Fresh meal prepping for pets ensures optimal nutrient retention and flavor, promoting better digestion and overall health. Frozen meal prepping offers convenience and extended shelf life, allowing pet owners to prepare meals in bulk without compromising safety. Choosing between fresh and frozen depends on your pet's dietary needs, lifestyle, and storage capabilities.
Table of Comparison
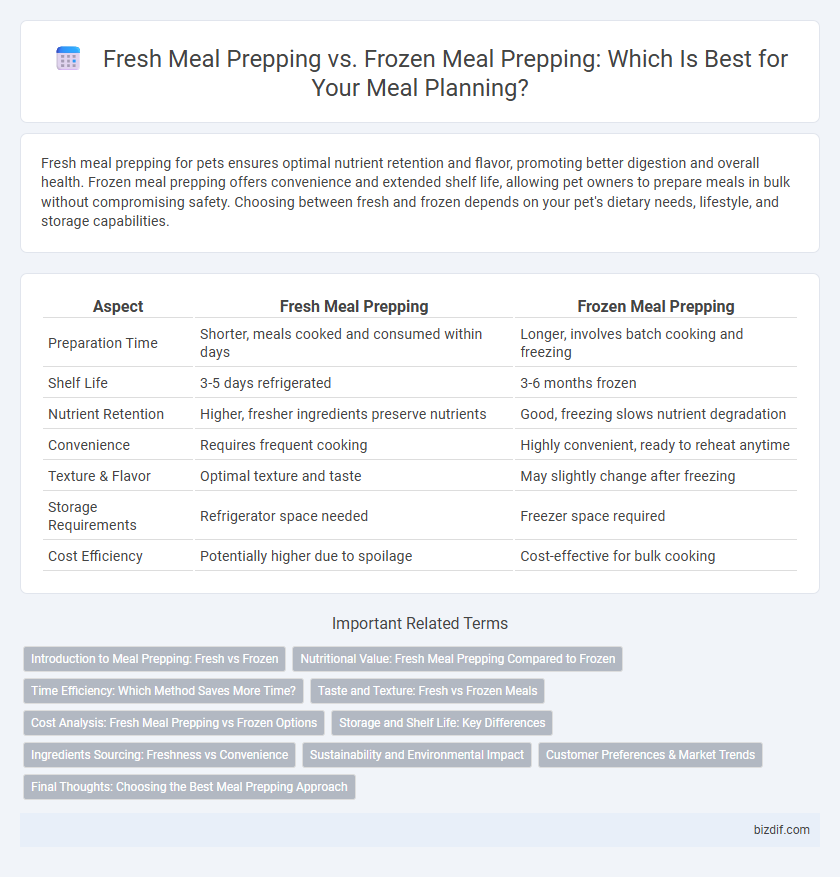
| Aspect | Fresh Meal Prepping | Frozen Meal Prepping |
|---|---|---|
| Preparation Time | Shorter, meals cooked and consumed within days | Longer, involves batch cooking and freezing |
| Shelf Life | 3-5 days refrigerated | 3-6 months frozen |
| Nutrient Retention | Higher, fresher ingredients preserve nutrients | Good, freezing slows nutrient degradation |
| Convenience | Requires frequent cooking | Highly convenient, ready to reheat anytime |
| Texture & Flavor | Optimal texture and taste | May slightly change after freezing |
| Storage Requirements | Refrigerator space needed | Freezer space required |
| Cost Efficiency | Potentially higher due to spoilage | Cost-effective for bulk cooking |
Introduction to Meal Prepping: Fresh vs Frozen
Fresh meal prepping preserves nutrients and flavors by using recently prepared ingredients, ideal for those valuing taste and texture. Frozen meal prepping offers long-term storage benefits and convenience, reducing spoilage and meal waste significantly. Choosing between fresh and frozen meal prep depends on lifestyle, storage capacity, and nutritional priorities.
Nutritional Value: Fresh Meal Prepping Compared to Frozen
Fresh meal prepping preserves higher levels of vitamins and antioxidants, as minimal cooking and no freezing reduce nutrient degradation. In contrast, frozen meal prepping can cause slight nutrient loss, especially in water-soluble vitamins like vitamin C and B-complex, due to blanching and freezing processes. However, freezing slows enzymatic activity and prevents spoilage, maintaining most macronutrients and minerals effectively over longer storage periods.
Time Efficiency: Which Method Saves More Time?
Fresh meal prepping typically saves time by eliminating thawing and reheating steps, allowing immediate consumption after cooking. Frozen meal prepping requires additional time for freezing and defrosting but enables bulk cooking and longer storage, reducing the need for daily preparation. Overall, frozen meal prepping offers greater long-term time efficiency for busy schedules, while fresh prepping suits those seeking quicker immediate meals.
Taste and Texture: Fresh vs Frozen Meals
Fresh meal prepping preserves vibrant flavors and crisp textures, offering a more satisfying eating experience compared to frozen meals. Freezing can cause ice crystals to form, leading to moisture loss and altered texture, often resulting in a softer or mushier consistency. While freezing extends shelf life, fresh meals maintain superior taste and mouthfeel due to minimal processing and immediate consumption.
Cost Analysis: Fresh Meal Prepping vs Frozen Options
Fresh meal prepping often incurs higher costs due to the frequent purchase of perishable ingredients and the lack of bulk buying discounts. Frozen meal prepping allows for cost savings by enabling bulk purchases, reducing food waste, and extending ingredient shelf life, which lowers overall grocery expenses. Evaluating cost-effectiveness depends on meal frequency, ingredient quality, and storage facilities.
Storage and Shelf Life: Key Differences
Fresh meal prepping requires refrigeration and typically lasts 3-5 days, ensuring optimal flavor and nutrient retention. Frozen meal prepping extends shelf life to several months by slowing bacterial growth, but may slightly affect texture and taste upon reheating. Proper storage containers and airtight sealing are essential in both methods to maintain food quality and prevent freezer burn or spoilage.
Ingredients Sourcing: Freshness vs Convenience
Fresh meal prepping relies on sourcing seasonal, local ingredients known for peak flavor and nutrient content, enhancing overall meal quality. Frozen meal prepping prioritizes convenience by using ingredients harvested and flash-frozen at their nutritional peak, allowing for extended shelf life without significant nutrient loss. Balancing freshness and convenience depends on individual lifestyle needs and access to quality food suppliers.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Fresh meal prepping reduces energy consumption by eliminating the need for prolonged freezing and thawing cycles, lowering carbon emissions compared to frozen meal prepping. Using local, seasonal ingredients in fresh meal prepping supports sustainable agriculture and decreases transportation-related pollution. Frozen meal prepping, while convenient for reducing food waste, often relies on energy-intensive storage and packaging, contributing to higher environmental impact.
Customer Preferences & Market Trends
Customer preferences increasingly favor fresh meal prepping for its perceived health benefits and superior taste, driving demand in urban markets with access to fresh ingredients. Frozen meal prepping maintains steady popularity due to convenience, longer shelf life, and portion control, appealing to busy professionals and budget-conscious consumers. Market trends indicate a growing hybrid approach, combining fresh and frozen elements to balance nutrition, flavor, and convenience.
Final Thoughts: Choosing the Best Meal Prepping Approach
Fresh meal prepping preserves maximum nutrient retention and flavor, ideal for those prioritizing taste and immediate consumption. Frozen meal prepping offers extended shelf life and convenience, reducing daily cooking time while maintaining reasonable nutritional value. Selecting the best approach depends on individual lifestyle, storage capacity, and meal variety preferences.
Fresh meal prepping vs frozen meal prepping Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com