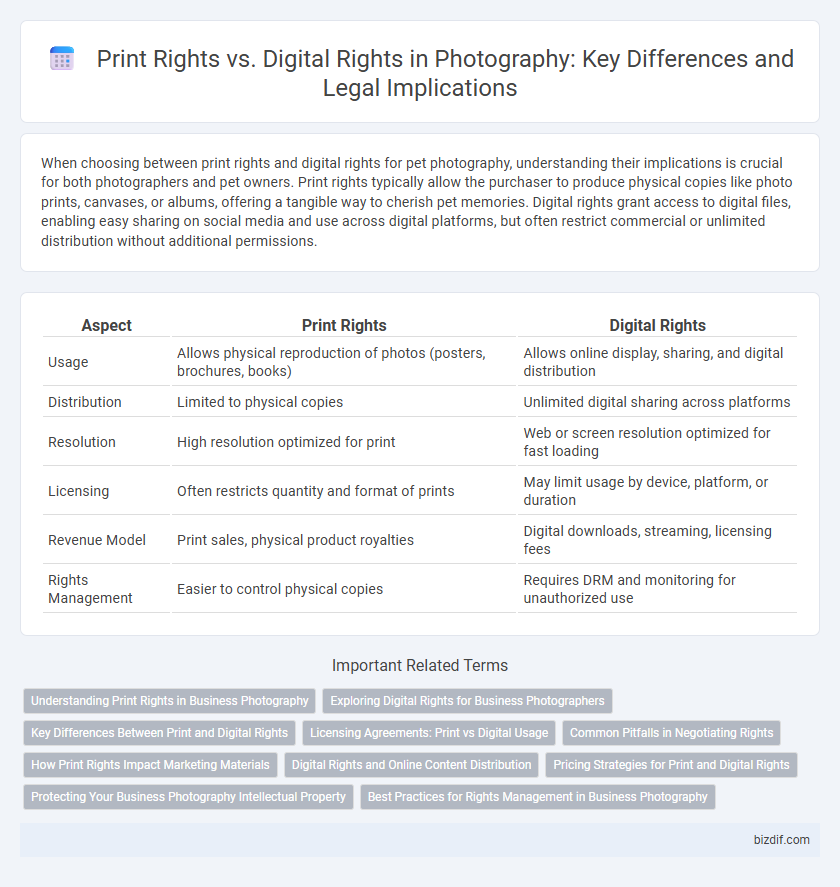
When choosing between print rights and digital rights for pet photography, understanding their implications is crucial for both photographers and pet owners. Print rights typically allow the purchaser to produce physical copies like photo prints, canvases, or albums, offering a tangible way to cherish pet memories. Digital rights grant access to digital files, enabling easy sharing on social media and use across digital platforms, but often restrict commercial or unlimited distribution without additional permissions.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Print Rights | Digital Rights |
|---|---|---|
| Usage | Allows physical reproduction of photos (posters, brochures, books) | Allows online display, sharing, and digital distribution |
| Distribution | Limited to physical copies | Unlimited digital sharing across platforms |
| Resolution | High resolution optimized for print | Web or screen resolution optimized for fast loading |
| Licensing | Often restricts quantity and format of prints | May limit usage by device, platform, or duration |
| Revenue Model | Print sales, physical product royalties | Digital downloads, streaming, licensing fees |
| Rights Management | Easier to control physical copies | Requires DRM and monitoring for unauthorized use |
Understanding Print Rights in Business Photography
Print rights in business photography grant clients permission to reproduce images in physical formats such as brochures, posters, and product packaging, ensuring brand visibility through tangible media. These rights are typically limited by scope, print run, and territory, making it essential for photographers to clearly define usage parameters in contracts to protect their work and income. Understanding print rights helps businesses leverage high-quality visuals for marketing while managing licensing costs and intellectual property compliance.
Exploring Digital Rights for Business Photographers
Business photographers benefit from exploring digital rights, as these licenses govern the reproduction, distribution, and display of images in online and multimedia formats. Unlike print rights, which restrict usage to physical copies like magazines or brochures, digital rights enable monetization opportunities across websites, social media, and digital advertising platforms. Securing comprehensive digital rights ensures control over image usage, protects against unauthorized exploitation, and maximizes revenue streams in the evolving digital marketplace.
Key Differences Between Print and Digital Rights
Print rights grant permission to reproduce images in physical formats such as magazines, books, and posters, typically involving limitations on geographic distribution and print run size. Digital rights allow usage of images on online platforms, social media, and digital advertising, often incorporating restrictions on file resolution, duration of use, and specific websites or applications. Understanding the distinction between print and digital rights is crucial for photographers to control image usage, monetize effectively, and protect intellectual property across different media channels.
Licensing Agreements: Print vs Digital Usage
Licensing agreements for print rights usually specify the physical reproduction of images in materials like magazines, books, or posters, emphasizing duration, territory, and quantity limitations. Digital rights licensing covers the use of images on websites, social media platforms, and digital advertising, often including specifications for resolution, file format, and online distribution scope. Clear differentiation between print and digital usage in contracts ensures photographers retain control over how their work is exploited and maximizes potential revenue streams.
Common Pitfalls in Negotiating Rights
Common pitfalls in negotiating print rights vs digital rights often stem from vague contract language that fails to specify usage scope, resulting in unintended restrictions or overreach. Photographers frequently overlook territorial limitations and duration clauses, which can cause conflicts when rights are extended beyond initial agreements. Misunderstanding exclusivity terms can also lead to lost revenue opportunities or legal disputes over simultaneous print and digital licensing.
How Print Rights Impact Marketing Materials
Print rights grant businesses the ability to reproduce photographic images on physical marketing materials such as brochures, posters, and business cards, enhancing brand visibility and tangible customer engagement. Securing print rights ensures legal protection and control over image usage, preventing unauthorized reproduction that could dilute brand integrity. Compared to digital rights, print rights typically involve specific limitations on the quantity and format of printed copies, influencing the scope and scale of marketing campaigns.
Digital Rights and Online Content Distribution
Digital rights in photography govern the licensing, usage, and distribution of images across online platforms, ensuring photographers maintain control over how their work is displayed and shared. These rights include the ability to restrict unauthorized reproductions, control metadata, and manage usage terms through digital rights management (DRM) technologies. Effective management of digital rights is essential for protecting image integrity, monetizing content, and preventing misuse or unauthorized online distribution.
Pricing Strategies for Print and Digital Rights
Print rights typically command higher pricing due to their tangible nature and limited reproduction, often involving exclusive or one-time fees based on print run size and distribution scope. Digital rights pricing varies with usage terms, incorporating factors such as licensing duration, resolution, and platform exclusivity to optimize revenue from online or multimedia exposure. Balancing print and digital rights pricing ensures maximizing profit while controlling image use across physical and digital channels.
Protecting Your Business Photography Intellectual Property
Print rights and digital rights are crucial components in protecting your business photography intellectual property, defining how images can be used, distributed, and monetized. Securing print rights controls reproduction on physical mediums such as posters and books, while digital rights manage online distribution, licensing, and prevention of unauthorized sharing. Clear delineation and enforcement of these rights safeguard photographers' revenue streams and maintain control over the integrity and usage of their visual content.
Best Practices for Rights Management in Business Photography
Print rights grant permission to reproduce photographs in physical formats such as posters, books, or magazines, while digital rights cover usage in online platforms, social media, and digital advertisements. Best practices for managing business photography rights include clearly defining scope, duration, and usage in contracts to avoid misuse and ensure proper licensing fees. Maintaining detailed records of print and digital rights agreements fosters transparency and protects the photographer's intellectual property across multiple channels.
Print Rights vs Digital Rights Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com