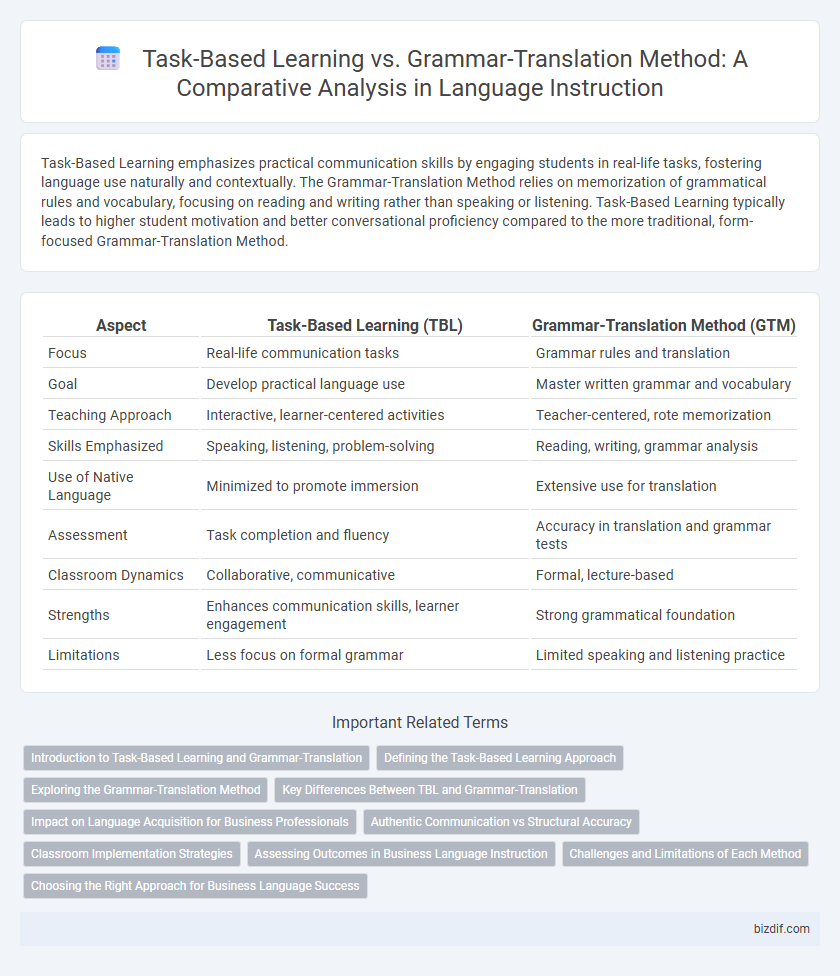
Task-Based Learning emphasizes practical communication skills by engaging students in real-life tasks, fostering language use naturally and contextually. The Grammar-Translation Method relies on memorization of grammatical rules and vocabulary, focusing on reading and writing rather than speaking or listening. Task-Based Learning typically leads to higher student motivation and better conversational proficiency compared to the more traditional, form-focused Grammar-Translation Method.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Task-Based Learning (TBL) | Grammar-Translation Method (GTM) |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Real-life communication tasks | Grammar rules and translation |
| Goal | Develop practical language use | Master written grammar and vocabulary |
| Teaching Approach | Interactive, learner-centered activities | Teacher-centered, rote memorization |
| Skills Emphasized | Speaking, listening, problem-solving | Reading, writing, grammar analysis |
| Use of Native Language | Minimized to promote immersion | Extensive use for translation |
| Assessment | Task completion and fluency | Accuracy in translation and grammar tests |
| Classroom Dynamics | Collaborative, communicative | Formal, lecture-based |
| Strengths | Enhances communication skills, learner engagement | Strong grammatical foundation |
| Limitations | Less focus on formal grammar | Limited speaking and listening practice |
Introduction to Task-Based Learning and Grammar-Translation
Task-Based Learning emphasizes practical communication skills by engaging students in meaningful tasks that reflect real-life language use, fostering fluency and interaction. The Grammar-Translation Method focuses on the explicit teaching of grammatical rules and vocabulary, prioritizing translation exercises and written accuracy over spoken proficiency. Task-Based Learning integrates language acquisition with task completion, while Grammar-Translation centers on language analysis and reading comprehension.
Defining the Task-Based Learning Approach
Task-Based Learning (TBL) emphasizes the completion of meaningful tasks to facilitate language acquisition, prioritizing communication and practical use over explicit grammar instruction. This approach engages learners in real-life scenarios, encouraging active problem-solving, collaboration, and contextual language use. Unlike the Grammar-Translation Method, which focuses on rote memorization and translation of grammatical rules, TBL fosters fluency through immersive, task-oriented experiences.
Exploring the Grammar-Translation Method
The Grammar-Translation Method emphasizes rote memorization of vocabulary and grammatical rules, often using direct translation between the target language and the native language. It prioritizes reading and writing skills over speaking and listening, with exercises centered on sentence parsing and written drills. This traditional approach contrasts sharply with Task-Based Learning's focus on practical communication and real-life interaction.
Key Differences Between TBL and Grammar-Translation
Task-Based Learning (TBL) emphasizes real-life communication and practical language use, promoting fluency through meaningful tasks, while the Grammar-Translation Method focuses on rote memorization of grammatical rules and vocabulary with translation exercises. TBL encourages learner engagement and interactive problem-solving, enhancing speaking and listening skills, whereas Grammar-Translation prioritizes reading and writing accuracy with limited conversational practice. Assessment in TBL measures task completion and language performance, contrasting with Grammar-Translation's focus on grammatical correctness and translation accuracy.
Impact on Language Acquisition for Business Professionals
Task-Based Learning enhances language acquisition for business professionals by promoting practical communication skills and real-world problem-solving, which are critical in corporate settings. In contrast, the Grammar-Translation Method emphasizes rote memorization of grammatical rules, often limiting learners' ability to engage in spontaneous dialogue and fluid business interactions. Empirical studies reveal that Task-Based Learning leads to higher retention rates and greater fluency, directly benefiting professionals who require adaptive language use in dynamic business environments.
Authentic Communication vs Structural Accuracy
Task-Based Learning emphasizes authentic communication by engaging learners in real-life tasks that promote fluency and practical language use, fostering spontaneous interaction. The Grammar-Translation Method prioritizes structural accuracy, focusing on the explicit teaching of grammar rules and the translation of texts to ensure precise linguistic forms. While Task-Based Learning supports communicative competence and learner autonomy, the Grammar-Translation Method centers on accuracy and systematic language analysis.
Classroom Implementation Strategies
Task-Based Learning emphasizes real-life communication through interactive tasks like role-plays and problem-solving activities, which foster language fluency and learner engagement. In contrast, the Grammar-Translation Method relies on direct instruction of grammatical rules and vocabulary, followed by translation exercises that focus on accuracy over fluency. Effective classroom implementation of Task-Based Learning involves group collaboration and meaningful context, whereas Grammar-Translation prioritizes individual work and written drills.
Assessing Outcomes in Business Language Instruction
Task-Based Learning in business language instruction emphasizes real-world communication skills, enhancing learners' ability to perform workplace tasks effectively. Grammar-Translation Method primarily develops reading and writing accuracy but often fails to improve practical speaking and listening competencies essential for business interactions. Assessing outcomes reveals that Task-Based Learning produces higher engagement and functional language use, leading to improved performance in professional contexts.
Challenges and Limitations of Each Method
Task-Based Learning faces challenges such as the need for extensive teacher training and difficulty in assessing language accuracy due to its focus on communication over form. The Grammar-Translation Method limits oral proficiency and communicative competence because it emphasizes rote memorization and translation without practical language use. Both methods struggle with balancing linguistic accuracy and real-world communication skills, impacting overall language acquisition effectiveness.
Choosing the Right Approach for Business Language Success
Task-Based Learning emphasizes practical communication and real-world business scenarios, enhancing learners' ability to use language effectively in professional contexts. The Grammar-Translation Method focuses on detailed grammatical rules and vocabulary translation, which may limit spontaneous business interactions and fluency. Selecting the right approach depends on prioritizing either functional communication skills or in-depth grammatical knowledge for specific business language success.
Task-Based Learning vs Grammar-Translation Method Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com