A Clinical Nutritionist specializes in evidence-based dietary plans tailored to manage specific health conditions in pets, focusing on scientifically validated nutrient needs and therapeutic interventions. In contrast, a Holistic Nutritionist emphasizes a whole-body approach, considering the pet's overall well-being, natural diet, and lifestyle factors to promote long-term health through balanced, natural nutrition. Both experts aim to optimize pet health but differ in methodology, with one rooted in clinical science and the other in integrative, natural practices.
Table of Comparison
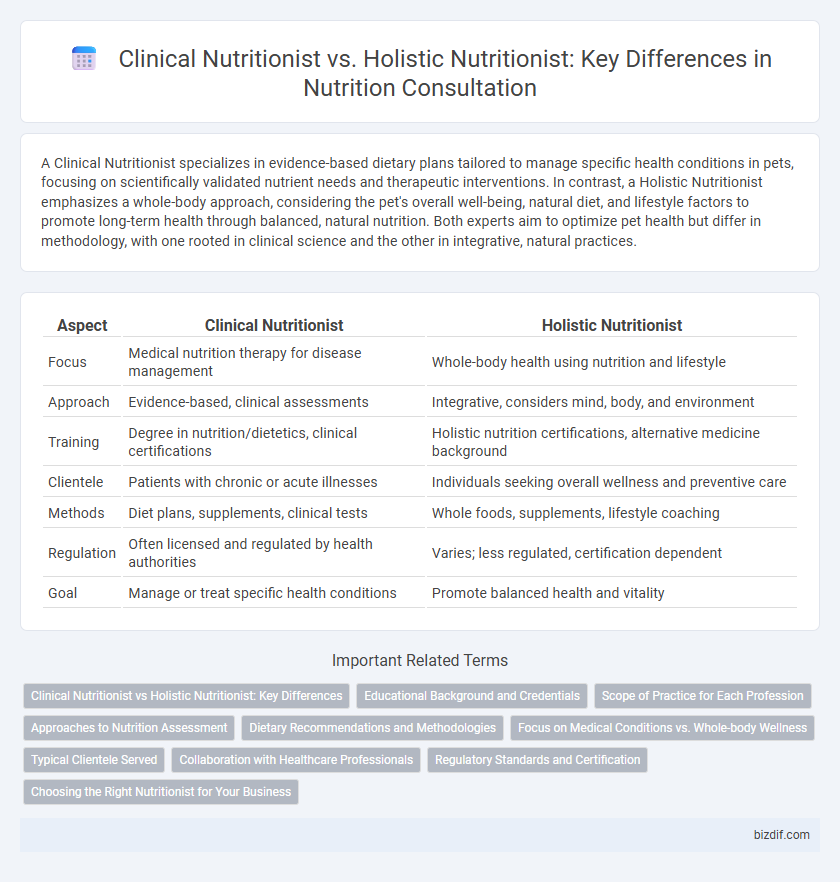
| Aspect | Clinical Nutritionist | Holistic Nutritionist |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Medical nutrition therapy for disease management | Whole-body health using nutrition and lifestyle |
| Approach | Evidence-based, clinical assessments | Integrative, considers mind, body, and environment |
| Training | Degree in nutrition/dietetics, clinical certifications | Holistic nutrition certifications, alternative medicine background |
| Clientele | Patients with chronic or acute illnesses | Individuals seeking overall wellness and preventive care |
| Methods | Diet plans, supplements, clinical tests | Whole foods, supplements, lifestyle coaching |
| Regulation | Often licensed and regulated by health authorities | Varies; less regulated, certification dependent |
| Goal | Manage or treat specific health conditions | Promote balanced health and vitality |
Clinical Nutritionist vs Holistic Nutritionist: Key Differences
Clinical nutritionists specialize in evidence-based dietary plans tailored to medical conditions, utilizing scientific research and clinical assessments to manage diseases such as diabetes and cardiovascular disorders. Holistic nutritionists emphasize whole-body wellness, incorporating lifestyle, emotional health, and natural remedies alongside nutrition to promote overall balance and prevent illness. The key difference lies in clinical nutritionists' focus on pathology and treatment protocols versus holistic nutritionists' broader approach to health through personalized, integrative strategies.
Educational Background and Credentials
Clinical nutritionists typically hold advanced degrees in dietetics or nutrition science and often possess certifications such as Registered Dietitian Nutritionist (RDN) credentials, ensuring rigorous training in medical nutrition therapy and evidence-based practice. Holistic nutritionists may acquire certifications from specialized institutes focusing on natural and integrative nutrition approaches, with education emphasizing whole-food diets, herbal supplements, and lifestyle factors, often without standardized licensure. Understanding these distinct educational backgrounds and credentialing paths helps clients choose the appropriate practitioner for personalized nutrition guidance.
Scope of Practice for Each Profession
Clinical nutritionists primarily focus on disease management and treatment through evidence-based dietary plans tailored to specific medical conditions, working closely with healthcare providers in clinical settings. Holistic nutritionists emphasize a whole-body approach, addressing lifestyle, mental well-being, and natural food sources to promote overall health and prevent illness. The scope of practice for clinical nutritionists is often regulated and limited to medical nutrition therapy, while holistic nutritionists operate more freely within wellness coaching and dietary guidance without prescription authority.
Approaches to Nutrition Assessment
Clinical nutritionists employ evidence-based methods such as biochemical analysis, clinical evaluations, and dietary intake assessments to identify nutritional deficiencies and medical conditions. Holistic nutritionists prioritize a comprehensive approach, incorporating lifestyle factors, emotional well-being, and environmental influences alongside dietary patterns in their assessments. Both approaches aim to tailor nutrition plans to individual needs but differ in their emphasis on conventional medical diagnostics versus integrative wellness factors.
Dietary Recommendations and Methodologies
Clinical nutritionists develop dietary recommendations based on scientific evidence and medical conditions, often using laboratory data and standardized protocols to manage diseases such as diabetes and cardiovascular issues. Holistic nutritionists emphasize whole-food-based diets and lifestyle factors, integrating mental, emotional, and environmental aspects into personalized nutrition plans. Both apply methodologies tailored to individual needs, but clinical approaches prioritize symptom management while holistic methods focus on overall well-being.
Focus on Medical Conditions vs. Whole-body Wellness
Clinical nutritionists specialize in creating dietary plans tailored to medical conditions such as diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and gastrointestinal disorders, emphasizing evidence-based interventions. Holistic nutritionists prioritize whole-body wellness by integrating physical, emotional, and environmental factors to promote overall health and prevent illness. Both approaches employ personalized strategies, but clinical nutrition focuses on managing specific diseases while holistic nutrition aims to enhance general well-being.
Typical Clientele Served
Clinical nutritionists typically serve patients with medical conditions such as diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, and digestive disorders, working closely with healthcare providers to develop therapeutic meal plans. Holistic nutritionists often support individuals seeking overall wellness, stress management, and lifestyle improvements through natural and plant-based dietary approaches. Both professionals tailor their guidance to meet the specific health goals and needs of their diverse client base.
Collaboration with Healthcare Professionals
Clinical nutritionists work closely with doctors, dietitians, and other healthcare providers to create evidence-based nutrition plans for patients with specific medical conditions. Holistic nutritionists emphasize a broader approach, integrating lifestyle, mental health, and natural therapies, often coordinating with alternative practitioners and wellness coaches. Effective collaboration between healthcare professionals and nutritionists ensures comprehensive patient care and optimized health outcomes.
Regulatory Standards and Certification
Clinical nutritionists adhere to strict regulatory standards set by medical boards, requiring accredited degrees and licensure, ensuring evidence-based practice in medical settings. Holistic nutritionists often obtain certifications from alternative or complementary health organizations, which may not be universally recognized or regulated, focusing on holistic wellness approaches. Understanding the differences in certification and regulatory requirements is crucial for selecting the appropriate nutrition expert based on individual health needs and desired treatment outcomes.
Choosing the Right Nutritionist for Your Business
Choosing the right nutritionist for your business depends on your goals: clinical nutritionists specialize in medically-approved dietary plans and nutritional therapy for disease management, while holistic nutritionists focus on natural, whole-food-based approaches and lifestyle integration. Clinical nutritionists often work closely with healthcare providers to tailor nutrition interventions supported by scientific research, making them ideal for organizations prioritizing evidence-based outcomes. Holistic nutritionists emphasize personalized, preventive care and addressing overall wellness, fitting businesses that value integrative and sustainable health strategies.
Clinical Nutritionist vs Holistic Nutritionist Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com