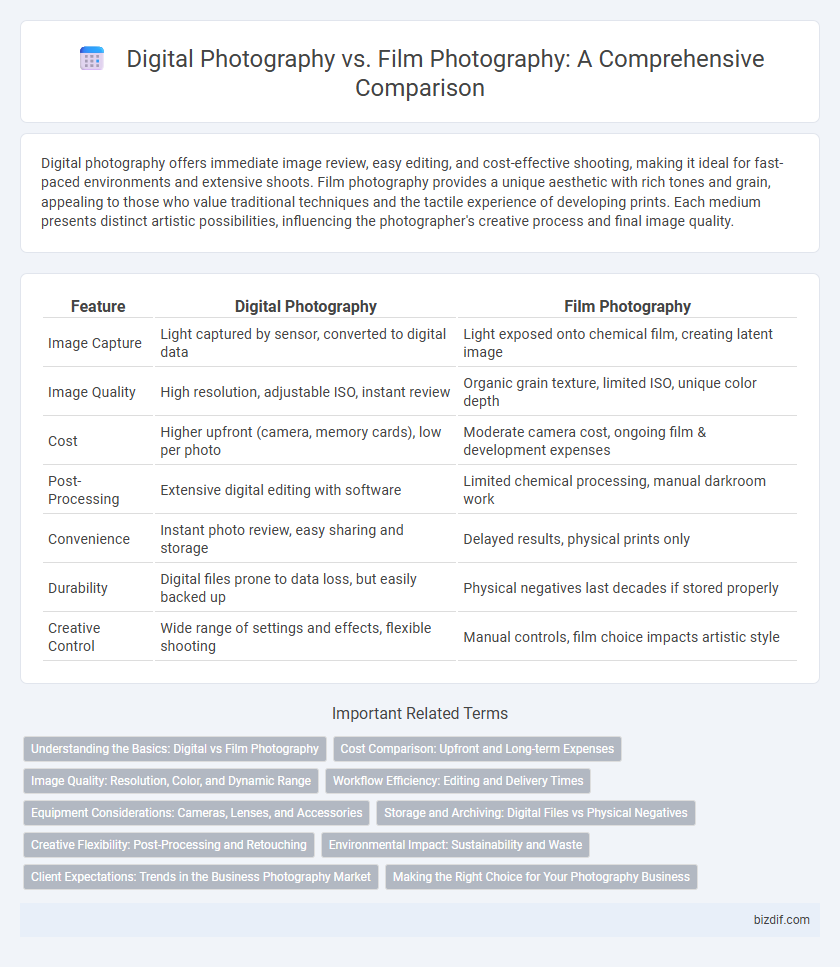
Digital photography offers immediate image review, easy editing, and cost-effective shooting, making it ideal for fast-paced environments and extensive shoots. Film photography provides a unique aesthetic with rich tones and grain, appealing to those who value traditional techniques and the tactile experience of developing prints. Each medium presents distinct artistic possibilities, influencing the photographer's creative process and final image quality.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Digital Photography | Film Photography |
|---|---|---|
| Image Capture | Light captured by sensor, converted to digital data | Light exposed onto chemical film, creating latent image |
| Image Quality | High resolution, adjustable ISO, instant review | Organic grain texture, limited ISO, unique color depth |
| Cost | Higher upfront (camera, memory cards), low per photo | Moderate camera cost, ongoing film & development expenses |
| Post-Processing | Extensive digital editing with software | Limited chemical processing, manual darkroom work |
| Convenience | Instant photo review, easy sharing and storage | Delayed results, physical prints only |
| Durability | Digital files prone to data loss, but easily backed up | Physical negatives last decades if stored properly |
| Creative Control | Wide range of settings and effects, flexible shooting | Manual controls, film choice impacts artistic style |
Understanding the Basics: Digital vs Film Photography
Digital photography captures images using electronic sensors, allowing immediate review and easy editing with software like Adobe Photoshop, while film photography relies on chemical exposure on physical film rolls, producing tangible negatives. Digital cameras offer higher versatility with adjustable ISO settings and instant feedback, whereas film cameras often provide richer color depth and dynamic range due to analog processing. Understanding these fundamental differences is crucial for photographers seeking to choose between the convenience and flexibility of digital or the aesthetic and traditional qualities of film.
Cost Comparison: Upfront and Long-term Expenses
Digital photography requires a higher initial investment in cameras and accessories, but offers lower ongoing costs due to free image storage and editing software availability. Film photography involves continuous expenses such as purchasing rolls of film, developing chemicals, and printing costs, which accumulate over time. Long-term, digital photography proves more cost-effective by eliminating recurring material and processing fees associated with film.
Image Quality: Resolution, Color, and Dynamic Range
Digital photography offers higher resolution sensors that capture fine details with precision, while film photography provides unique color rendition and grain structure valued by enthusiasts. Advances in digital cameras have significantly improved dynamic range, enabling better capture of both shadows and highlights compared to traditional film. Color accuracy in digital is enhanced through sensor technology and post-processing flexibility, whereas film relies on chemical emulsions that produce distinct, often warmer tones.
Workflow Efficiency: Editing and Delivery Times
Digital photography streamlines workflow efficiency by enabling instant image review, rapid file transfer, and non-destructive editing in software like Adobe Lightroom or Capture One. Film photography involves a lengthier process, requiring development, scanning, and physical printing before any digital editing can occur. Consequently, digital workflows significantly reduce delivery times for clients and expedite overall project turnaround.
Equipment Considerations: Cameras, Lenses, and Accessories
Digital photography equipment typically includes mirrorless or DSLR cameras with advanced autofocus systems, interchangeable lenses optimized for electronic sensors, and accessories like memory cards and battery packs that support extended shooting. Film photography relies on mechanical or electronically controlled film cameras, a variety of manual focus lenses designed for specific film formats, and accessories such as film rolls, light meters, and darkroom tools for development and printing. Lens compatibility, sensor or film size, and the need for digital workflow accessories versus chemical development tools critically influence the choice between digital and film photography gear.
Storage and Archiving: Digital Files vs Physical Negatives
Digital photography offers convenient storage with files easily saved on hard drives, cloud services, and external SSDs, enabling quick access and duplication. In contrast, film photography relies on physical negatives that require careful handling, controlled environments, and durable archival materials to prevent degradation over time. While digital files face risks of data corruption or obsolescence without proper backups, film negatives provide a tangible, long-lasting record when stored correctly, appealing to archival longevity and authenticity.
Creative Flexibility: Post-Processing and Retouching
Digital photography offers unparalleled creative flexibility through advanced post-processing and retouching tools like Adobe Photoshop and Lightroom, enabling photographers to manipulate color, exposure, and composition with precision. Film photography requires physical manipulation of negatives or prints, limiting the extent and speed of creative adjustments compared to digital workflows. The instant feedback and vast editing possibilities of digital files empower photographers to experiment extensively and achieve desired artistic effects efficiently.
Environmental Impact: Sustainability and Waste
Digital photography significantly reduces environmental impact by eliminating the need for chemical processing and film production, which generate hazardous waste and consume substantial resources. Film photography relies on plastic-based films and toxic chemicals like silver halide, contributing to landfill waste and water pollution. Sustainable practices in digital photography, such as energy-efficient devices and recyclable electronic components, further enhance its eco-friendly profile compared to traditional film methods.
Client Expectations: Trends in the Business Photography Market
Client expectations in business photography increasingly favor digital photography due to its faster turnaround times, higher image flexibility, and seamless integration with digital marketing channels. Film photography retains a niche appeal for its aesthetic qualities and authenticity, often sought after for luxury branding and artistic projects. Market trends indicate a growing demand for hybrid approaches that combine digital efficiency with film's distinctive visual style to meet diverse client preferences.
Making the Right Choice for Your Photography Business
Choosing between digital photography and film photography depends on your business model and target audience preferences. Digital photography offers faster turnaround, flexible editing options, and lower ongoing costs, making it ideal for commercial and event photography requiring quick delivery. Film photography, valued for its unique aesthetic and authenticity, suits niche markets such as fine art and portrait studios seeking a vintage or handcrafted feel.
Digital Photography vs Film Photography Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com