RAW format captures all image data from the camera sensor, allowing extensive post-processing flexibility and higher quality edits. JPEG format compresses images, reducing file size at the expense of some detail and dynamic range, making it ideal for quick sharing and smaller storage needs. Photographers seeking maximum control over exposure, color, and detail prefer RAW, while those prioritizing convenience and faster workflow often choose JPEG.
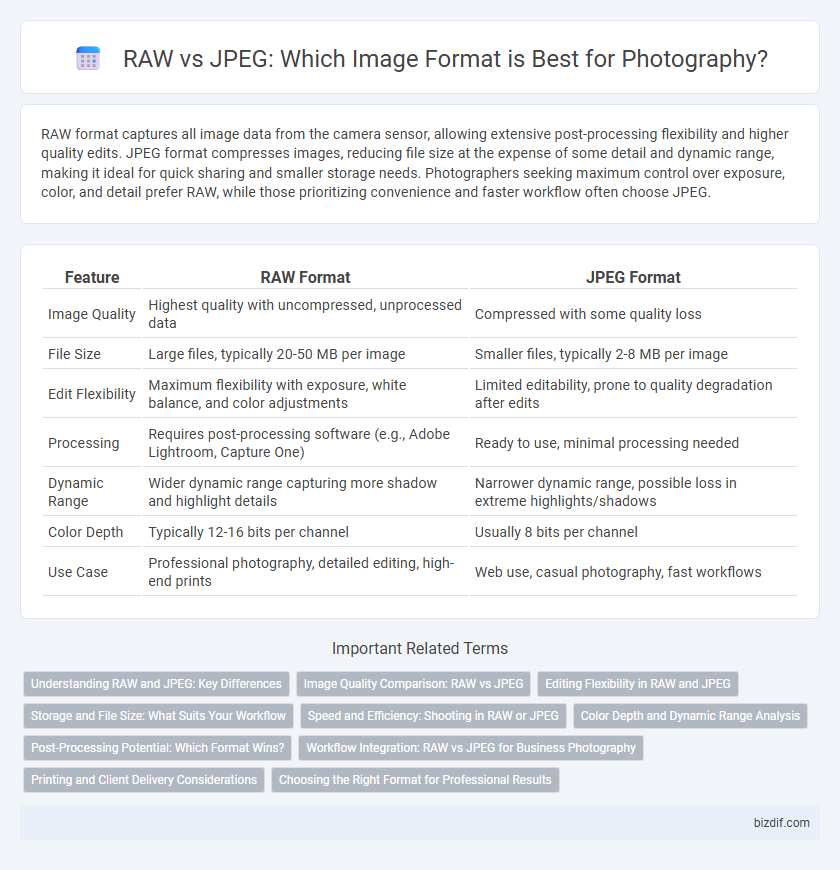
Table of Comparison
| Feature | RAW Format | JPEG Format |
|---|---|---|
| Image Quality | Highest quality with uncompressed, unprocessed data | Compressed with some quality loss |
| File Size | Large files, typically 20-50 MB per image | Smaller files, typically 2-8 MB per image |
| Edit Flexibility | Maximum flexibility with exposure, white balance, and color adjustments | Limited editability, prone to quality degradation after edits |
| Processing | Requires post-processing software (e.g., Adobe Lightroom, Capture One) | Ready to use, minimal processing needed |
| Dynamic Range | Wider dynamic range capturing more shadow and highlight details | Narrower dynamic range, possible loss in extreme highlights/shadows |
| Color Depth | Typically 12-16 bits per channel | Usually 8 bits per channel |
| Use Case | Professional photography, detailed editing, high-end prints | Web use, casual photography, fast workflows |
Understanding RAW and JPEG: Key Differences
RAW format preserves unprocessed image data directly from the camera sensor, offering superior flexibility for post-processing, including extensive adjustments to exposure, white balance, and color grading. JPEG format applies in-camera compression and processing, creating smaller files that are immediately usable but with reduced dynamic range and less latitude for editing. Choosing between RAW and JPEG depends on balancing the need for maximum image quality and editing control against convenience and storage efficiency.
Image Quality Comparison: RAW vs JPEG
RAW format preserves uncompressed and unprocessed image data directly from the camera sensor, offering superior image quality with higher dynamic range and color depth compared to JPEG. JPEG files use lossy compression that reduces file size but sacrifices detail and subtle color gradations, often resulting in artifacts and lower overall image fidelity. Photographers seeking maximum post-processing flexibility and image quality typically prefer RAW, while JPEG suits those needing smaller files and quicker sharing without extensive editing.
Editing Flexibility in RAW and JPEG
RAW format offers unparalleled editing flexibility by preserving all image data captured by the camera sensor, allowing extensive adjustments in exposure, white balance, and color grading without quality loss. JPEG files apply compression and image processing in-camera, limiting the extent of post-processing adjustments and often resulting in degraded image quality when edited heavily. Photographers seeking maximum control over image refinement and professional results consistently prefer RAW for its non-destructive editing capabilities and greater dynamic range retention.
Storage and File Size: What Suits Your Workflow
RAW format offers significantly larger file sizes compared to JPEG, requiring more storage capacity but preserving maximum image data for extensive post-processing flexibility. JPEG files are compressed, resulting in smaller sizes that save storage space and enable quicker transfer and sharing, ideal for workflows prioritizing efficiency over editing potential. Choosing between RAW and JPEG depends on balancing storage availability with the desired level of control during editing and image quality requirements.
Speed and Efficiency: Shooting in RAW or JPEG
Shooting in JPEG format offers faster processing and smaller file sizes, enabling quicker image review and efficient storage management ideal for rapid workflows. RAW format preserves maximum image data and detail but requires longer processing time and larger storage capacity, affecting speed during shooting and post-production. Photographers choosing JPEG optimize for speed and efficiency, while those prioritizing image quality and editing flexibility opt for the RAW format despite slower performance.
Color Depth and Dynamic Range Analysis
RAW format preserves higher color depth, typically 12 to 14 bits per channel, enabling more precise color gradations and smoother transitions compared to JPEG's 8 bits per channel. This extended bit depth in RAW files supports a broader dynamic range, allowing photographers to recover highlight and shadow details more effectively during post-processing. JPEG compression reduces color information and dynamic range, resulting in potential banding and loss of subtle tonal variations critical for professional image editing.
Post-Processing Potential: Which Format Wins?
RAW format offers superior post-processing potential due to its uncompressed data, preserving maximum image detail and dynamic range for extensive adjustments in exposure, white balance, and color grading. JPEG files are compressed and lose some image quality, limiting flexibility in editing and increasing the risk of artifacts when altering highlights or shadows. Photographers seeking optimal control and image quality in post-processing overwhelmingly prefer RAW to achieve professional-grade results.
Workflow Integration: RAW vs JPEG for Business Photography
RAW format provides unparalleled image quality and extensive editing flexibility, making it ideal for business photographers who require precise control over exposure, color correction, and detail recovery in post-processing workflows. JPEG files offer immediate usability with smaller file sizes and faster processing times, enabling quicker turnaround for projects where speed is prioritized over maximum image fidelity. Integrating RAW into workflow systems demands robust storage solutions and advanced editing software, whereas JPEG simplifies file management and sharing across client platforms.
Printing and Client Delivery Considerations
RAW format preserves maximum image data and dynamic range, enabling superior print quality with enhanced detail and color accuracy, ideal for large-format prints and professional client presentations. JPEG files offer smaller sizes and faster processing, suitable for quick client delivery and web use but may compromise print quality due to compression artifacts and reduced tonal depth. Choosing RAW ensures optimal flexibility in post-processing for print, while JPEG expedites workflow when immediate client review and distribution are prioritized.
Choosing the Right Format for Professional Results
RAW format offers photographers uncompressed, high-bit-depth image files that retain maximum detail and dynamic range for extensive post-processing flexibility. JPEG format compresses images into smaller, widely compatible files by sacrificing some image quality and color information, suitable for quick sharing and minimal editing. Choosing RAW ensures professional-grade results with optimal image control, whereas JPEG suits faster workflows and limited editing needs.
RAW Format vs JPEG Format Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com