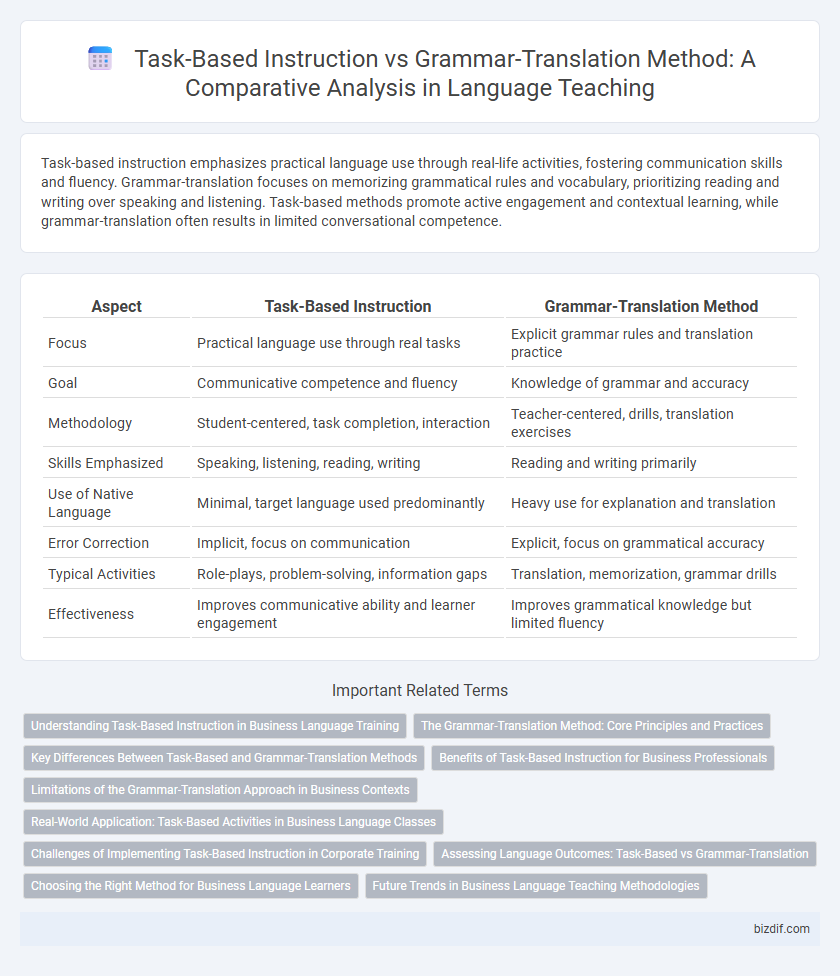
Task-based instruction emphasizes practical language use through real-life activities, fostering communication skills and fluency. Grammar-translation focuses on memorizing grammatical rules and vocabulary, prioritizing reading and writing over speaking and listening. Task-based methods promote active engagement and contextual learning, while grammar-translation often results in limited conversational competence.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Task-Based Instruction | Grammar-Translation Method |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Practical language use through real tasks | Explicit grammar rules and translation practice |
| Goal | Communicative competence and fluency | Knowledge of grammar and accuracy |
| Methodology | Student-centered, task completion, interaction | Teacher-centered, drills, translation exercises |
| Skills Emphasized | Speaking, listening, reading, writing | Reading and writing primarily |
| Use of Native Language | Minimal, target language used predominantly | Heavy use for explanation and translation |
| Error Correction | Implicit, focus on communication | Explicit, focus on grammatical accuracy |
| Typical Activities | Role-plays, problem-solving, information gaps | Translation, memorization, grammar drills |
| Effectiveness | Improves communicative ability and learner engagement | Improves grammatical knowledge but limited fluency |
Understanding Task-Based Instruction in Business Language Training
Task-based instruction in business language training emphasizes real-world communication skills through practical tasks, promoting active language use and problem-solving. Unlike the grammar-translation method, which focuses on rote memorization and grammatical rules, task-based instruction enhances fluency and contextual understanding vital for professional interactions. This approach fosters effective business communication by integrating industry-specific scenarios that improve language retention and practical application.
The Grammar-Translation Method: Core Principles and Practices
The Grammar-Translation Method centers on the direct teaching of grammar rules and vocabulary through translation exercises between the target language and the native language. This traditional method emphasizes written language over speaking skills, using repetitive drills and rote memorization to develop reading comprehension and written accuracy. Its core practices include detailed grammatical analysis, sentence parsing, and translation of classical texts, which prioritize linguistic form over communicative competence.
Key Differences Between Task-Based and Grammar-Translation Methods
Task-based instruction emphasizes practical communication and real-life language use through meaningful tasks, while the grammar-translation method focuses on explicit grammar rules and direct translation exercises. Task-based learning promotes fluency and interactive skills by engaging learners in problem-solving activities, contrasting with the grammar-translation approach that prioritizes accuracy and written language proficiency. Key differences include the learner's active role in task completion versus passive knowledge acquisition and the contextualized use of language versus isolated grammar drills.
Benefits of Task-Based Instruction for Business Professionals
Task-based instruction enhances communication skills by simulating real-world business scenarios, enabling professionals to apply language practically and confidently. This approach fosters critical thinking and problem-solving abilities through interactive tasks, which directly improve workplace collaboration and negotiation. Unlike grammar-translation methods, task-based instruction prioritizes fluency and functional language use, accelerating language acquisition tailored to business contexts.
Limitations of the Grammar-Translation Approach in Business Contexts
The grammar-translation approach often limits business language learners' ability to engage in authentic communication and practical problem-solving, as it emphasizes rote memorization and isolated grammatical rules. This method rarely develops oral proficiency or real-time interaction skills, which are crucial in dynamic business environments. Consequently, learners may struggle with negotiating, presenting ideas, and building professional relationships in global markets.
Real-World Application: Task-Based Activities in Business Language Classes
Task-based instruction in business language classes emphasizes real-world application through interactive activities such as role-plays, simulations, and case studies, enabling learners to practice authentic communication scenarios like negotiations and presentations. This approach enhances practical language skills by focusing on meaning and context rather than isolated grammar rules characteristic of grammar-translation methods. As a result, students develop greater fluency and confidence in using business terminology and expressions in professional settings.
Challenges of Implementing Task-Based Instruction in Corporate Training
Implementing task-based instruction (TBI) in corporate training faces challenges such as aligning tasks with specific business objectives and varied employee language proficiency levels. Unlike the grammar-translation method, TBI requires significant time investment for developing authentic, context-relevant tasks that promote active communication and problem-solving. Training facilitators often need specialized skills to effectively design and manage these interactive learning experiences, which can impact corporate training budgets and timelines.
Assessing Language Outcomes: Task-Based vs Grammar-Translation
Task-based instruction emphasizes authentic language use and communicative competence, assessing outcomes through practical performance tasks and real-life scenarios. Grammar-translation methods primarily focus on accuracy in grammar rules and vocabulary, with assessments based on written translation and rote memorization. Task-based assessments better capture learners' ability to apply language skills dynamically, whereas grammar-translation tends to measure static knowledge of linguistic forms.
Choosing the Right Method for Business Language Learners
Task-based instruction enhances communication skills by engaging business language learners in real-world tasks such as negotiations and presentations, promoting practical usage over rote memorization. In contrast, grammar-translation emphasizes accuracy through direct translation and explicit grammar rules, which may slow conversational fluency. Selecting task-based instruction for business contexts supports quicker adaptation to professional environments, improving both linguistic competence and job performance.
Future Trends in Business Language Teaching Methodologies
Task-based instruction in business language teaching emphasizes practical communication skills and real-world problem-solving, aligning with the growing demand for workplace readiness and cross-cultural competence. Emerging trends favor integrating technology-enhanced tasks, such as virtual simulations and AI-driven language assessment, to enhance learner engagement and personalized feedback. Future methodologies will likely blend task-based approaches with adaptive digital tools to meet evolving global business communication needs efficiently.
Task-based instruction vs grammar-translation Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com