Reactive shopping occurs when consumers make purchases in response to immediate needs or stimuli, often leading to impulse buys and less thoughtful decisions. Proactive shopping involves planning and researching products beforehand, allowing shoppers to make informed choices that align with their long-term goals and budget. Emphasizing proactive shopping can reduce unnecessary expenses and increase overall satisfaction with purchases.
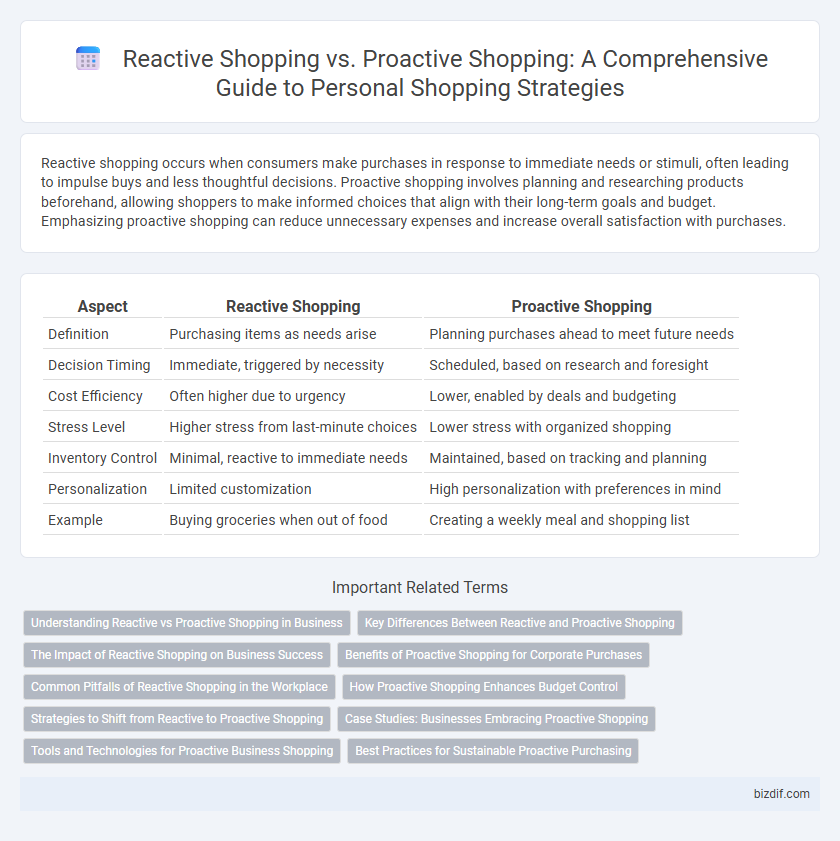
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Reactive Shopping | Proactive Shopping |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Purchasing items as needs arise | Planning purchases ahead to meet future needs |
| Decision Timing | Immediate, triggered by necessity | Scheduled, based on research and foresight |
| Cost Efficiency | Often higher due to urgency | Lower, enabled by deals and budgeting |
| Stress Level | Higher stress from last-minute choices | Lower stress with organized shopping |
| Inventory Control | Minimal, reactive to immediate needs | Maintained, based on tracking and planning |
| Personalization | Limited customization | High personalization with preferences in mind |
| Example | Buying groceries when out of food | Creating a weekly meal and shopping list |
Understanding Reactive vs Proactive Shopping in Business
Reactive shopping occurs when customers make purchasing decisions based on immediate needs, often triggered by sudden demands or external stimuli, resulting in spontaneous and short-term focused buying behavior. Proactive shopping involves strategic planning where consumers anticipate future needs and research products in advance, enabling businesses to tailor marketing approaches that foster customer loyalty and long-term engagement. Understanding the distinctions between reactive and proactive shopping empowers businesses to align inventory management, promotional efforts, and customer service strategies effectively.
Key Differences Between Reactive and Proactive Shopping
Reactive shopping occurs when consumers make purchases in response to immediate needs or external triggers like sales or stock shortages, often leading to impulse buying. Proactive shopping involves planned purchases based on research, budgeting, and anticipating future needs, resulting in more strategic and cost-effective decisions. Key differences include timing, decision-making process, and control over spending, where proactive shoppers exercise greater foresight and avoid last-minute pressures seen in reactive shopping.
The Impact of Reactive Shopping on Business Success
Reactive shopping often leads to unpredictable sales patterns that challenge inventory management and increase operational costs. Businesses relying heavily on reactive shopping may face reduced customer loyalty due to inconsistent product availability and missed opportunities for targeted marketing. Prioritizing proactive shopping strategies enables companies to anticipate demand, optimize stock levels, and enhance overall business performance.
Benefits of Proactive Shopping for Corporate Purchases
Proactive shopping in corporate purchases streamlines budget management by enabling companies to anticipate needs and secure better pricing through bulk orders and early negotiations. This approach reduces last-minute expenses and supply chain disruptions, ensuring consistent stock levels and operational efficiency. Leveraging data analytics for forecasting enhances decision-making, optimizing resource allocation and maximizing cost savings.
Common Pitfalls of Reactive Shopping in the Workplace
Reactive shopping in the workplace often leads to rushed purchasing decisions, resulting in higher costs and suboptimal product choices. Employees may override established budgets and procurement protocols, causing inefficiencies and potential overspending. Lack of strategic planning in reactive shopping decreases overall productivity and complicates inventory management.
How Proactive Shopping Enhances Budget Control
Proactive shopping enhances budget control by encouraging thorough planning and prioritizing purchases based on a predefined list, reducing impulsive spending and unnecessary expenses. Utilizing tools such as budgeting apps and price comparison websites allows shoppers to allocate funds efficiently and avoid overspending. This approach leads to smarter financial decisions, timely purchases, and maximized value within the set budget.
Strategies to Shift from Reactive to Proactive Shopping
Implementing detailed budgeting and prioritization techniques enables shoppers to transition from reactive to proactive shopping, reducing impulse purchases and improving financial control. Utilizing shopping lists based on well-researched needs and forecasting future requirements fosters a more strategic approach, minimizing last-minute decisions. Leveraging digital tools such as expense tracking apps and personalized alerts supports continuous monitoring and adjustment of shopping habits, reinforcing proactive purchasing behavior.
Case Studies: Businesses Embracing Proactive Shopping
Leading retailers like Amazon and Sephora demonstrate the success of proactive shopping through personalized recommendations and predictive analytics, significantly enhancing customer engagement and sales. Case studies reveal these businesses use AI-driven algorithms to anticipate consumer needs, streamlining the shopping experience and boosting loyalty. Companies adopting proactive shopping report higher conversion rates and improved inventory management compared to reactive shopping models.
Tools and Technologies for Proactive Business Shopping
Proactive shopping leverages advanced tools and technologies such as AI-driven analytics, inventory management systems, and automated procurement software to forecast demand and optimize purchasing decisions. These innovations enable businesses to anticipate needs, reduce costs, and maintain optimal stock levels. Utilizing IoT sensors and blockchain technology further enhances transparency and real-time tracking in the supply chain.
Best Practices for Sustainable Proactive Purchasing
Sustainable proactive purchasing involves planning purchases carefully to reduce waste and environmental impact, prioritizing quality over quantity and opting for eco-friendly brands with transparent supply chains. Engaging in thorough research before buying and setting long-term needs rather than impulse desires ensures more responsible consumption patterns. Utilizing tools like reusable shopping lists and prioritizing products with minimal packaging also supports sustainable proactive shopping habits that benefit both the consumer and the planet.
Reactive Shopping vs Proactive Shopping Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com