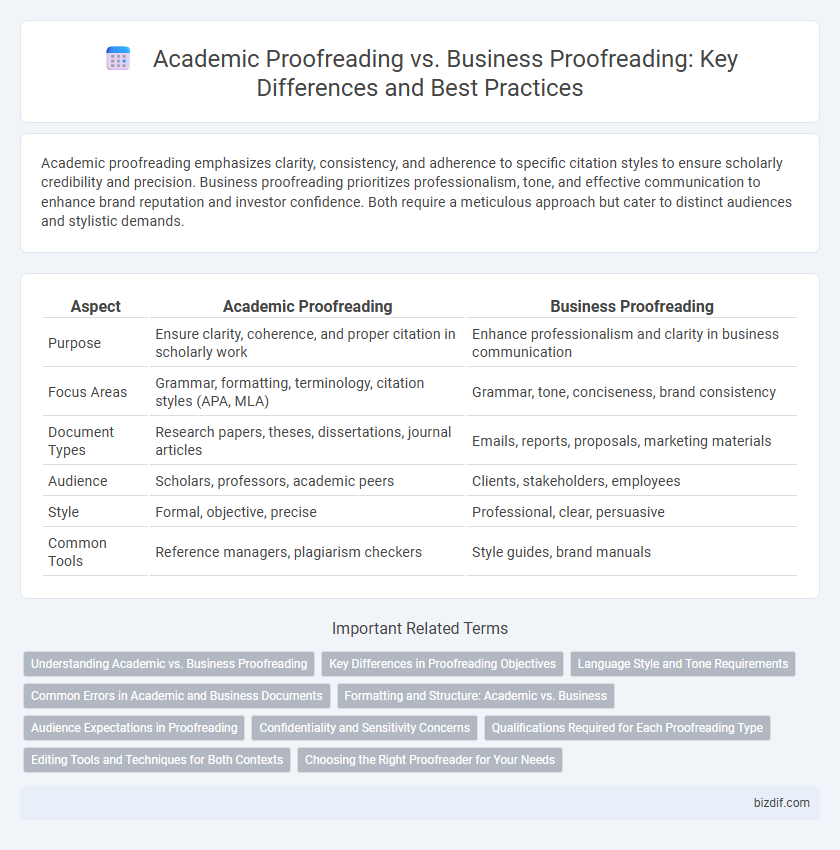
Academic proofreading emphasizes clarity, consistency, and adherence to specific citation styles to ensure scholarly credibility and precision. Business proofreading prioritizes professionalism, tone, and effective communication to enhance brand reputation and investor confidence. Both require a meticulous approach but cater to distinct audiences and stylistic demands.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Academic Proofreading | Business Proofreading |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Ensure clarity, coherence, and proper citation in scholarly work | Enhance professionalism and clarity in business communication |
| Focus Areas | Grammar, formatting, terminology, citation styles (APA, MLA) | Grammar, tone, conciseness, brand consistency |
| Document Types | Research papers, theses, dissertations, journal articles | Emails, reports, proposals, marketing materials |
| Audience | Scholars, professors, academic peers | Clients, stakeholders, employees |
| Style | Formal, objective, precise | Professional, clear, persuasive |
| Common Tools | Reference managers, plagiarism checkers | Style guides, brand manuals |
Understanding Academic vs. Business Proofreading
Academic proofreading emphasizes clarity, proper citation, and adherence to specific style guides such as APA, MLA, or Chicago, ensuring that research papers, theses, and dissertations meet scholarly standards. Business proofreading prioritizes concise, persuasive language and error-free documents like reports, proposals, and marketing materials to maintain professionalism and enhance brand credibility. Understanding these differences helps tailor proofreading techniques to the distinct purposes, audiences, and stylistic requirements of academic and business contexts.
Key Differences in Proofreading Objectives
Academic proofreading prioritizes accuracy in grammar, punctuation, and citation consistency to ensure clarity and credibility in scholarly work. Business proofreading focuses on maintaining professionalism, brand voice, and persuasive tone to enhance communication effectiveness and stakeholder trust. The key difference lies in academic proofreading emphasizing formal correctness and adherence to style guides, while business proofreading targets clarity and impact in commercial communications.
Language Style and Tone Requirements
Academic proofreading demands a formal, precise language style with technical terminology and an objective tone suitable for scholarly communication. Business proofreading requires a clear, concise language style emphasizing professionalism and persuasive tone aligned with brand voice and target audience. Both styles necessitate error-free grammar and syntax but differ significantly in tone to meet distinct contextual goals.
Common Errors in Academic and Business Documents
Academic proofreading often targets errors such as citation mistakes, complex sentence structures, and subject-specific terminology inconsistencies, which can undermine clarity and credibility. Business proofreading focuses on eliminating spelling errors, formatting issues, and jargon misuse to ensure professional communication and brand consistency. Both types require attention to detail but prioritize different common errors aligned with their unique document goals.
Formatting and Structure: Academic vs. Business
Academic proofreading emphasizes strict adherence to formatting guidelines such as APA, MLA, or Chicago style, ensuring citations, headings, and references follow institutional standards. Business proofreading prioritizes clarity and consistency in formatting, focusing on professional presentation through bullet points, concise paragraphs, and standardized fonts to enhance readability. While academic documents require structured sections like abstracts and literature reviews, business texts are often organized for quick scanning with clear calls to action and streamlined layouts.
Audience Expectations in Proofreading
Academic proofreading demands precise adherence to disciplinary terminology and citation standards to meet scholarly audience expectations, ensuring clarity and credibility in research communication. Business proofreading prioritizes accuracy, professionalism, and concise language tailored to corporate stakeholders, enhancing persuasive impact and brand reputation. Understanding the target audience's expectations drives the choice of tone, style, and formatting in both academic and business proofreading contexts.
Confidentiality and Sensitivity Concerns
Academic proofreading demands strict confidentiality due to the sensitive nature of unpublished research, ensuring intellectual property and data privacy are rigorously protected. Business proofreading involves handling proprietary information, financial data, and strategic documents that require heightened security measures to prevent leaks and maintain competitive advantage. Both fields prioritize confidentiality but differ in the type of sensitive content and the consequences of breaches.
Qualifications Required for Each Proofreading Type
Academic proofreading requires familiarity with specific citation styles such as APA, MLA, or Chicago, along with expertise in subject-specific terminology and scholarly writing conventions. Business proofreading demands proficiency in corporate language, brand voice consistency, and understanding of industry-specific jargon to ensure clear and professional communication. Both types require excellent grammar and spelling skills, but academic proofreaders often hold advanced degrees, while business proofreaders may have backgrounds in marketing, communications, or business administration.
Editing Tools and Techniques for Both Contexts
Academic proofreading relies heavily on specialized tools such as reference managers and plagiarism checkers, alongside grammar and style guides tailored to scholarly writing. Business proofreading incorporates software that emphasizes clarity, consistency, and brand voice, including advanced grammar checkers and collaborative platforms for real-time editing. Both contexts benefit from techniques like multiple revision rounds and peer reviews, but they prioritize distinct criteria aligned with their specific audience and purpose.
Choosing the Right Proofreader for Your Needs
Academic proofreading demands expertise in specialized terminology, citation styles, and adherence to institutional guidelines, ensuring clarity and credibility in scholarly work. Business proofreading prioritizes conciseness, professional tone, and brand consistency to enhance communication and client trust. Selecting the right proofreader involves assessing their familiarity with your industry's language, document purpose, and formatting requirements to guarantee precision and impact.
Academic proofreading vs Business proofreading Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com