Vegetarian meal prepping for pets involves carefully selecting plant-based ingredients that provide essential nutrients like protein, vitamins, and minerals, ensuring a balanced diet tailored to their specific needs. Omnivore meal prepping, on the other hand, incorporates both animal proteins and plant foods, offering a broader range of amino acids and nutrients vital for optimal health. Choosing between these approaches depends on the pet's dietary requirements and any allergies, with proper meal prepping enhancing digestion and overall well-being.
Table of Comparison
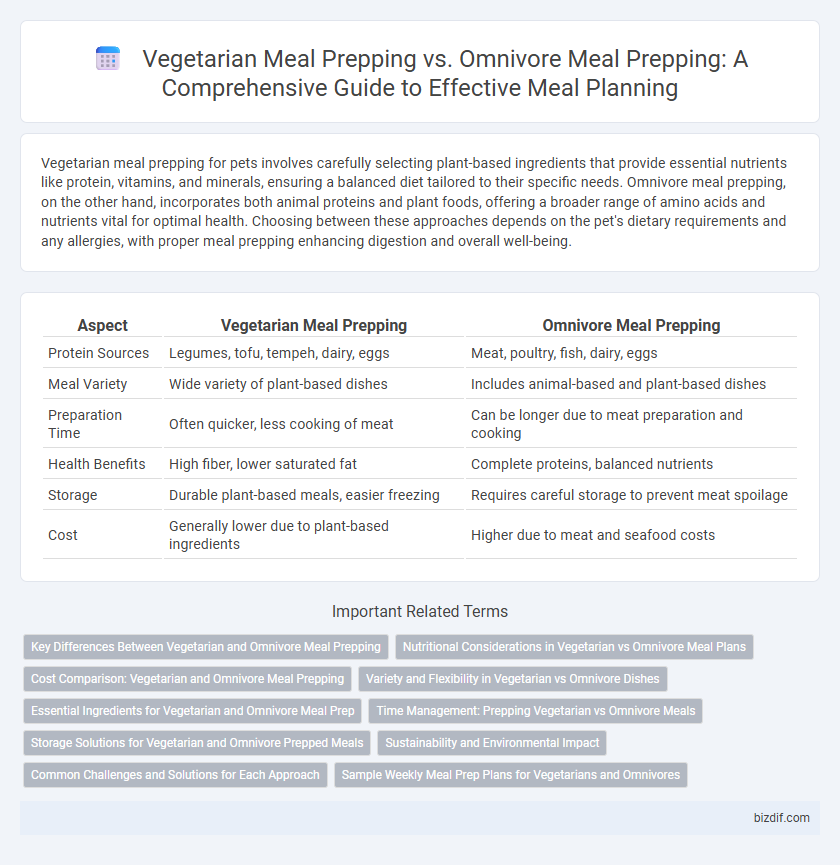
| Aspect | Vegetarian Meal Prepping | Omnivore Meal Prepping |
|---|---|---|
| Protein Sources | Legumes, tofu, tempeh, dairy, eggs | Meat, poultry, fish, dairy, eggs |
| Meal Variety | Wide variety of plant-based dishes | Includes animal-based and plant-based dishes |
| Preparation Time | Often quicker, less cooking of meat | Can be longer due to meat preparation and cooking |
| Health Benefits | High fiber, lower saturated fat | Complete proteins, balanced nutrients |
| Storage | Durable plant-based meals, easier freezing | Requires careful storage to prevent meat spoilage |
| Cost | Generally lower due to plant-based ingredients | Higher due to meat and seafood costs |
Key Differences Between Vegetarian and Omnivore Meal Prepping
Vegetarian meal prepping centers on plant-based proteins like beans, lentils, tofu, and a diverse range of vegetables, while omnivore meal prepping includes animal proteins such as chicken, beef, fish, and eggs. Nutrient planning in vegetarian prepping emphasizes obtaining sufficient vitamin B12, iron, and complete amino acids through plant combinations or supplements, contrasting with omnivore prepping where these nutrients are more readily available from animal sources. Shelf life and storage strategies also differ; vegetarian meals often require careful handling of cooked legumes and greens to maintain freshness, whereas omnivore meals focus on proper refrigeration and cooking temperatures to prevent bacterial growth in meat products.
Nutritional Considerations in Vegetarian vs Omnivore Meal Plans
Vegetarian meal prepping emphasizes plant-based proteins like legumes, tofu, and quinoa to ensure adequate intake of essential amino acids, fiber, and micronutrients such as iron and vitamin B12, which may require supplementation. Omnivore meal prepping offers diverse nutrient sources including complete proteins from meat, fish, and dairy, along with heme iron and vitamin B12, supporting muscle maintenance and overall nutrient balance. Both meal plans demand strategic planning to meet daily requirements for iron, calcium, omega-3 fatty acids, and protein quality, with vegetarian plans often requiring fortified foods or supplements to address potential nutritional gaps.
Cost Comparison: Vegetarian and Omnivore Meal Prepping
Vegetarian meal prepping typically offers a cost advantage over omnivore meal prepping due to the lower price of plant-based proteins like beans, lentils, and tofu compared to meat and seafood. Bulk purchasing of vegetables, grains, and legumes further reduces expenses, making vegetarian diets more budget-friendly for meal preparation. In contrast, omnivore meal prepping incurs higher costs from animal protein sources and often requires additional spending on refrigeration and preservation.
Variety and Flexibility in Vegetarian vs Omnivore Dishes
Vegetarian meal prepping offers greater variety through a diverse range of plant-based proteins, grains, and vegetables that can be easily combined into flavorful dishes, enhancing nutritional flexibility. Omnivore meal prepping provides flexibility by incorporating multiple protein sources such as poultry, beef, fish, and eggs, allowing for varied textures and tastes in meals. Both approaches can maximize meal diversity, but vegetarian prepping often emphasizes creative use of legumes, tofu, and seasonal produce to maintain nutritional balance and appeal.
Essential Ingredients for Vegetarian and Omnivore Meal Prep
Vegetarian meal prepping essential ingredients include plant-based proteins such as lentils, chickpeas, tofu, quinoa, and a variety of fresh vegetables like spinach, bell peppers, and sweet potatoes which provide necessary vitamins and minerals. Omnivore meal prepping relies on a combination of lean meats such as chicken breast, turkey, and fish, alongside whole grains like brown rice and nutrient-dense vegetables to balance protein, fiber, and micronutrient intake. Both approaches require thoughtful selection of staples that support balanced macronutrients and long-lasting freshness for effective weekly meal planning.
Time Management: Prepping Vegetarian vs Omnivore Meals
Vegetarian meal prepping often requires less time due to the simplicity of plant-based ingredients and fewer cooking steps compared to omnivore meal prepping, which involves additional tasks like handling raw meat and longer cooking times to ensure safety. Bulk-cooking grains, legumes, and vegetables for vegetarian meals can streamline the process, while omnivore meal prepping frequently demands careful portioning and temperature control. Efficient time management in meal prepping hinges on ingredient choice, with vegetarian options generally offering faster preparation and cleanup.
Storage Solutions for Vegetarian and Omnivore Prepped Meals
Vegetarian meal prepping often requires moisture-resistant containers to preserve fresh produce and prevent sogginess, while omnivore meal prepping benefits from airtight containers that maintain the quality of cooked meats and prevent cross-contamination. Vacuum-sealed bags and glass containers with secure lids are ideal for extending the shelf life of both vegetarian and omnivore meals, ensuring nutrient retention and taste. Proper labeling and portioned storage solutions streamline meal organization, reduce food waste, and enhance meal planning efficiency for diverse dietary preferences.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Vegetarian meal prepping significantly reduces environmental impact by lowering greenhouse gas emissions and conserving water resources compared to omnivore meal prepping. Plant-based ingredients require fewer natural resources and result in less deforestation and habitat loss, promoting sustainability. Choosing vegetarian meal prep supports a reduced carbon footprint and aligns with eco-friendly lifestyle goals.
Common Challenges and Solutions for Each Approach
Vegetarian meal prepping often faces challenges like ensuring adequate protein intake and variety to prevent meal fatigue, solvable by incorporating diverse plant-based proteins such as legumes, tofu, and quinoa. Omnivore meal prepping typically struggles with balancing meat portions and managing cooking times for different protein sources, which can be addressed through batch cooking and portioning meats separately for easy reheating. Both approaches benefit from planning meals around seasonal produce and using versatile spices to enhance flavor while maintaining nutritional balance.
Sample Weekly Meal Prep Plans for Vegetarians and Omnivores
Sample weekly meal prep plans for vegetarians often emphasize plant-based proteins like lentils, chickpeas, tofu, and quinoa, paired with a variety of colorful vegetables and whole grains to ensure balanced nutrition. Omnivore meal prep plans typically incorporate lean meats such as chicken breast, fish, or turkey alongside vegetables, legumes, and complex carbohydrates for sustained energy. Both approaches benefit from batch cooking and portion control, enabling easy customization to meet specific dietary preferences and nutritional requirements.
Vegetarian meal prepping vs omnivore meal prepping Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com