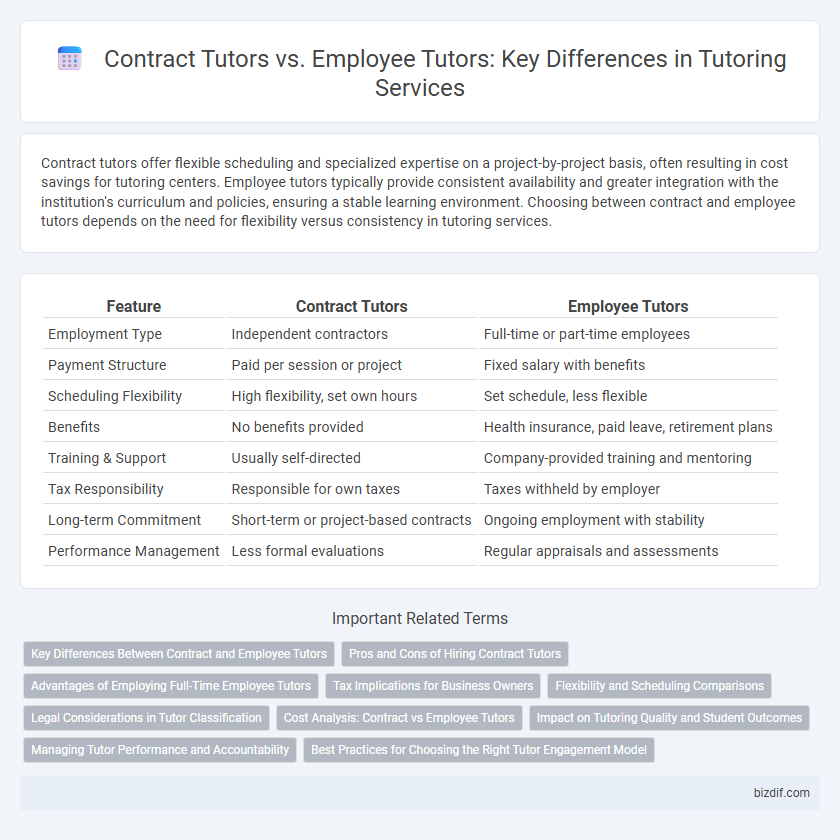
Contract tutors offer flexible scheduling and specialized expertise on a project-by-project basis, often resulting in cost savings for tutoring centers. Employee tutors typically provide consistent availability and greater integration with the institution's curriculum and policies, ensuring a stable learning environment. Choosing between contract and employee tutors depends on the need for flexibility versus consistency in tutoring services.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Contract Tutors | Employee Tutors |
|---|---|---|
| Employment Type | Independent contractors | Full-time or part-time employees |
| Payment Structure | Paid per session or project | Fixed salary with benefits |
| Scheduling Flexibility | High flexibility, set own hours | Set schedule, less flexible |
| Benefits | No benefits provided | Health insurance, paid leave, retirement plans |
| Training & Support | Usually self-directed | Company-provided training and mentoring |
| Tax Responsibility | Responsible for own taxes | Taxes withheld by employer |
| Long-term Commitment | Short-term or project-based contracts | Ongoing employment with stability |
| Performance Management | Less formal evaluations | Regular appraisals and assessments |
Key Differences Between Contract and Employee Tutors
Contract tutors operate as independent contractors, managing their own schedules and taxes, while employee tutors receive regular salaries, benefits, and employer-provided resources. Employee tutors often have set work hours and adherence to company policies, whereas contract tutors enjoy greater flexibility but less job security. The distinction significantly impacts payment structure, legal obligations, and long-term commitment in tutoring roles.
Pros and Cons of Hiring Contract Tutors
Hiring contract tutors offers flexibility and cost savings by enabling institutions to scale tutoring services on demand without long-term commitments or benefits expenses. Contract tutors often bring specialized expertise and adaptability but may lack consistent availability and institutional loyalty compared to employee tutors. Potential downsides include less control over tutor quality and reduced integration with the educational organization's culture and curriculum.
Advantages of Employing Full-Time Employee Tutors
Employing full-time employee tutors ensures consistent quality control and loyalty, enhancing student outcomes through dedicated expertise and alignment with institution standards. Full-time tutors benefit from structured professional development and access to resources, fostering long-term growth and stability. This approach reduces administrative overhead related to contract negotiations and turnover, creating a more efficient and cohesive tutoring program.
Tax Implications for Business Owners
Contract tutors are considered independent contractors, requiring business owners to issue 1099 forms and avoid payroll taxes such as Social Security and Medicare, which can reduce overall tax liabilities. Employee tutors, in contrast, necessitate withholding income taxes, paying employer payroll taxes, and providing benefits, increasing administrative burden and costs for business owners. Understanding these tax implications helps business owners optimize expenses and compliance when deciding between contract and employee tutoring arrangements.
Flexibility and Scheduling Comparisons
Contract tutors offer greater flexibility with customizable schedules, enabling sessions to be arranged based on student availability and specific needs. Employee tutors typically follow fixed working hours set by the institution, which can limit adaptability in accommodating last-minute changes or diverse time zones. This scheduling flexibility makes contract tutors ideal for personalized and irregular tutoring demands.
Legal Considerations in Tutor Classification
Contract tutors are classified as independent contractors, granting them flexibility but requiring compliance with IRS guidelines to avoid misclassification penalties. Employee tutors receive benefits such as minimum wage, overtime pay, and workers' compensation, while employers must adhere to labor laws and tax withholding requirements. Proper legal classification impacts liability, tax obligations, and eligibility for unemployment benefits, making it essential for tutoring agencies to carefully assess the nature of their tutor relationships.
Cost Analysis: Contract vs Employee Tutors
Contract tutors often incur lower upfront costs due to the absence of employee benefits such as health insurance and retirement contributions, allowing tutoring centers to maintain flexible staffing budgets. Employee tutors typically demand higher overall compensation packages, including salaries, taxes, and benefits, which increase fixed labor costs for institutions. A thorough cost analysis reveals that while contract tutors reduce fixed expenses, employee tutors may offer greater long-term value through enhanced loyalty and consistency in service delivery.
Impact on Tutoring Quality and Student Outcomes
Contract tutors often bring specialized expertise and flexibility, which can enhance tutoring quality by tailoring sessions to student needs. Employee tutors benefit from consistent training, accountability, and alignment with institutional goals, promoting sustained improvements in student outcomes. The choice between contract and employee tutors significantly influences the effectiveness and personalization of educational support.
Managing Tutor Performance and Accountability
Contract tutors offer flexible engagement terms but pose challenges in consistent performance tracking and accountability due to variable commitment levels. Employee tutors are subject to structured performance evaluations and clear accountability frameworks, facilitating standardized quality control and professional development. Implementing tailored management systems enhances oversight effectiveness across both contract and employee tutor models.
Best Practices for Choosing the Right Tutor Engagement Model
Selecting the ideal tutor engagement model hinges on aligning educational goals with operational needs; contract tutors offer flexibility and cost-efficiency, while employee tutors provide consistency and deeper institutional integration. Best practices involve evaluating factors such as budget constraints, frequency of tutoring sessions, quality control measures, and long-term commitment potential to optimize student outcomes. Schools and tutoring centers should implement clear performance metrics and feedback mechanisms regardless of the model to ensure tutor effectiveness and maintain high educational standards.
Contract tutors vs employee tutors Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com