Automated QA in translation pet ensures rapid and consistent error detection by leveraging advanced algorithms to identify discrepancies in terminology, syntax, and formatting. Manual QA offers nuanced insights by allowing human reviewers to assess context, tone, and cultural relevance, which automated tools might overlook. Combining both methods optimizes translation accuracy and maintains the integrity of the original content.
Table of Comparison
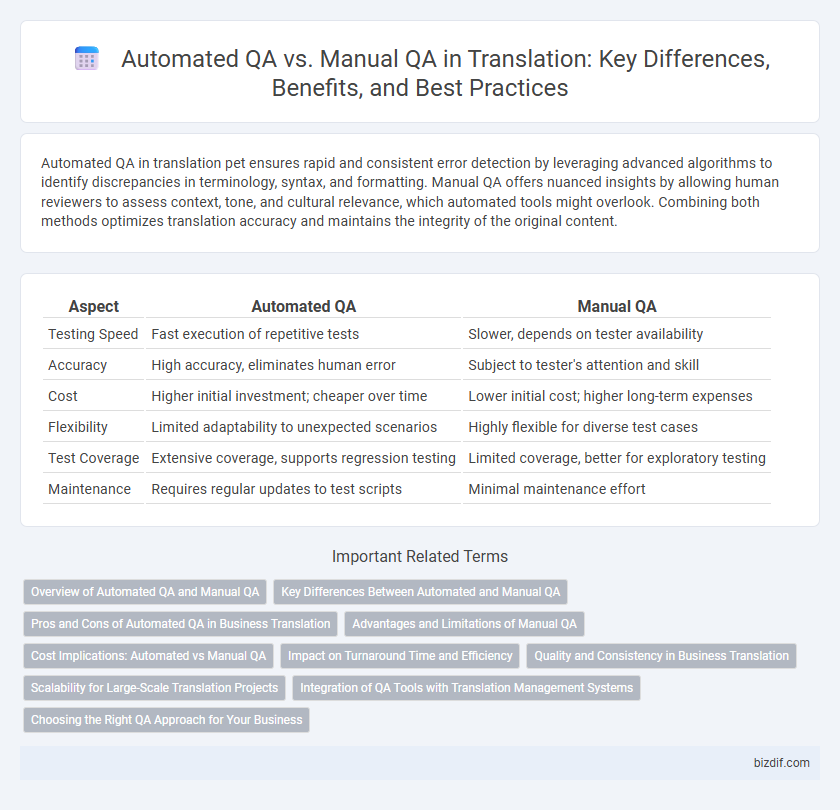
| Aspect | Automated QA | Manual QA |
|---|---|---|
| Testing Speed | Fast execution of repetitive tests | Slower, depends on tester availability |
| Accuracy | High accuracy, eliminates human error | Subject to tester's attention and skill |
| Cost | Higher initial investment; cheaper over time | Lower initial cost; higher long-term expenses |
| Flexibility | Limited adaptability to unexpected scenarios | Highly flexible for diverse test cases |
| Test Coverage | Extensive coverage, supports regression testing | Limited coverage, better for exploratory testing |
| Maintenance | Requires regular updates to test scripts | Minimal maintenance effort |
Overview of Automated QA and Manual QA
Automated QA in translation leverages software tools to quickly identify errors such as inconsistencies, missing tags, and formatting issues, improving efficiency and reducing repetitive tasks. Manual QA involves human reviewers who assess context, cultural nuances, and linguistic accuracy that automated tools may miss, ensuring high-quality and contextually appropriate translations. Combining automated and manual QA processes offers a comprehensive approach to maintaining translation accuracy and consistency.
Key Differences Between Automated and Manual QA
Automated QA in translation leverages software tools to quickly detect linguistic inconsistencies, terminology errors, and formatting issues, ensuring consistent results across large volumes. Manual QA relies on human expertise to evaluate context, cultural nuances, and idiomatic expressions, allowing for more nuanced error identification that machines may miss. The key differences include speed and scalability of automated checks versus the depth and contextual understanding of manual reviews.
Pros and Cons of Automated QA in Business Translation
Automated QA in business translation enhances efficiency by rapidly identifying inconsistencies, terminology errors, and formatting issues across large volumes of text, reducing turnaround time significantly. However, it may struggle with contextual nuances, cultural subtleties, and idiomatic expressions, potentially leading to inaccuracies that require manual review. Despite this limitation, integrating automated QA tools improves scalability and cost-effectiveness, especially for repetitive tasks and standardized content.
Advantages and Limitations of Manual QA
Manual QA in translation offers nuanced understanding of context, cultural relevance, and idiomatic expressions that automated QA tools often miss. It allows human reviewers to identify subtle errors in tone, style, and localization, ensuring higher quality and accuracy tailored to the target audience. However, manual QA can be time-consuming, costly, and prone to human error, limiting scalability for large volumes of content.
Cost Implications: Automated vs Manual QA
Automated QA significantly reduces long-term costs by minimizing the need for repetitive manual testing and accelerating the translation validation process. Manual QA incurs higher ongoing expenses due to labor-intensive workflows and slower processing times, especially in large-scale or multilingual projects. Investing in automated tools delivers better ROI by streamlining quality assurance and reducing human error in translation workflows.
Impact on Turnaround Time and Efficiency
Automated QA in translation significantly reduces turnaround time by instantly identifying errors and ensuring consistency across large volumes of text, boosting overall efficiency. Manual QA, while thorough in detecting nuanced linguistic issues, often requires more time and resources, potentially delaying project completion. Integrating automated QA tools streamlines the workflow and enhances productivity, yet reliant human review remains crucial for maintaining high-quality, contextually accurate translations.
Quality and Consistency in Business Translation
Automated QA in business translation ensures consistent application of terminology and style by rapidly detecting errors such as missing tags, inconsistent terminology, and formatting issues, significantly enhancing overall translation quality. Manual QA offers nuanced judgment, capturing context-specific nuances and subtle language variations that automated tools may miss, ensuring culturally appropriate and precise translations. Combining automated and manual QA processes optimizes both quality and consistency, reducing error rates while maintaining the linguistic accuracy essential for professional business communication.
Scalability for Large-Scale Translation Projects
Automated QA enables rapid processing of vast translation volumes, ensuring consistent application of linguistic rules and terminology across large-scale projects. Manual QA, while offering nuanced cultural and contextual insights, often struggles with scalability due to time and resource constraints. Leveraging automated tools alongside targeted manual reviews optimizes quality assurance efficiency and accuracy in extensive translation workflows.
Integration of QA Tools with Translation Management Systems
Integration of automated QA tools with Translation Management Systems (TMS) enhances error detection efficiency by enabling real-time quality checks during the translation workflow. Manual QA, while providing nuanced linguistic validation, often lacks seamless connectivity with TMS platforms, resulting in slower feedback loops. Automated QA tools support consistency across large volumes of content through scalable integration, improving overall translation quality and project turnaround time.
Choosing the Right QA Approach for Your Business
Choosing the right QA approach for translation depends on project scope, budget, and desired accuracy. Automated QA tools rapidly detect terminology inconsistencies, formatting errors, and basic linguistic issues, ideal for large-scale or repetitive content. Manual QA, conducted by experienced linguists, ensures nuanced understanding and cultural appropriateness, critical for high-stakes or marketing materials where precision and localization matter most.
Automated QA vs Manual QA Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com