Synchronous delivery in online course creation provides real-time interaction between instructors and students, enhancing engagement and immediate feedback. Asynchronous delivery offers flexible learning schedules, allowing students to access course materials and complete assignments at their own pace. Choosing between synchronous and asynchronous methods depends on course objectives, learner preferences, and the desired level of interactivity.
Table of Comparison
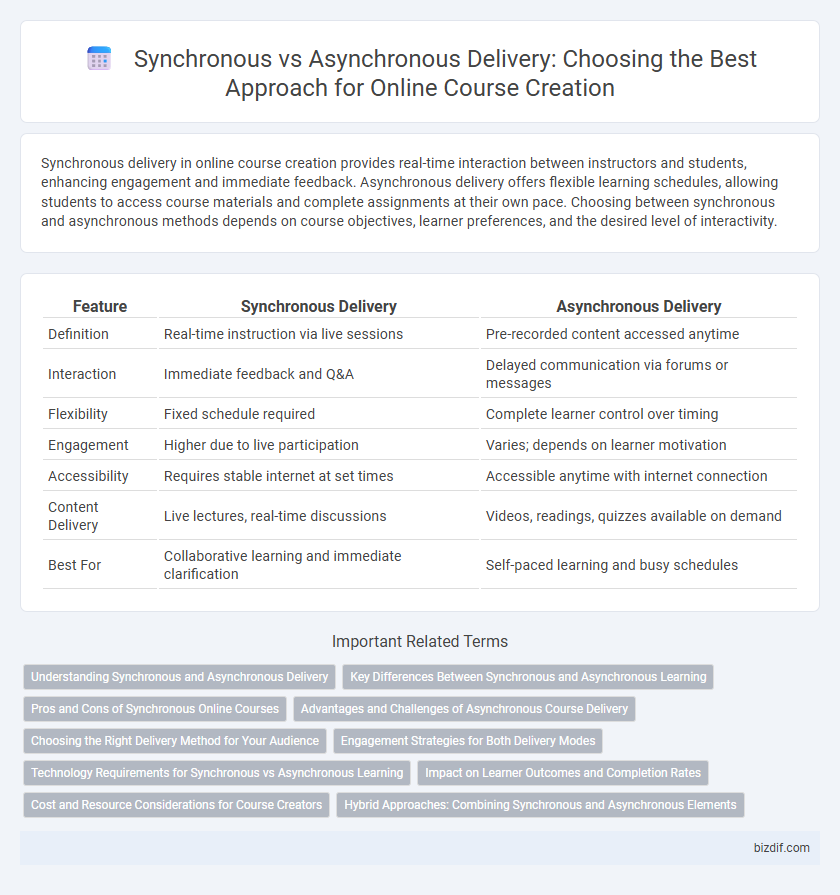
| Feature | Synchronous Delivery | Asynchronous Delivery |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Real-time instruction via live sessions | Pre-recorded content accessed anytime |
| Interaction | Immediate feedback and Q&A | Delayed communication via forums or messages |
| Flexibility | Fixed schedule required | Complete learner control over timing |
| Engagement | Higher due to live participation | Varies; depends on learner motivation |
| Accessibility | Requires stable internet at set times | Accessible anytime with internet connection |
| Content Delivery | Live lectures, real-time discussions | Videos, readings, quizzes available on demand |
| Best For | Collaborative learning and immediate clarification | Self-paced learning and busy schedules |
Understanding Synchronous and Asynchronous Delivery
Synchronous delivery in online courses involves real-time interaction between instructors and learners through live video, chat, or webinars, enabling immediate feedback and collaborative discussion. Asynchronous delivery allows students to access course materials, such as recorded lectures and assignments, at their own pace, providing flexibility and accommodating diverse schedules. Understanding the differences between these delivery methods helps educators design effective online learning experiences that balance engagement with convenience.
Key Differences Between Synchronous and Asynchronous Learning
Synchronous learning requires real-time interaction between instructors and students, enabling immediate feedback and collaborative discussions, typically through live video sessions or webinars. Asynchronous learning allows students to access course materials, lectures, and assignments at their own pace, promoting flexibility and self-directed study without the need for simultaneous participation. The key differences lie in timing and interaction, with synchronous emphasizing live engagement and asynchronous focusing on independent, flexible learning schedules.
Pros and Cons of Synchronous Online Courses
Synchronous online courses offer real-time interaction, which fosters immediate feedback and dynamic discussions, enhancing student engagement and motivation. However, they require strict scheduling, which can limit flexibility for learners in different time zones or with conflicting commitments. Technical issues such as internet connectivity problems can disrupt the flow and negatively impact the learning experience in synchronous settings.
Advantages and Challenges of Asynchronous Course Delivery
Asynchronous course delivery offers flexibility by allowing learners to access materials and complete assignments at their own pace, accommodating diverse schedules and learning styles. It promotes self-directed learning but can lead to feelings of isolation and delayed feedback, which may hinder student engagement and motivation. Effective asynchronous courses require well-structured content, clear instructions, and proactive communication channels to overcome these challenges and maximize learner success.
Choosing the Right Delivery Method for Your Audience
Selecting the right delivery method for online course creation depends on audience preferences, learning styles, and time availability. Synchronous delivery fosters real-time interaction and immediate feedback, ideal for learners who benefit from live engagement and structured schedules. Asynchronous delivery offers flexibility, allowing learners to access materials at their own pace, which suits audiences with varied time zones or busy routines.
Engagement Strategies for Both Delivery Modes
Synchronous delivery enhances engagement through real-time interaction tools such as live polls, breakout rooms, and immediate feedback, fostering a dynamic learning environment. Asynchronous delivery boosts engagement by leveraging discussion forums, interactive quizzes, and multimedia content that learners can access at their own pace, promoting reflective learning. Effective online course creation combines these strategies to maximize participation and knowledge retention across diverse learner preferences.
Technology Requirements for Synchronous vs Asynchronous Learning
Synchronous learning requires robust, real-time communication tools such as video conferencing platforms, high-speed internet, and reliable audio-visual equipment to ensure seamless interaction between instructors and students. In contrast, asynchronous learning relies on learning management systems (LMS) that support content hosting, discussion boards, and flexible access, minimizing the need for constant connectivity. Both delivery methods benefit from mobile compatibility and cloud storage, but synchronous courses demand higher technological infrastructure to facilitate live participation.
Impact on Learner Outcomes and Completion Rates
Synchronous delivery promotes real-time interaction and immediate feedback, often leading to higher engagement and improved learner outcomes due to structured schedules and social presence. Asynchronous delivery offers flexibility and self-paced learning, which can increase completion rates for learners requiring adaptable timing but may reduce accountability and immediate support. Combining both methods in blended courses tends to optimize learner satisfaction, knowledge retention, and completion rates by balancing engagement with flexibility.
Cost and Resource Considerations for Course Creators
Synchronous delivery requires real-time instructor involvement, increasing costs related to scheduling, live facilitation, and technical support. Asynchronous delivery minimizes these expenses by allowing pre-recorded content reuse, reducing the need for ongoing instructor time and live support staff. Course creators must weigh higher upfront investments for synchronous engagement against lower, scalable resource demands in asynchronous models.
Hybrid Approaches: Combining Synchronous and Asynchronous Elements
Hybrid approaches in online course creation integrate synchronous delivery, which offers real-time interaction and immediate feedback, with asynchronous components that provide flexibility and self-paced learning. This combination enhances learner engagement by accommodating diverse learning styles and schedules, leveraging tools such as live webinars, discussion forums, and pre-recorded lectures. Data shows hybrid models improve retention rates and learner satisfaction by balancing structure with autonomy.
Synchronous delivery vs Asynchronous delivery Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com