Travel insurance offers comprehensive coverage for unexpected events such as trip cancellations, medical emergencies, and lost luggage, providing peace of mind for travelers. Self-insurance requires setting aside personal funds to cover potential travel risks, which can save costs upfront but may lead to significant financial loss if emergencies occur. Evaluating the likelihood of risks and personal financial stability helps determine the best approach between travel insurance and self-insurance for a secure journey.
Table of Comparison
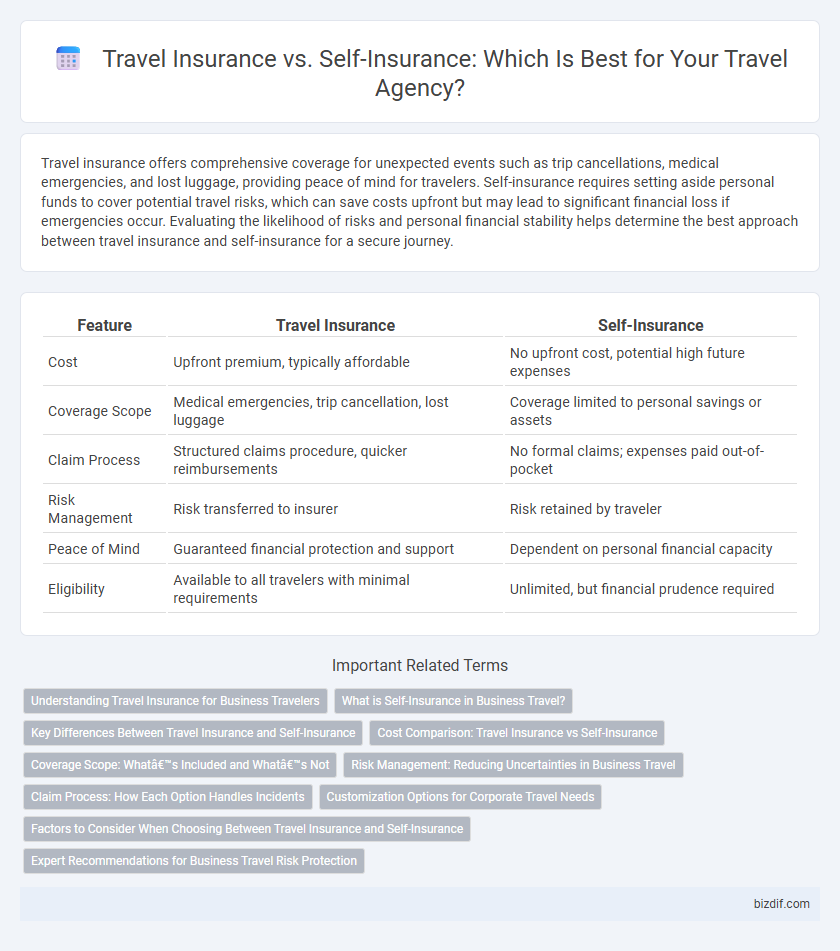
| Feature | Travel Insurance | Self-Insurance |
|---|---|---|
| Cost | Upfront premium, typically affordable | No upfront cost, potential high future expenses |
| Coverage Scope | Medical emergencies, trip cancellation, lost luggage | Coverage limited to personal savings or assets |
| Claim Process | Structured claims procedure, quicker reimbursements | No formal claims; expenses paid out-of-pocket |
| Risk Management | Risk transferred to insurer | Risk retained by traveler |
| Peace of Mind | Guaranteed financial protection and support | Dependent on personal financial capacity |
| Eligibility | Available to all travelers with minimal requirements | Unlimited, but financial prudence required |
Understanding Travel Insurance for Business Travelers
Business travelers benefit from comprehensive travel insurance that covers trip cancellations, medical emergencies, and lost luggage, minimizing financial risks associated with unforeseen events. Self-insurance requires setting aside significant funds to cover potential expenses, which may not be practical or sufficient for unpredictable travel disruptions. Understanding the specific coverage details of travel insurance plans ensures optimal protection tailored to the complex needs of corporate travel.
What is Self-Insurance in Business Travel?
Self-insurance in business travel refers to a risk management strategy where companies set aside funds internally to cover potential travel-related expenses instead of purchasing external travel insurance policies. This approach allows businesses to directly handle costs associated with trip cancellations, medical emergencies, or lost luggage, potentially reducing premiums and administrative overhead. Effective self-insurance requires thorough risk assessment, sufficient financial reserves, and a clear plan for reimbursing employees in case of travel incidents.
Key Differences Between Travel Insurance and Self-Insurance
Travel insurance offers comprehensive coverage for trip cancellations, medical emergencies, lost luggage, and travel delays, providing a safety net backed by insurance companies. Self-insurance requires travelers to personally set aside funds to cover unexpected expenses, lacking the immediate financial support and legal protections that travel insurance provides. Key differences include risk management, coverage scope, and financial security during unforeseen travel disruptions.
Cost Comparison: Travel Insurance vs Self-Insurance
Travel insurance typically involves a fixed premium that covers a wide range of risks such as trip cancellations, medical emergencies, and lost luggage, offering financial protection for unexpected events. Self-insurance requires travelers to set aside a personal fund to cover potential expenses, which may appear cost-effective upfront but can lead to significant out-of-pocket costs if major incidents occur. Comparing costs, travel insurance provides predictable budgeting with coverage benefits, while self-insurance carries risk of higher expenses without guaranteed reimbursement.
Coverage Scope: What’s Included and What’s Not
Travel insurance typically covers trip cancellations, medical emergencies, lost luggage, and travel delays, providing comprehensive protection for unforeseen events during your trip. Self-insurance involves setting aside personal funds to cover potential losses but lacks the specific benefits and safeguards offered by standardized policies. Understanding the limitations of self-insurance, such as missing coverage for emergency evacuation or supplier insolvency, is crucial when comparing it to the broader scope of travel insurance coverage.
Risk Management: Reducing Uncertainties in Business Travel
Travel insurance offers comprehensive coverage for unexpected events such as trip cancellations, medical emergencies, and lost luggage, effectively minimizing financial risks in business travel. Self-insurance, while potentially cost-saving, requires substantial reserves and assumes full responsibility for all travel-related incidents, increasing exposure to uncertainties. Strategic risk management in business travel prioritizes insured plans to ensure financial stability and seamless operations.
Claim Process: How Each Option Handles Incidents
Travel insurance providers streamline the claim process by offering dedicated support teams that handle incident verification, documentation, and reimbursements efficiently, often within 10 to 15 business days. Self-insurance requires travelers to personally manage all claim procedures, including gathering evidence, contacting service providers, and absorbing initial costs, which can delay reimbursement and increase financial risk. The structured claim systems of travel insurance minimize stress and ensure quicker resolution compared to the time-consuming, self-managed approach of self-insurance.
Customization Options for Corporate Travel Needs
Corporate travel insurance offers extensive customization options tailored to company-specific risks, including coverage for trip cancellations, medical emergencies, and liability protection. Self-insurance requires businesses to allocate internal funds for potential travel-related losses but lacks the flexibility to adapt to varying travel plans and unforeseen incidents. Utilizing specialized travel insurance allows corporations to select precise coverage limits and benefits aligned with employee travel profiles and organizational policies.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Between Travel Insurance and Self-Insurance
Evaluating travel insurance versus self-insurance requires analyzing trip cost, risk tolerance, and coverage benefits such as medical emergencies, trip cancellations, and lost baggage protection. Travelers should consider financial capacity to absorb unexpected expenses versus the premium costs and claim processes of travel insurance policies. Assessing destination-specific risks and personal health conditions also plays a critical role in making an informed decision between these two options.
Expert Recommendations for Business Travel Risk Protection
Experts recommend travel insurance over self-insurance for business travel risk protection due to comprehensive coverage against trip cancellations, medical emergencies, and lost luggage. Travel insurance policies often include 24/7 assistance and tailored options for high-risk destinations, which self-insurance lacks. Business travelers benefit from reduced financial exposure and peace of mind by relying on reputable insurers rather than assuming all risks independently.
Travel insurance vs Self-insurance Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com