Cold meal prep for pets offers convenience and retains more nutrients by avoiding heat-related degradation, making it ideal for sensitive ingredients like vegetables and supplements. Hot meal prep can enhance flavor and digestibility, especially for proteins, but requires careful cooling and storage to prevent bacterial growth. Choosing between cold and hot meal prep depends on your pet's dietary needs and the type of ingredients used.
Table of Comparison
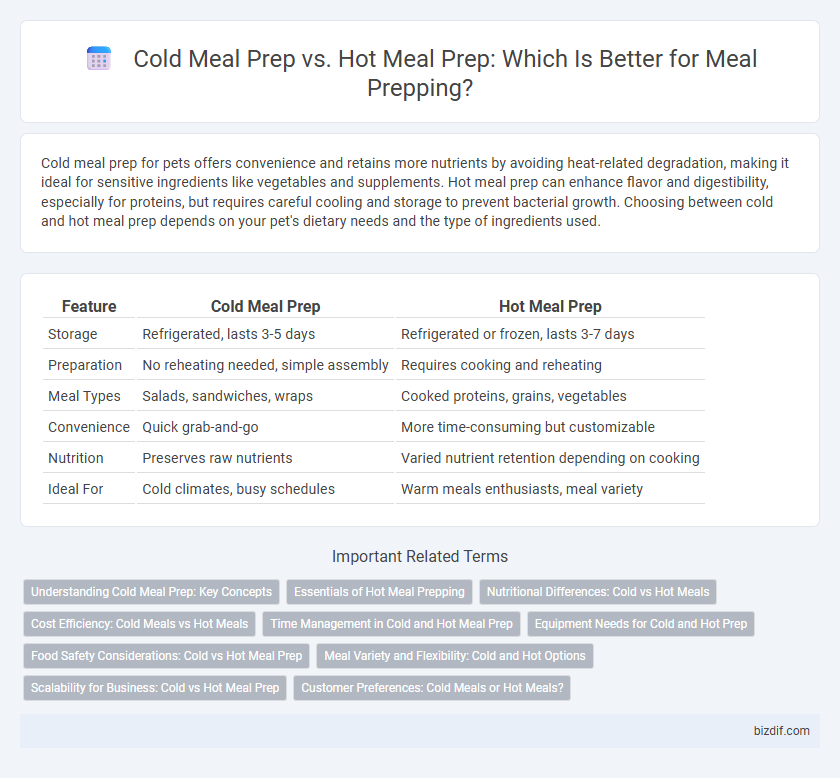
| Feature | Cold Meal Prep | Hot Meal Prep |
|---|---|---|
| Storage | Refrigerated, lasts 3-5 days | Refrigerated or frozen, lasts 3-7 days |
| Preparation | No reheating needed, simple assembly | Requires cooking and reheating |
| Meal Types | Salads, sandwiches, wraps | Cooked proteins, grains, vegetables |
| Convenience | Quick grab-and-go | More time-consuming but customizable |
| Nutrition | Preserves raw nutrients | Varied nutrient retention depending on cooking |
| Ideal For | Cold climates, busy schedules | Warm meals enthusiasts, meal variety |
Understanding Cold Meal Prep: Key Concepts
Cold meal prep involves preparing meals that are intended to be eaten without reheating, focusing on fresh, nutrient-dense ingredients such as salads, grain bowls, and wraps. This method emphasizes the importance of proper food storage techniques like refrigeration and airtight containers to maintain freshness and prevent spoilage. Understanding cold meal prep also includes recognizing the benefits of convenience, time-saving, and preserving the natural flavors and textures of ingredients.
Essentials of Hot Meal Prepping
Hot meal prepping requires proper cooking techniques to ensure food safety and flavor retention during reheating. Essential elements include choosing ingredients that maintain texture and nutritional value after being heated multiple times, such as lean proteins and steamed vegetables. Using airtight containers prevents moisture loss and preserves heat-sensitive nutrients, making meals enjoyable and healthy throughout the week.
Nutritional Differences: Cold vs Hot Meals
Cold meal prep preserves more heat-sensitive nutrients, such as vitamin C and certain B vitamins, which can degrade during cooking. Hot meal prep enhances the bioavailability of some nutrients like lycopene and beta-carotene by breaking down cell walls in vegetables. Choosing between cold and hot meal prep depends on maximizing nutrient retention based on specific ingredients and dietary goals.
Cost Efficiency: Cold Meals vs Hot Meals
Cold meal prep offers significant cost efficiency by reducing the need for reheating appliances and energy consumption, lowering electricity bills over time. Ingredients for cold meals, such as salads, sandwiches, and wraps, often require less cooking time and simpler preparation, minimizing utility costs compared to hot meals. Hot meal prep incurs higher expenses due to ongoing energy use for cooking and reheating, impacting both household budgets and resource efficiency.
Time Management in Cold and Hot Meal Prep
Cold meal prep saves time by allowing multiple meals to be prepared and stored simultaneously without the need for reheating, making it ideal for quick grab-and-go options. Hot meal prep requires additional time for cooking and reheating, but it offers the advantage of fresh, warm meals that can be ready just before eating. Efficient time management in cold meal prep revolves around batch cooking and refrigeration, while hot meal prep demands precise scheduling to ensure meals are cooked at the right time for optimal taste and safety.
Equipment Needs for Cold and Hot Prep
Cold meal prep requires minimal equipment such as airtight containers, a sharp chef's knife for fresh produce, salad spinners, and a reliable refrigerator or cooler to maintain freshness. Hot meal prep demands additional tools like stovetops, ovens, slow cookers, and microwave-safe containers that withstand reheating while preserving food quality. Both approaches benefit from meal prep tools like portion scales, cutting boards, and insulated lunch bags to streamline cooking and storage efficiency.
Food Safety Considerations: Cold vs Hot Meal Prep
Cold meal prep requires strict temperature control to prevent bacterial growth, maintaining foods at or below 40degF (4degC) during storage and transportation. Hot meal prep demands rapid cooling from 140degF to 70degF within two hours and further to 40degF within four hours to reduce pathogen risks. Proper handling and reheating to an internal temperature of 165degF (74degC) are critical for both methods to ensure food safety and minimize contamination.
Meal Variety and Flexibility: Cold and Hot Options
Cold meal prepping offers greater variety and flexibility by including diverse ingredients like salads, sandwiches, and chilled grains that maintain freshness without reheating. Hot meal prep provides options such as soups, stir-fries, and casseroles, catering to preferences for warm, comforting dishes that can be easily reheated. Combining both cold and hot meal prep strategies maximizes nutritional balance and adapts to different daily schedules and taste preferences.
Scalability for Business: Cold vs Hot Meal Prep
Cold meal prep offers higher scalability for businesses due to easier mass production, longer shelf life, and reduced refrigeration costs. Hot meal prep requires specialized equipment and immediate consumption, limiting batch sizes and increasing labor expenses. Choosing cold meal prep enhances operational efficiency and supports larger order volumes with consistent quality.
Customer Preferences: Cold Meals or Hot Meals?
Customer preferences for meal prepping often divide between cold meals and hot meals based on convenience and taste. Cold meal preps like salads, overnight oats, and sushi bowls appeal to those seeking quick, grab-and-go options with fresh ingredients that retain nutrients without reheating. Hot meal preps attract customers who prefer comforting, cooked dishes such as stews and casseroles that offer warmth and enhanced flavors through reheating.
Cold meal prep vs hot meal prep Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com