Fact-checking in proofreading pet content ensures the accuracy of information about pet care, health, and behavior, preventing the spread of misinformation. Language-checking focuses on correcting grammar, spelling, punctuation, and style to enhance readability and clarity. Both processes are essential to produce reliable and professional pet-related content that builds trust with readers.
Table of Comparison
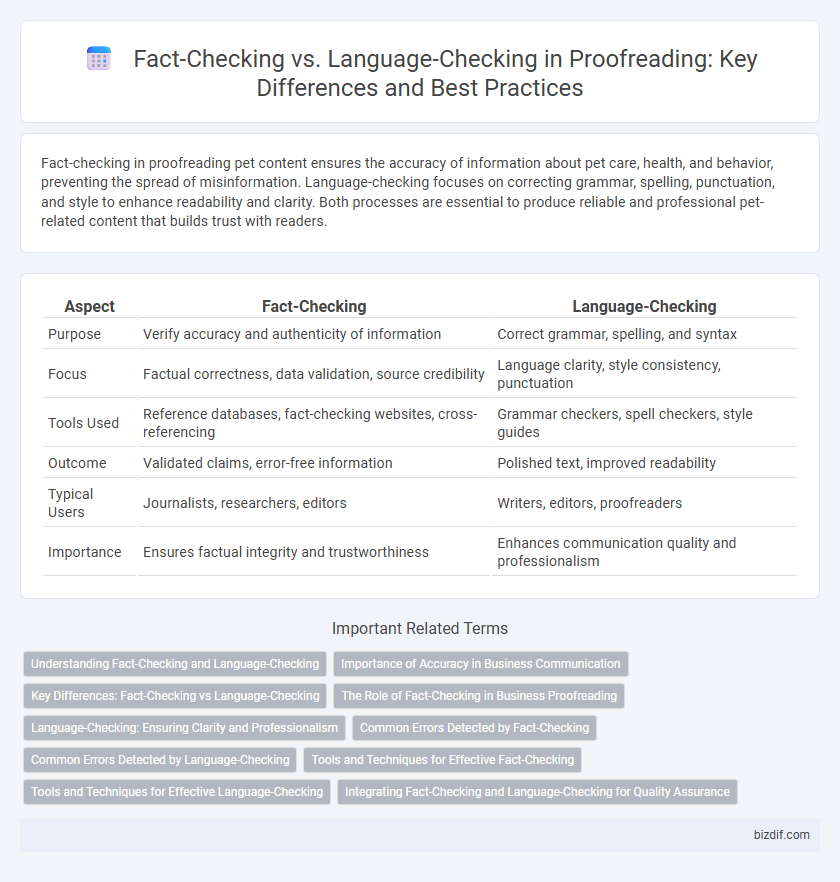
| Aspect | Fact-Checking | Language-Checking |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Verify accuracy and authenticity of information | Correct grammar, spelling, and syntax |
| Focus | Factual correctness, data validation, source credibility | Language clarity, style consistency, punctuation |
| Tools Used | Reference databases, fact-checking websites, cross-referencing | Grammar checkers, spell checkers, style guides |
| Outcome | Validated claims, error-free information | Polished text, improved readability |
| Typical Users | Journalists, researchers, editors | Writers, editors, proofreaders |
| Importance | Ensures factual integrity and trustworthiness | Enhances communication quality and professionalism |
Understanding Fact-Checking and Language-Checking
Fact-checking verifies the accuracy and truthfulness of information by cross-referencing credible sources and data, ensuring content reliability. Language-checking focuses on grammar, spelling, punctuation, and syntax to enhance clarity and readability without altering factual content. Effective proofreading combines both fact-checking and language-checking to maintain the integrity and professionalism of a document.
Importance of Accuracy in Business Communication
Fact-checking ensures the reliability of information in business communication by verifying data, dates, and figures, which prevents misinformation and builds trust with stakeholders. Language-checking enhances clarity and professionalism by correcting grammar, punctuation, and syntax, reducing misunderstandings and improving readability. Combining both processes is critical for maintaining accuracy and credibility in all corporate documents.
Key Differences: Fact-Checking vs Language-Checking
Fact-checking verifies the accuracy and truthfulness of content by reviewing data, sources, and claims for factual correctness. Language-checking focuses on grammar, syntax, punctuation, and style to ensure clear and error-free communication. Both processes improve text quality but serve distinct roles: factual integrity versus linguistic precision.
The Role of Fact-Checking in Business Proofreading
Fact-checking in business proofreading ensures accuracy by verifying data, statistics, and claims to maintain credibility and prevent misinformation. It complements language-checking, which focuses on grammar, syntax, and style, by addressing factual integrity rather than linguistic correctness. Effective business documents rely on rigorous fact-checking to build trust with clients and stakeholders, minimizing legal risks and enhancing professional reputation.
Language-Checking: Ensuring Clarity and Professionalism
Language-checking enhances document clarity by identifying and correcting grammatical errors, spelling mistakes, and awkward phrasing to ensure readability and professionalism. Advanced proofreading tools apply linguistic rules and style guidelines to maintain consistency in tone and terminology throughout the text. Proper language-checking not only improves communication effectiveness but also upholds the credibility and polished appearance of written content.
Common Errors Detected by Fact-Checking
Fact-checking identifies common errors such as incorrect dates, misattributed quotes, and false statistics that can undermine a text's credibility. Unlike language-checking, which focuses on grammar, spelling, and syntax, fact-checking ensures the accuracy and reliability of factual information. Verifying sources and cross-referencing data are essential steps to detect and correct these factual inaccuracies.
Common Errors Detected by Language-Checking
Language-checking tools commonly detect errors such as grammar mistakes, incorrect punctuation, spelling errors, and inconsistent verb tense usage. They identify issues with sentence structure, subject-verb agreement, and improper word choice to enhance overall text clarity and readability. Unlike fact-checking, which verifies the accuracy of information, language-checking focuses on the correctness and fluency of written language.
Tools and Techniques for Effective Fact-Checking
Effective fact-checking leverages tools such as Snopes, FactCheck.org, and Google Fact Check Explorer to verify claims against reliable databases and news sources. Techniques include cross-referencing multiple credible references and using automated software to detect inconsistencies or outdated information. These methods ensure accuracy beyond basic language-checking tools like Grammarly or Hemingway, which primarily focus on grammar and style rather than factual correctness.
Tools and Techniques for Effective Language-Checking
Effective language-checking relies on advanced tools such as Grammarly, Hemingway Editor, and ProWritingAid, which utilize natural language processing and machine learning algorithms to identify grammar, syntax, and style errors. Techniques including real-time error detection, context-aware suggestions, and customized style guides enhance the accuracy and consistency of proofreading. Integrating AI-powered language-checking tools with manual review ensures comprehensive correction of linguistic nuances and improves overall text clarity.
Integrating Fact-Checking and Language-Checking for Quality Assurance
Integrating fact-checking and language-checking enhances quality assurance by ensuring both accuracy and clarity in texts. Fact-checking verifies the validity of information, while language-checking improves grammar, syntax, and style, collectively producing reliable and polished content. Leveraging advanced software and expert review optimizes this dual process, minimizing errors and elevating overall document integrity.
Fact-checking vs Language-checking Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com