Vegetarian nutrition for pets emphasizes plant-based proteins and fiber-rich ingredients that support digestive health and provide essential vitamins. Keto nutrition focuses on high-fat, low-carbohydrate diets that promote fat burning and maintain stable energy levels in pets. Choosing between the two requires considering your pet's specific health needs, activity level, and any dietary sensitivities.
Table of Comparison
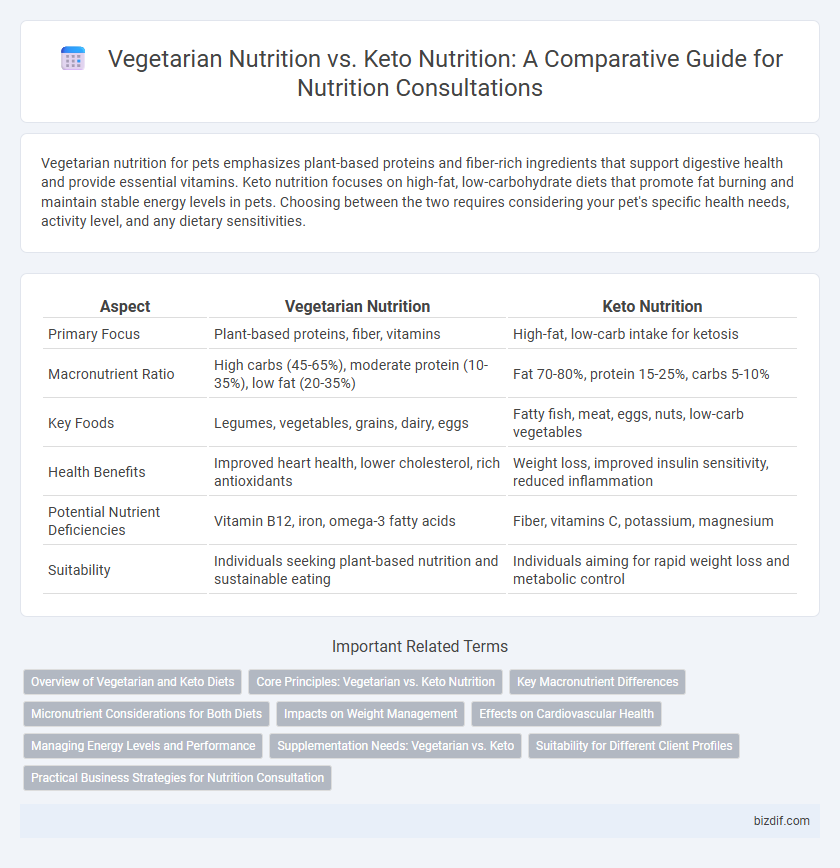
| Aspect | Vegetarian Nutrition | Keto Nutrition |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Plant-based proteins, fiber, vitamins | High-fat, low-carb intake for ketosis |
| Macronutrient Ratio | High carbs (45-65%), moderate protein (10-35%), low fat (20-35%) | Fat 70-80%, protein 15-25%, carbs 5-10% |
| Key Foods | Legumes, vegetables, grains, dairy, eggs | Fatty fish, meat, eggs, nuts, low-carb vegetables |
| Health Benefits | Improved heart health, lower cholesterol, rich antioxidants | Weight loss, improved insulin sensitivity, reduced inflammation |
| Potential Nutrient Deficiencies | Vitamin B12, iron, omega-3 fatty acids | Fiber, vitamins C, potassium, magnesium |
| Suitability | Individuals seeking plant-based nutrition and sustainable eating | Individuals aiming for rapid weight loss and metabolic control |
Overview of Vegetarian and Keto Diets
Vegetarian nutrition emphasizes plant-based foods rich in fiber, vitamins, and antioxidants, supporting heart health and weight management through diverse legumes, grains, fruits, and vegetables. In contrast, keto nutrition prioritizes high-fat, low-carbohydrate intake to induce ketosis, promoting rapid fat burning and appetite suppression with foods like fatty fish, oils, and low-carb vegetables. Both diets influence metabolic pathways differently, requiring tailored nutrient planning to meet individual health goals and maintain nutrient balance.
Core Principles: Vegetarian vs. Keto Nutrition
Vegetarian nutrition emphasizes plant-based foods rich in fiber, vitamins, and antioxidants, promoting heart health and sustainable weight management through balanced intake of vegetables, fruits, legumes, and whole grains. Keto nutrition focuses on high-fat, low-carbohydrate intake to induce ketosis, improving fat metabolism and supporting weight loss by restricting carbs to typically less than 50 grams per day. Both dietary approaches prioritize nutrient density but differ significantly in macronutrient distribution and metabolic adaptations.
Key Macronutrient Differences
Vegetarian nutrition emphasizes a higher intake of carbohydrates and fiber from plant-based sources, with protein primarily derived from legumes, grains, and nuts, while fats tend to be unsaturated and moderate in quantity. Keto nutrition focuses on high fat intake, moderate protein, and very low carbohydrate consumption to induce ketosis, relying on fats from sources like oils, avocados, and animal products. The key macronutrient difference lies in carbohydrate restriction for keto diets versus carbohydrate abundance in vegetarian diets, impacting energy metabolism and dietary planning.
Micronutrient Considerations for Both Diets
Vegetarian nutrition often requires careful attention to micronutrients such as vitamin B12, iron, zinc, and omega-3 fatty acids, which are typically found in animal products but can be sourced from fortified foods and supplements. Keto nutrition emphasizes adequate intake of electrolytes like magnesium, potassium, and sodium to prevent imbalances due to carbohydrate restriction and promotes fat-soluble vitamins A, D, E, and K from higher fat sources. Both diets benefit from targeted micronutrient supplementation and food choices to support optimal metabolic and physiological functions.
Impacts on Weight Management
Vegetarian nutrition, rich in fiber, antioxidants, and low-calorie plant-based foods, supports weight management by enhancing satiety and reducing overall calorie intake. Keto nutrition emphasizes high-fat, low-carbohydrate intake, promoting rapid fat loss through ketosis but may pose challenges in long-term adherence and nutrient balance. Both diets influence metabolism differently, requiring personalized consultation to optimize weight management outcomes.
Effects on Cardiovascular Health
Vegetarian nutrition, rich in fiber, antioxidants, and unsaturated fats, has been shown to reduce LDL cholesterol and improve endothelial function, thereby lowering the risk of cardiovascular disease. Keto nutrition emphasizes high fat and low carbohydrate intake, which may improve triglyceride levels and increase HDL cholesterol but can raise LDL cholesterol in some individuals, potentially impacting cardiovascular health negatively. Balancing nutrient quality and individual response is critical when evaluating the cardiovascular effects of these dietary patterns.
Managing Energy Levels and Performance
Vegetarian nutrition emphasizes complex carbohydrates, fiber, and plant-based proteins to provide sustained energy and support endurance during physical activity. Keto nutrition relies on high-fat, low-carbohydrate intake to promote ketosis, using fat as the primary fuel source which can enhance performance in endurance sports by stabilizing energy levels. Both diets require careful nutrient planning to prevent deficiencies and optimize metabolic efficiency for energy management and athletic performance.
Supplementation Needs: Vegetarian vs. Keto
Vegetarian nutrition often requires supplementation of vitamin B12, iron, omega-3 fatty acids, and vitamin D due to limited animal product intake. Keto nutrition, characterized by very low carbohydrate and high-fat intake, may need supplementation of electrolytes, magnesium, fiber, and certain vitamins like potassium to counteract nutrient imbalances and support metabolic functions. Both diets benefit from tailored supplementation strategies that address their unique nutritional gaps and promote overall health optimization.
Suitability for Different Client Profiles
Vegetarian nutrition suits clients seeking plant-based diets rich in fiber, antioxidants, and essential vitamins, benefiting heart health and weight management. Keto nutrition targets individuals requiring rapid fat loss or improved insulin sensitivity by promoting high fat, moderate protein, and very low carbohydrate intake. Tailoring nutrition plans depends on health goals, metabolic conditions, and lifestyle preferences to ensure optimal client outcomes.
Practical Business Strategies for Nutrition Consultation
Vegetarian nutrition consultations emphasize plant-based protein sources, fiber-rich foods, and essential micronutrients like iron and B12, which helps clients achieve balanced diets while reducing chronic disease risks. Keto nutrition consultations prioritize macronutrient tracking, fat-adaptation strategies, and monitoring ketone levels to support clients aiming for weight loss or metabolic control. Integrating personalized meal planning software and outcome tracking tools enhances client adherence and business scalability for nutrition consultants specializing in both vegetarian and keto diets.
Vegetarian Nutrition vs Keto Nutrition Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com