A Minimum Viable Product (MVP) allows developers to launch an app with core features to quickly gather user feedback and validate the concept. Developing a full-featured product requires more time and resources but delivers a comprehensive user experience tailored to market demands. Prioritizing an MVP minimizes risk and accelerates iterations, essential for successful app development in competitive environments.
Table of Comparison
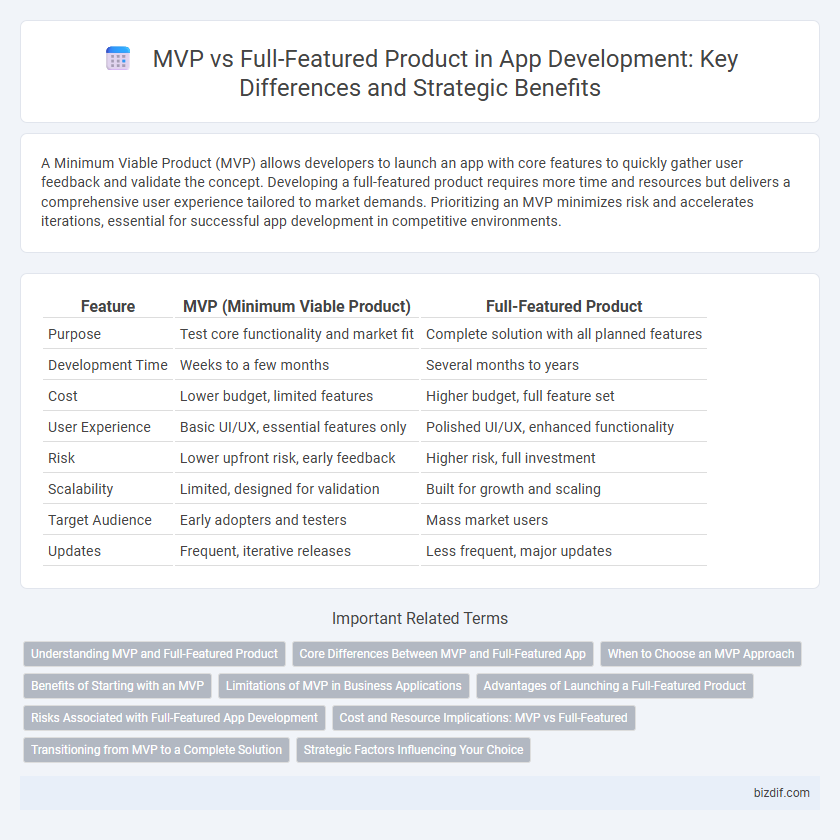
| Feature | MVP (Minimum Viable Product) | Full-Featured Product |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Test core functionality and market fit | Complete solution with all planned features |
| Development Time | Weeks to a few months | Several months to years |
| Cost | Lower budget, limited features | Higher budget, full feature set |
| User Experience | Basic UI/UX, essential features only | Polished UI/UX, enhanced functionality |
| Risk | Lower upfront risk, early feedback | Higher risk, full investment |
| Scalability | Limited, designed for validation | Built for growth and scaling |
| Target Audience | Early adopters and testers | Mass market users |
| Updates | Frequent, iterative releases | Less frequent, major updates |
Understanding MVP and Full-Featured Product
An MVP (Minimum Viable Product) focuses on delivering core functionalities to validate the product concept swiftly with minimal resources. In contrast, a full-featured product encompasses comprehensive features designed to provide a complete user experience and support long-term scalability. Understanding the distinction helps development teams allocate resources effectively and prioritize features based on user feedback and business goals.
Core Differences Between MVP and Full-Featured App
An MVP (Minimum Viable Product) focuses on delivering the essential features that address the primary user problem, enabling rapid market entry and early user feedback collection. In contrast, a full-featured product includes comprehensive functionalities, enhanced user interface design, and scalability, aiming to offer a complete solution with long-term user engagement. The core difference lies in the development approach: MVP prioritizes speed and learning, while full-featured apps emphasize robustness, extensive testing, and polished user experience.
When to Choose an MVP Approach
Choosing an MVP approach is ideal when seeking rapid market validation with minimal resources, enabling teams to test core functionalities and gather user feedback efficiently. Startups and product teams benefit from launching a simplified version to identify customer needs and reduce development risks before investing in a full-featured product. This strategy accelerates learning cycles while optimizing budget allocation and time-to-market.
Benefits of Starting with an MVP
Starting with a Minimum Viable Product (MVP) allows app developers to validate core functionalities with real user feedback, reducing development costs and time. It minimizes risks by focusing on essential features, enabling faster iterations and improvements based on actual market demand. This approach accelerates go-to-market strategies and enhances the likelihood of product-market fit before investing in a full-featured product.
Limitations of MVP in Business Applications
MVPs in business applications often lack scalability, advanced features, and robust security measures, limiting their effectiveness in complex enterprise environments. These prototypes may result in incomplete user experiences and insufficient integration capabilities, reducing overall market competitiveness. The trade-off between rapid deployment and functional depth makes MVPs less suitable for mission-critical applications requiring comprehensive functionality and reliability.
Advantages of Launching a Full-Featured Product
Launching a full-featured product accelerates market penetration by offering comprehensive solutions that meet diverse user needs, enhancing customer satisfaction and retention. This approach establishes a stronger brand presence and competitive edge through rich functionalities and seamless user experiences. Investors and stakeholders are more attracted to robust, mature products demonstrating clear value propositions and scalable opportunities.
Risks Associated with Full-Featured App Development
Developing a full-featured app presents significant risks including high initial costs, extended time to market, and increased complexity that can overwhelm development teams and lead to quality issues. These risks often result in delayed launches, budget overruns, and difficulty in adapting to user feedback or market changes. In contrast, focusing on a Minimum Viable Product (MVP) helps mitigate these risks by enabling faster releases and iterative improvements based on real user data.
Cost and Resource Implications: MVP vs Full-Featured
Developing an MVP requires significantly lower cost and fewer resources compared to a full-featured product, as it focuses on core functionalities to validate market demand quickly. Full-featured products demand extensive investment in design, development, testing, and maintenance, impacting budgets and timelines substantially. Optimizing resource allocation between MVP and full-featured stages enhances project efficiency and reduces financial risks.
Transitioning from MVP to a Complete Solution
Transitioning from an MVP to a full-featured product requires strategic planning, incorporating user feedback and scaling infrastructure to handle increased demand. Prioritizing feature development based on data-driven insights ensures alignment with market needs and enhances product-market fit. Investing in robust architecture and scalable codebases facilitates seamless expansion while maintaining system performance and user experience.
Strategic Factors Influencing Your Choice
Choosing between an MVP and a full-featured product hinges on strategic factors such as time-to-market, budget constraints, and target audience feedback. MVPs enable rapid validation of core features, minimizing development costs while gathering essential user insights for iterative improvement. In contrast, full-featured products require substantial initial investment and longer development cycles but aim to deliver comprehensive functionality to meet broader market demands from launch.
MVP vs Full-Featured Product Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com