RAW files capture all the data from a camera's sensor, providing greater flexibility for editing exposure, white balance, and color correction without quality loss. JPEG files are compressed and processed in-camera, resulting in smaller file sizes but less latitude for adjustments and potential image degradation. Photographers seeking maximum control and image quality typically prefer RAW, while JPEG suits quick sharing and reduced storage needs.
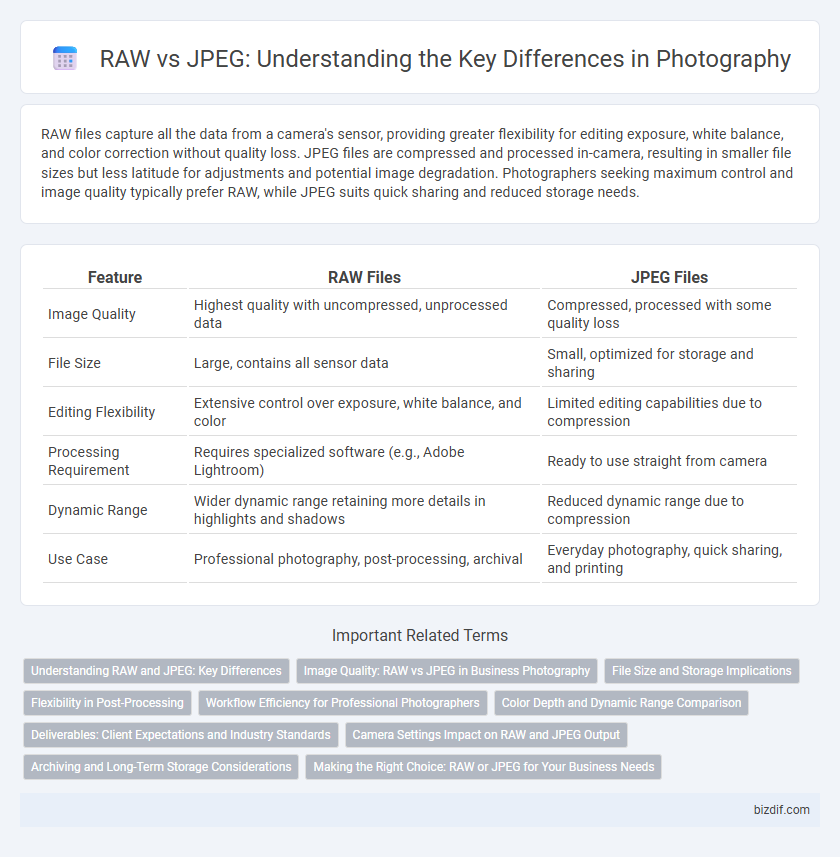
Table of Comparison
| Feature | RAW Files | JPEG Files |
|---|---|---|
| Image Quality | Highest quality with uncompressed, unprocessed data | Compressed, processed with some quality loss |
| File Size | Large, contains all sensor data | Small, optimized for storage and sharing |
| Editing Flexibility | Extensive control over exposure, white balance, and color | Limited editing capabilities due to compression |
| Processing Requirement | Requires specialized software (e.g., Adobe Lightroom) | Ready to use straight from camera |
| Dynamic Range | Wider dynamic range retaining more details in highlights and shadows | Reduced dynamic range due to compression |
| Use Case | Professional photography, post-processing, archival | Everyday photography, quick sharing, and printing |
Understanding RAW and JPEG: Key Differences
RAW files capture unprocessed image data directly from the camera sensor, preserving maximum detail and dynamic range for extensive post-processing flexibility. JPEG files apply in-camera compression and adjustments, resulting in smaller file sizes but with some loss of image quality and limited editing potential. Choosing RAW or JPEG depends on the need for image quality, storage capacity, and workflow efficiency in photography.
Image Quality: RAW vs JPEG in Business Photography
RAW files retain uncompressed image data with higher bit depth, preserving maximum detail and dynamic range essential for professional business photography. JPEG files use lossy compression, resulting in reduced image quality and limited post-processing flexibility critical for high-stakes commercial projects. Choosing RAW ensures superior color accuracy and sharpness, enhancing brand presentation through pristine visuals.
File Size and Storage Implications
RAW files, containing uncompressed and unprocessed image data, typically have significantly larger file sizes compared to JPEG files, which use lossy compression to reduce file size. This difference impacts storage capacity, with RAW files requiring substantially more memory on hard drives or memory cards, influencing the choice of storage solutions for photographers. Consequently, managing large volumes of RAW files demands higher-capacity or faster storage options, while JPEGs offer efficient storage and easier sharing due to their compact size.
Flexibility in Post-Processing
RAW files provide superior flexibility in post-processing by preserving uncompressed and unprocessed image data captured from the camera sensor, allowing extensive adjustments to exposure, white balance, and color grading without degrading image quality. JPEG files apply in-camera compression and processing, limiting the extent of corrections and often resulting in a loss of detail when altering brightness or shadows. Photographers seeking maximum creative control and higher dynamic range prefer RAW for its ability to retain fine image details during editing workflows.
Workflow Efficiency for Professional Photographers
RAW files retain uncompressed, high dynamic range data, allowing professional photographers extensive flexibility in post-processing to optimize exposure, color grading, and detail recovery. JPEG files, while compressed and smaller in size, enable faster workflow through immediate usability and reduced editing time, making them ideal for quick delivery and efficient file management. Balancing RAW and JPEG usage enhances workflow efficiency by blending comprehensive image control with streamlined editing and sharing processes.
Color Depth and Dynamic Range Comparison
RAW files retain higher color depth, typically 12 to 14 bits per channel, compared to JPEG's 8-bit depth, allowing for smoother color gradients and more accurate tonal transitions. The dynamic range in RAW formats captures a broader spectrum of light intensities, preserving details in both shadows and highlights that JPEG compression often loses. Photographers benefit from enhanced post-processing flexibility with RAW files, enabling precise adjustments without significant quality degradation.
Deliverables: Client Expectations and Industry Standards
RAW files provide clients with maximum image quality and editing flexibility, allowing professional photographers to meet high industry standards for print and digital media. JPEG files offer smaller sizes and faster delivery, aligning with client expectations for quick turnaround and convenience in web use or social sharing. Deliverables often balance RAW's detailed quality with JPEG's ready-to-use accessibility, tailoring outputs to client needs and project requirements.
Camera Settings Impact on RAW and JPEG Output
Camera settings such as white balance, exposure, and picture style directly influence JPEG files as these settings are baked into the image during capture, affecting color rendition and contrast permanently. In RAW files, these settings serve as metadata, allowing extensive post-processing flexibility without degrading image quality, since the raw sensor data remains unaltered. Understanding the impact of ISO and dynamic range also underscores the advantage of RAW files in maintaining detail and reducing noise compared to JPEG compression limitations.
Archiving and Long-Term Storage Considerations
RAW files preserve all image data captured by the camera sensor, making them the ideal choice for archiving and long-term storage due to their lossless nature and greater editing flexibility. JPEG files use lossy compression, which reduces file size but discards some image information, potentially degrading quality over time with repeated edits and saves. For professional photographers and archivists, maintaining a catalog of RAW files ensures maximum image integrity and future-proofing in digital asset management systems.
Making the Right Choice: RAW or JPEG for Your Business Needs
Choosing between RAW and JPEG files depends on your business's priorities such as image quality, editing flexibility, and storage capacity. RAW files preserve uncompressed, high-dynamic-range data, essential for professional retouching and maintaining maximum detail in commercial photography. JPEG files, being compressed and universally compatible, are ideal for quick delivery and saving storage space when extensive post-processing is unnecessary.
RAW Files vs JPEG Files Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com