Feature-Driven Development prioritizes building software around predefined features, ensuring timely delivery and measurable progress by breaking down tasks into manageable units. User-Driven Development emphasizes understanding and incorporating user needs and feedback throughout the development process, resulting in a product that aligns closely with user expectations. Balancing both approaches can lead to an app that is both functionally robust and highly user-centric.
Table of Comparison
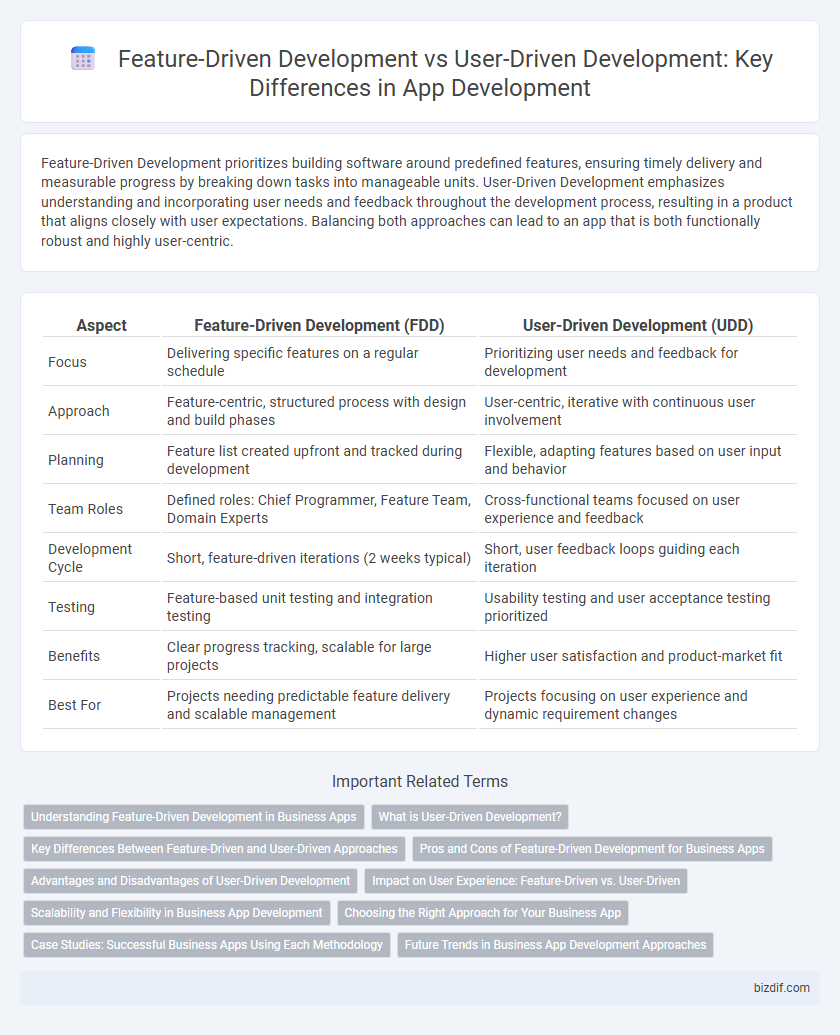
| Aspect | Feature-Driven Development (FDD) | User-Driven Development (UDD) |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Delivering specific features on a regular schedule | Prioritizing user needs and feedback for development |
| Approach | Feature-centric, structured process with design and build phases | User-centric, iterative with continuous user involvement |
| Planning | Feature list created upfront and tracked during development | Flexible, adapting features based on user input and behavior |
| Team Roles | Defined roles: Chief Programmer, Feature Team, Domain Experts | Cross-functional teams focused on user experience and feedback |
| Development Cycle | Short, feature-driven iterations (2 weeks typical) | Short, user feedback loops guiding each iteration |
| Testing | Feature-based unit testing and integration testing | Usability testing and user acceptance testing prioritized |
| Benefits | Clear progress tracking, scalable for large projects | Higher user satisfaction and product-market fit |
| Best For | Projects needing predictable feature delivery and scalable management | Projects focusing on user experience and dynamic requirement changes |
Understanding Feature-Driven Development in Business Apps
Feature-Driven Development (FDD) in business apps emphasizes building software around distinct, client-valued features that align with business goals and user requirements. This method enhances project visibility by breaking down complex systems into manageable, feature-based increments, improving delivery speed and quality. Prioritizing features that drive business value ensures alignment between development efforts and strategic objectives, optimizing resource allocation and stakeholder satisfaction.
What is User-Driven Development?
User-Driven Development (UDD) is a software development approach that prioritizes the needs, feedback, and behaviors of end-users throughout the app creation process. It emphasizes direct user involvement in defining features, usability testing, and iterative improvements based on real user insights to ensure the final product aligns closely with user expectations. This approach contrasts with Feature-Driven Development by centering the development cycle around actual user experience rather than predefined feature sets.
Key Differences Between Feature-Driven and User-Driven Approaches
Feature-Driven Development (FDD) centers on building software by defining and delivering specific, measurable features in short iterations, prioritizing technical tasks and progress tracking. User-Driven Development (UDD) emphasizes user needs and experiences, focusing on gathering user feedback and adapting the product based on real-world usage and user stories. The key difference lies in FDD's feature-centric workflow aimed at system functionality versus UDD's user-centric approach targeting usability and satisfaction.
Pros and Cons of Feature-Driven Development for Business Apps
Feature-Driven Development (FDD) offers structured progress through clearly defined features, making it ideal for delivering complex business apps on time and within budget. This method ensures continuous client involvement and measurable progress, reducing project risks and improving predictability. However, FDD can be less flexible in accommodating evolving user needs compared to User-Driven Development, potentially limiting responsiveness to user feedback during app iteration.
Advantages and Disadvantages of User-Driven Development
User-Driven Development (UDD) prioritizes user needs and feedback, resulting in highly intuitive and customer-centric applications that enhance user satisfaction and engagement. However, UDD can lead to longer development cycles due to constant iterations and changes based on evolving user input, potentially increasing project costs and complexity. Balancing user feedback with technical feasibility is essential to avoid scope creep and maintain efficient delivery timelines.
Impact on User Experience: Feature-Driven vs. User-Driven
Feature-Driven Development prioritizes delivering specific functionalities based on predefined business requirements, often leading to a structured but less personalized user experience. User-Driven Development centers on real-time feedback and user behavior analysis, resulting in highly tailored features that enhance satisfaction and engagement. Emphasizing user needs in development cycles significantly improves usability and adaptability of the app.
Scalability and Flexibility in Business App Development
Feature-Driven Development (FDD) emphasizes scalable architecture by focusing on building and refining specific features iteratively, which allows business apps to expand systematically without compromising performance. User-Driven Development (UDD) prioritizes flexibility by continuously integrating user feedback, ensuring the app adapts fluidly to evolving business needs and user behaviors. Balancing FDD's structured scalability with UDD's adaptive flexibility enhances the long-term viability and responsiveness of business applications in dynamic markets.
Choosing the Right Approach for Your Business App
Feature-Driven Development (FDD) emphasizes building apps through clearly defined features that align with project milestones and technical requirements, ensuring efficient iterations and scalability. User-Driven Development (UDD) centers on continuous user feedback, prioritizing usability and personalized experiences to meet end-user needs effectively. Selecting the right approach depends on your business goals: FDD suits apps requiring rapid, structured releases, while UDD is ideal for customer-centric applications demanding adaptability and engagement.
Case Studies: Successful Business Apps Using Each Methodology
Feature-Driven Development (FDD) propelled the success of apps like Spotify by emphasizing iterative feature delivery aligned with technical precision, enhancing scalability and maintainability. User-Driven Development (UDD) underpinned apps like Airbnb, prioritizing real user feedback and behavioral data to tailor features directly to user needs, boosting engagement and satisfaction. Case studies reveal FDD excels in complex, data-intensive platforms, while UDD drives growth in consumer-facing applications focused on user experience.
Future Trends in Business App Development Approaches
Feature-Driven Development (FDD) emphasizes structured, feature-centric progress that suits scalable enterprise applications, while User-Driven Development (UDD) centers on adaptive designs shaped by real-time user feedback and behaviors. Future trends in business app development point toward hybrid methodologies that integrate FDD's systematic workflow with UDD's user experience optimizations to enhance agility and customer satisfaction. Embracing AI-powered analytics and continuous user engagement tools further accelerates this convergence, driving more personalized and responsive business applications.
Feature-Driven Development vs User-Driven Development Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com