Hot holding ensures pet meals remain at a safe temperature above 140degF, preventing bacterial growth and preserving nutrient quality until serving. Cold storage, maintained below 40degF, slows down spoilage and keeps ingredients fresh for longer periods, making it ideal for long-term meal prepping. Proper temperature control in both methods is essential to maintain pet food safety and nutritional value.
Table of Comparison
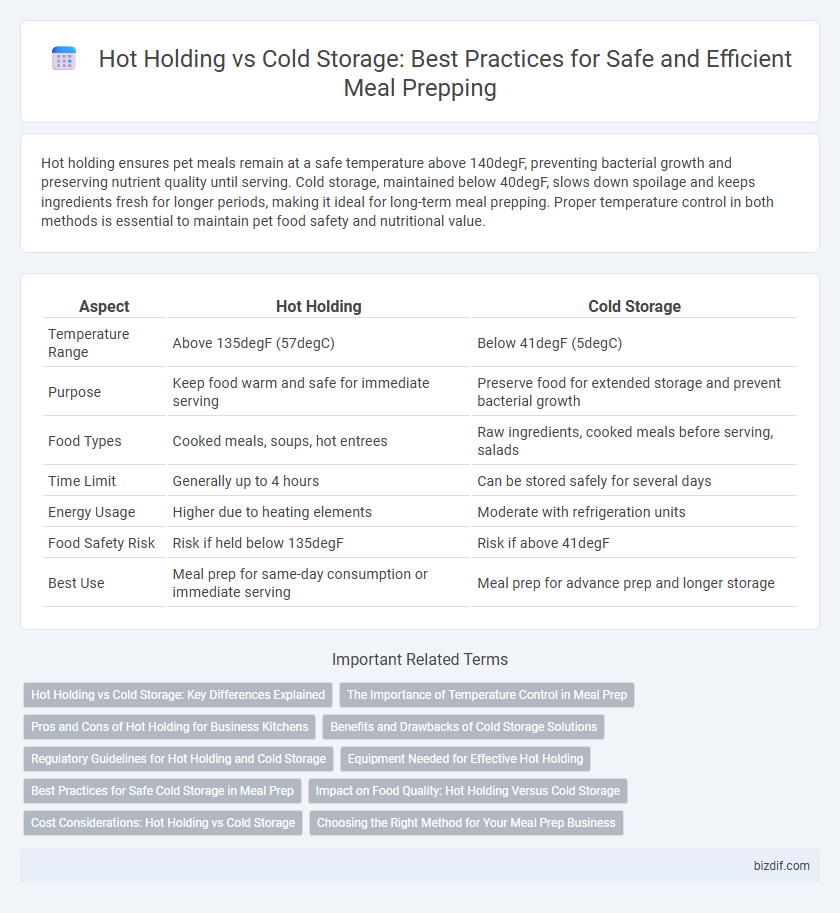
| Aspect | Hot Holding | Cold Storage |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature Range | Above 135degF (57degC) | Below 41degF (5degC) |
| Purpose | Keep food warm and safe for immediate serving | Preserve food for extended storage and prevent bacterial growth |
| Food Types | Cooked meals, soups, hot entrees | Raw ingredients, cooked meals before serving, salads |
| Time Limit | Generally up to 4 hours | Can be stored safely for several days |
| Energy Usage | Higher due to heating elements | Moderate with refrigeration units |
| Food Safety Risk | Risk if held below 135degF | Risk if above 41degF |
| Best Use | Meal prep for same-day consumption or immediate serving | Meal prep for advance prep and longer storage |
Hot Holding vs Cold Storage: Key Differences Explained
Hot holding maintains cooked meals at temperatures above 140degF (60degC) to prevent bacterial growth and ensure food safety during service. Cold storage keeps ingredients or prepared dishes below 40degF (4degC), slowing microbial activity to preserve freshness and extend shelf life. Understanding these temperature controls is essential for meal prepping to balance food quality, safety, and efficient workflow.
The Importance of Temperature Control in Meal Prep
Maintaining precise temperature control during meal prepping is critical to prevent bacterial growth and ensure food safety, with hot holding requiring temperatures above 135degF (57degC) and cold storage needing below 40degF (4degC). Proper hot holding preserves the quality and freshness of cooked meals, while cold storage slows down enzymatic activity and microbial proliferation in perishable ingredients. Effective temperature regulation reduces the risk of foodborne illnesses and extends shelf life, making it a cornerstone of safe and efficient meal preparation practices.
Pros and Cons of Hot Holding for Business Kitchens
Hot holding in business kitchens ensures food safety by keeping prepared meals at a consistent temperature above 140degF, reducing the risk of bacterial growth. It benefits meal prepping by maintaining food warmth for immediate service, minimizing reheating time, and preserving texture and flavor, yet it consumes more energy and risks drying out meals if not properly managed. Proper hot holding equipment and techniques are essential to balance food quality, safety, and operational efficiency in commercial kitchen environments.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Cold Storage Solutions
Cold storage solutions in meal prepping preserve freshness and extend shelf life by slowing bacterial growth, making them ideal for storing perishable ingredients like dairy, meats, and vegetables. They require consistent refrigeration temperatures between 32degF and 40degF to maintain food safety and prevent spoilage. However, cold storage demands reliable electricity and can limit meal accessibility, potentially leading to increased preparation time during busy schedules.
Regulatory Guidelines for Hot Holding and Cold Storage
Regulatory guidelines for hot holding require maintaining cooked food at temperatures above 135degF (57degC) to prevent bacterial growth and ensure food safety. Cold storage regulations mandate keeping perishable items at or below 41degF (5degC) to inhibit microbial activity and preserve freshness. Compliance with these temperature controls is critical for minimizing foodborne illness risks during meal prepping and storage.
Equipment Needed for Effective Hot Holding
Effective hot holding requires specialized equipment such as insulated food warmers, steam tables, and heat lamps to maintain safe temperatures above 135degF (57degC). Commercial-grade hot holding cabinets with precise temperature controls ensure food remains evenly heated without drying out. Utilizing these tools minimizes bacterial growth and preserves meal quality for extended periods during meal prepping.
Best Practices for Safe Cold Storage in Meal Prep
Maintaining proper cold storage temperatures below 40degF (4degC) is essential for inhibiting bacterial growth in meal prepping. Use airtight containers and label meals with preparation dates to ensure food safety and freshness. Regularly monitor and clean refrigerators to prevent cross-contamination and maintain optimal storage conditions.
Impact on Food Quality: Hot Holding Versus Cold Storage
Hot holding maintains food at temperatures above 140degF (60degC), preventing bacterial growth while preserving texture and flavor for short durations. Cold storage keeps food below 40degF (4degC), slowing microbial activity and enzymatic reactions, thereby extending shelf life and retaining nutritional value. Both methods impact food quality by balancing safety and freshness, with hot holding suited for immediate service and cold storage ideal for longer preservation.
Cost Considerations: Hot Holding vs Cold Storage
Hot holding requires continuous energy consumption to maintain safe temperatures, leading to higher utility costs compared to cold storage. Cold storage systems, such as refrigerators and freezers, rely on intermittent cooling cycles, making them more energy-efficient and cost-effective for long-term food preservation. Initial investment in cold storage equipment may be higher, but operational expenses are generally lower than those associated with hot holding units.
Choosing the Right Method for Your Meal Prep Business
Selecting between hot holding and cold storage in meal prepping hinges on food safety, quality, and energy efficiency. Hot holding maintains prepared dishes at temperatures above 140degF (60degC) to prevent bacterial growth, making it ideal for immediate service or same-day consumption. Cold storage, typically below 40degF (4degC), extends shelf life and preserves freshness, suited for batch preparation and longer distribution cycles in your meal prep business.
Hot Holding vs Cold Storage Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com