Proofreading in translation ensures the accuracy, grammar, and style of the text after the initial translation phase, catching errors and inconsistencies to enhance overall quality. Post-editing involves revising machine-translated content to improve readability, coherence, and correctness, bridging the gap between raw automated output and a polished final product. Both processes are essential in delivering precise and fluent translations, tailored to the target audience's expectations.
Table of Comparison
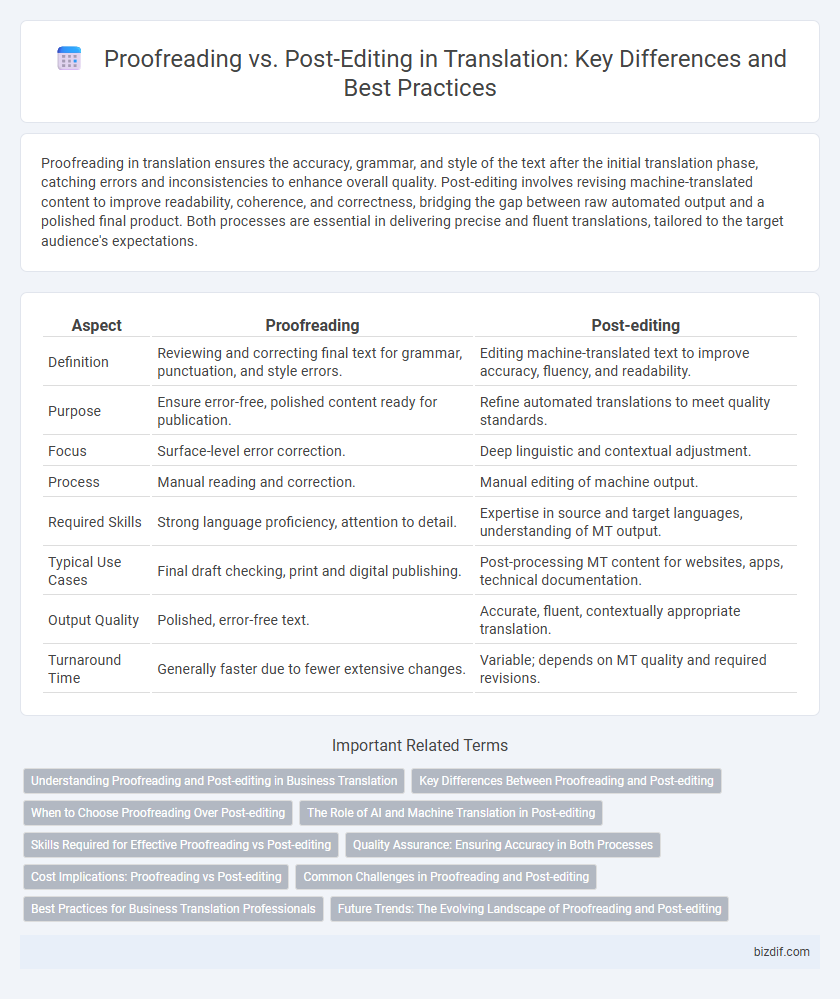
| Aspect | Proofreading | Post-editing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Reviewing and correcting final text for grammar, punctuation, and style errors. | Editing machine-translated text to improve accuracy, fluency, and readability. |
| Purpose | Ensure error-free, polished content ready for publication. | Refine automated translations to meet quality standards. |
| Focus | Surface-level error correction. | Deep linguistic and contextual adjustment. |
| Process | Manual reading and correction. | Manual editing of machine output. |
| Required Skills | Strong language proficiency, attention to detail. | Expertise in source and target languages, understanding of MT output. |
| Typical Use Cases | Final draft checking, print and digital publishing. | Post-processing MT content for websites, apps, technical documentation. |
| Output Quality | Polished, error-free text. | Accurate, fluent, contextually appropriate translation. |
| Turnaround Time | Generally faster due to fewer extensive changes. | Variable; depends on MT quality and required revisions. |
Understanding Proofreading and Post-editing in Business Translation
Proofreading in business translation involves meticulously reviewing translated documents to ensure linguistic accuracy, consistency, and error-free text that aligns with the original message. Post-editing focuses on refining machine-translated content by correcting inaccuracies, improving fluency, and adapting terminology to meet specific business requirements. Both processes enhance translation quality, but post-editing integrates advanced technology workflows, while proofreading relies on expert human review for precision.
Key Differences Between Proofreading and Post-editing
Proofreading involves reviewing text to identify and correct spelling, grammar, and punctuation errors without altering the original meaning, whereas post-editing focuses on refining machine-translated content to enhance accuracy, coherence, and fluency. Proofreading is typically applied to human-written documents, prioritizing linguistic correctness, while post-editing addresses translation quality issues stemming from automated processes. The key differences lie in the objectives, methods, and types of content each process targets within the translation workflow.
When to Choose Proofreading Over Post-editing
Choose proofreading over post-editing when dealing with texts that have been translated by professional human translators, ensuring minor errors or formatting issues are corrected for accuracy and fluency. Proofreading is ideal for final quality assurance in legal documents, literary works, or marketing materials where nuances and style are critical. When high-quality source translations exist with minimal machine-generated content, proofreading maintains the original voice and context more effectively than post-editing.
The Role of AI and Machine Translation in Post-editing
AI-driven machine translation rapidly generates initial drafts, making post-editing essential for enhancing accuracy and cultural relevance. Post-editors apply linguistic expertise to refine AI outputs, correcting errors and adapting tone to target audiences. This synergy between human skills and AI technology optimizes translation quality and efficiency in global communications.
Skills Required for Effective Proofreading vs Post-editing
Effective proofreading requires a keen eye for grammar, punctuation, and consistency to identify and correct errors without altering the original meaning. Post-editing demands advanced linguistic skills, including familiarity with machine translation outputs and the ability to improve fluency, coherence, and style while maintaining accuracy. Both processes benefit from deep cultural knowledge and subject-matter expertise to ensure the final text aligns with the target audience's expectations.
Quality Assurance: Ensuring Accuracy in Both Processes
Proofreading and post-editing are critical quality assurance steps that ensure accuracy and consistency in translation projects. Proofreading involves reviewing the translated text for grammatical, spelling, and typographical errors, while post-editing focuses on correcting machine-translated content to meet human translation standards. Both processes utilize linguistic expertise and specialized software tools to maintain high-quality, error-free deliverables.
Cost Implications: Proofreading vs Post-editing
Proofreading typically incurs lower costs as it involves correcting grammar, punctuation, and spelling in text already translated by humans. Post-editing, which requires refining machine-translated content for accuracy and fluency, often demands more time and expertise, leading to higher expenses. Businesses must weigh these cost differences against desired quality and project turnaround times to determine the most cost-effective approach.
Common Challenges in Proofreading and Post-editing
Common challenges in proofreading include identifying subtle grammatical errors, inconsistent terminology, and maintaining the original tone of the text. Post-editing often struggles with machine translation inaccuracies, such as awkward phrasing or context misinterpretation, requiring both linguistic expertise and technical knowledge. Both processes demand meticulous attention to detail to ensure accuracy, fluency, and cultural relevance in the final translation.
Best Practices for Business Translation Professionals
Proofreading in business translation emphasizes accuracy, consistency, and linguistic quality by thoroughly checking grammar, punctuation, and style after initial translation. Post-editing requires advanced skills to review machine-translated content, improving clarity, cultural relevance, and terminological precision to meet client specifications. Effective use of specialized software tools, adherence to industry standards like ISO 17100, and strong subject-matter expertise are essential best practices for professionals optimizing translation quality and efficiency.
Future Trends: The Evolving Landscape of Proofreading and Post-editing
Advancements in artificial intelligence and machine learning are driving the evolution of proofreading and post-editing, with automated tools increasingly integrated into translation workflows. The future will emphasize hybrid human-AI collaboration to enhance accuracy, efficiency, and speed in language services. Emerging trends suggest a shift towards adaptive post-editing practices that leverage real-time data analytics and contextual understanding for more precise localization.
Proofreading vs Post-editing Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com