Post-editing enhances raw machine translation by refining and correcting inaccuracies, ensuring higher quality and more natural-sounding text. While raw machine translation offers quick, immediate results, it often requires significant revisions to meet professional standards. Effective post-editing balances speed and accuracy, making translations more reliable for sensitive or complex content.
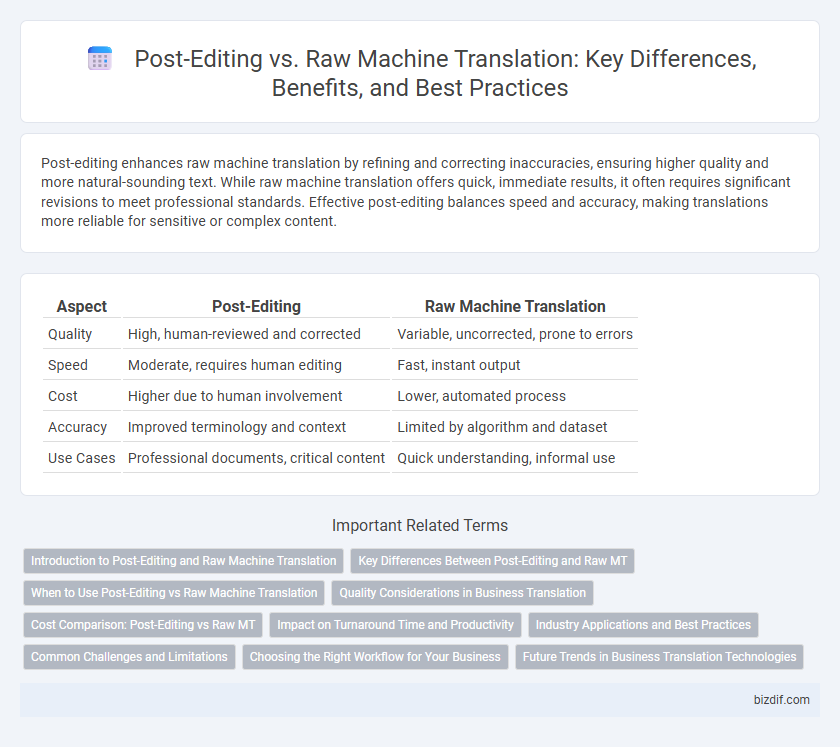
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Post-Editing | Raw Machine Translation |
|---|---|---|
| Quality | High, human-reviewed and corrected | Variable, uncorrected, prone to errors |
| Speed | Moderate, requires human editing | Fast, instant output |
| Cost | Higher due to human involvement | Lower, automated process |
| Accuracy | Improved terminology and context | Limited by algorithm and dataset |
| Use Cases | Professional documents, critical content | Quick understanding, informal use |
Introduction to Post-Editing and Raw Machine Translation
Post-editing involves human translators revising machine-generated translations to improve accuracy, fluency, and cultural relevance. Raw Machine Translation delivers automated text conversion without human intervention, often producing errors that affect readability and context. Effective use of post-editing enhances the quality of machine translation outputs, making them suitable for professional and commercial use.
Key Differences Between Post-Editing and Raw MT
Post-Editing involves human intervention to review and refine Machine Translation output, enhancing accuracy, fluency, and contextual relevance, whereas Raw Machine Translation delivers unedited, automated translations directly from AI engines. Key differences include quality assurance, with Post-Editing ensuring error correction and cultural appropriateness, while Raw MT prioritizes speed over linguistic precision. Post-Editing often requires professional linguists and domain expertise, contrasting with Raw MT's fully automated, immediate translation process.
When to Use Post-Editing vs Raw Machine Translation
Post-editing is ideal for content requiring high accuracy, such as legal documents or marketing materials, where clarity and cultural nuance are critical. Raw machine translation suits informal or internal communications where speed outweighs perfect grammar and style. Choosing between post-editing and raw machine translation depends on the desired quality, budget constraints, and turnaround time.
Quality Considerations in Business Translation
Post-editing enhances raw machine translation by improving accuracy, ensuring terminology consistency, and addressing contextual nuances essential in business translation. Quality considerations include reducing errors, refining tone, and ensuring compliance with industry-specific language standards. Employing skilled post-editors significantly elevates translation reliability and client satisfaction in professional settings.
Cost Comparison: Post-Editing vs Raw MT
Post-editing machine translation (PEMT) incurs higher costs than raw machine translation (MT) due to the involvement of skilled human editors who refine and correct automated outputs for accuracy and fluency. Raw MT offers a cost-effective solution by delivering instant translations without human intervention, but often sacrifices quality, necessitating further revisions that can raise overall expenses. Businesses must balance budget constraints and quality requirements when choosing between raw MT's low-cost speed and PEMT's enhanced linguistic accuracy and reliability.
Impact on Turnaround Time and Productivity
Post-editing of machine translation significantly reduces turnaround time by minimizing the need for extensive manual corrections while ensuring higher translation quality compared to raw machine translation. Productivity increases as post-editors refine output quickly, leveraging automated initial drafts instead of translating from scratch. This balanced approach optimizes workflow efficiency, delivering faster project completion without compromising accuracy.
Industry Applications and Best Practices
Post-editing enhances raw machine translation output by improving accuracy, fluency, and industry-specific terminology adherence, making it essential in sectors like legal, medical, and technical documentation. Raw machine translation offers quick, cost-effective solutions for real-time communication and content with less critical accuracy needs, such as social media or user-generated content. Best practices recommend combining machine translation engines with skilled human post-editors to balance efficiency and quality, ensuring compliance with industry standards and reducing localization errors.
Common Challenges and Limitations
Post-editing addresses common challenges in raw machine translation by refining inaccuracies such as mistranslations, inconsistent terminology, and awkward phrasing that often occur in automated outputs. Limitations of raw machine translation include a lack of contextual understanding, idiomatic expression errors, and difficulty handling domain-specific jargon. Effective post-editing improves translation quality, fluency, and cultural relevance, bridging the gap between raw output and human-level accuracy.
Choosing the Right Workflow for Your Business
Post-editing ensures higher accuracy and fluency by allowing human translators to refine raw machine translation output, making it ideal for businesses requiring quality content. Raw machine translation offers speed and cost-efficiency but may sacrifice context and nuance, suitable for rapid information dissemination or internal use. Evaluating content purpose, target audience, and budget helps determine whether post-editing or raw machine translation optimally supports your business workflow.
Future Trends in Business Translation Technologies
Future trends in business translation technologies prioritize hybrid solutions that combine raw machine translation with advanced post-editing to enhance accuracy and contextual relevance. Neural machine translation models integrated with artificial intelligence enable real-time language processing, reducing turnaround time while maintaining high linguistic quality. Adoption of adaptive learning systems allows continuous improvement in translation outputs, catering to industry-specific terminology and evolving business communication needs.
Post-Editing vs Raw Machine Translation Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com