Effective professional organizing for pets involves striking a balance between archiving and purging pet-related items. Archiving preserves important documents, medical records, and sentimental keepsakes, ensuring easy access and long-term organization. Purging removes outdated, unused, or unnecessary items such as old toys, expired food, and worn-out bedding, creating a clutter-free and functional space for your pet's needs.
Table of Comparison
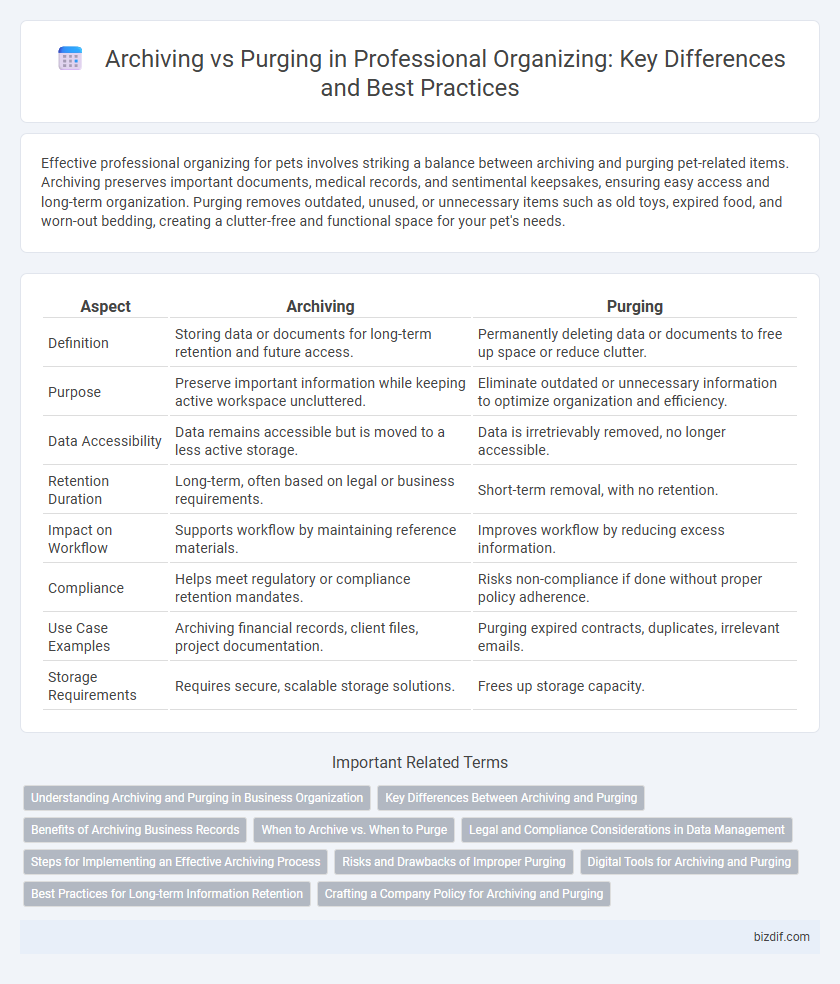
| Aspect | Archiving | Purging |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Storing data or documents for long-term retention and future access. | Permanently deleting data or documents to free up space or reduce clutter. |
| Purpose | Preserve important information while keeping active workspace uncluttered. | Eliminate outdated or unnecessary information to optimize organization and efficiency. |
| Data Accessibility | Data remains accessible but is moved to a less active storage. | Data is irretrievably removed, no longer accessible. |
| Retention Duration | Long-term, often based on legal or business requirements. | Short-term removal, with no retention. |
| Impact on Workflow | Supports workflow by maintaining reference materials. | Improves workflow by reducing excess information. |
| Compliance | Helps meet regulatory or compliance retention mandates. | Risks non-compliance if done without proper policy adherence. |
| Use Case Examples | Archiving financial records, client files, project documentation. | Purging expired contracts, duplicates, irrelevant emails. |
| Storage Requirements | Requires secure, scalable storage solutions. | Frees up storage capacity. |
Understanding Archiving and Purging in Business Organization
Archiving in business organization involves systematically storing important documents and data for future reference, ensuring compliance with legal and operational requirements. Purging refers to the deliberate deletion of obsolete or redundant records to optimize storage capacity and improve information management efficiency. Effective archiving and purging strategies help maintain a well-organized digital and physical workspace while reducing risks associated with data overload and compliance breaches.
Key Differences Between Archiving and Purging
Archiving involves systematically storing important documents and data for long-term retention, ensuring easy retrieval and compliance with legal requirements. Purging refers to the permanent removal or destruction of unnecessary or outdated files to free up physical or digital space and enhance organizational efficiency. Key differences lie in purpose--archiving preserves valuable information for future use, while purging eliminates redundant data to maintain order and reduce clutter.
Benefits of Archiving Business Records
Archiving business records ensures long-term accessibility and compliance with legal regulations, safeguarding critical information for audits and future reference. It enhances operational efficiency by organizing data systematically, reducing retrieval time and minimizing the risk of accidental loss or damage. Proper archiving also supports data security protocols, protecting sensitive information while maintaining an accurate historical record essential for strategic decision-making.
When to Archive vs. When to Purge
Archiving is ideal for storing essential documents and records that must be retained for legal, financial, or historical purposes, ensuring easy access while reducing clutter. Purging should be done when items are outdated, irrelevant, or no longer provide value, freeing up physical and digital space to enhance organization efficiency. Evaluating document lifecycle, compliance requirements, and usage frequency helps determine the best approach between archiving and purging.
Legal and Compliance Considerations in Data Management
Legal and compliance considerations in data management demand strict adherence to archiving and purging protocols to ensure regulatory compliance and mitigate risks. Archiving involves securely storing data for mandated retention periods to support audits and legal holds, while purging ensures timely deletion of unnecessary or obsolete information to prevent data breaches and reduce liability. Organizations must implement policies aligned with industry standards such as GDPR, HIPAA, and SOX to maintain data integrity and safeguard sensitive information.
Steps for Implementing an Effective Archiving Process
Begin by categorizing documents based on relevance, retention period, and regulatory requirements to ensure compliance and ease of retrieval. Develop a structured digital or physical filing system with clear labels and indexing to enhance accessibility and prevent data loss. Regularly review archived materials to update retention schedules and purge obsolete files, maintaining an efficient and clutter-free repository.
Risks and Drawbacks of Improper Purging
Improper purging of documents in professional organizing can lead to the loss of critical information, legal non-compliance, and decreased operational efficiency. Accidental disposal of essential records may result in costly recovery efforts and damage to business credibility. Failure to follow retention policies risks data breaches and potential fines, emphasizing the importance of strategic archiving over indiscriminate purging.
Digital Tools for Archiving and Purging
Digital tools for archiving such as Evernote, Google Drive, and Dropbox provide secure storage and easy retrieval of important documents, enhancing organization efficiency. Purging tools like CCleaner and Duplicate File Finder automate the removal of outdated files and duplicates, freeing up valuable digital space. Leveraging these tools streamlines document management by balancing long-term storage with effective decluttering.
Best Practices for Long-term Information Retention
Effective long-term information retention in professional organizing balances archiving and purging by identifying documents with ongoing legal, financial, or historical value for secure storage. Best practices include implementing a consistent labeling system, utilizing digital archiving tools with metadata tagging, and adhering to retention schedules aligned with regulatory requirements. Regular audits ensure obsolete or redundant files are purged, optimizing space and maintaining organized, accessible records.
Crafting a Company Policy for Archiving and Purging
Crafting a company policy for archiving and purging ensures systematic management of records, balancing regulatory compliance with operational efficiency. Clear guidelines on retention periods, document classifications, and secure disposal methods minimize risks associated with data clutter and legal liabilities. Implementing automated tools for tracking and timely purging enhances information governance and supports sustainable organizational workflows.
archiving vs purging Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com