Serverless architecture eliminates the need for managing server infrastructure, allowing pet app developers to scale automatically and reduce operational costs. Traditional hosting requires manual server configuration and maintenance, which can lead to higher expenses and slower scalability. Choosing serverless enhances flexibility and accelerates deployment, making it ideal for dynamic pet apps with fluctuating user demands.
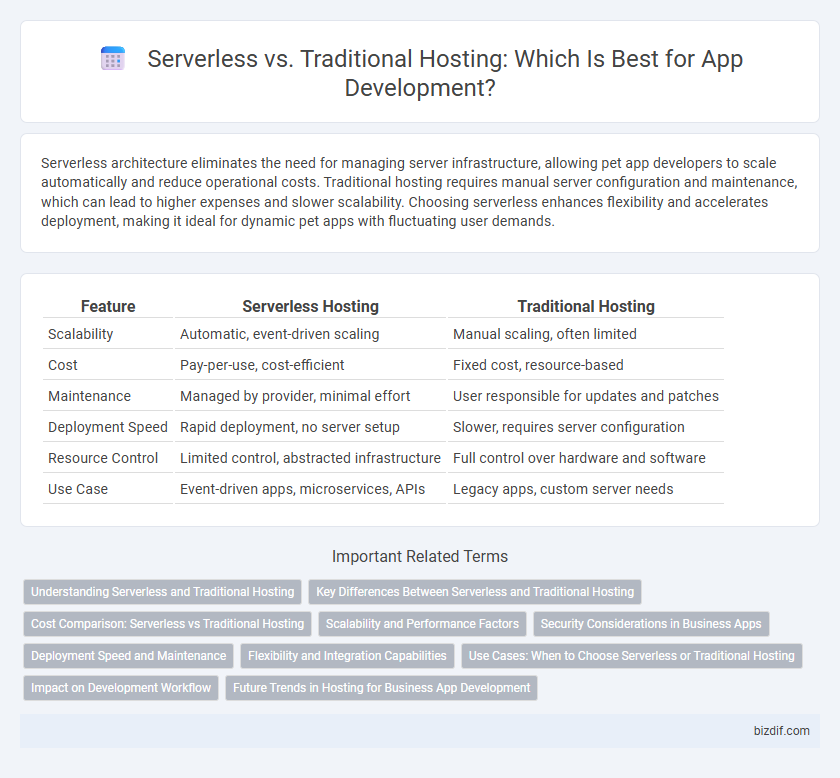
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Serverless Hosting | Traditional Hosting |
|---|---|---|
| Scalability | Automatic, event-driven scaling | Manual scaling, often limited |
| Cost | Pay-per-use, cost-efficient | Fixed cost, resource-based |
| Maintenance | Managed by provider, minimal effort | User responsible for updates and patches |
| Deployment Speed | Rapid deployment, no server setup | Slower, requires server configuration |
| Resource Control | Limited control, abstracted infrastructure | Full control over hardware and software |
| Use Case | Event-driven apps, microservices, APIs | Legacy apps, custom server needs |
Understanding Serverless and Traditional Hosting
Serverless hosting enables app developers to run code without managing servers, automatically scaling resources based on demand and charging only for actual usage, which reduces operational overhead and costs. Traditional hosting involves provisioning fixed server resources, requiring developers to handle server maintenance, updates, and scalability, often leading to higher resource consumption and management complexity. Understanding these fundamental differences helps in selecting the optimal infrastructure for app performance, cost efficiency, and development agility.
Key Differences Between Serverless and Traditional Hosting
Serverless hosting eliminates the need for server management by automatically scaling resources based on demand, while traditional hosting requires manual provisioning and maintenance of physical or virtual servers. In serverless architecture, billing is usage-based, charging only for compute time consumed, whereas traditional hosting often involves fixed costs regardless of traffic fluctuations. Serverless environments enhance agility and rapid deployment, contrasting with the slower update cycles and rigid infrastructure constraints of traditional hosting models.
Cost Comparison: Serverless vs Traditional Hosting
Serverless architecture reduces costs by charging only for actual usage, eliminating expenses related to idle server time, while traditional hosting requires fixed payments regardless of traffic fluctuations. Traditional hosting often incurs additional costs for maintaining, scaling, and managing dedicated servers, which can lead to higher overhead. Evaluating expected workload and traffic patterns is crucial, as serverless is cost-effective for variable demand, whereas traditional hosting may be more predictable for steady, high-volume applications.
Scalability and Performance Factors
Serverless architecture offers automatic scaling by dynamically allocating resources in response to real-time demand, eliminating the need for manual server management and reducing latency during traffic spikes. Traditional hosting relies on pre-provisioned servers that require capacity planning and may experience performance bottlenecks when faced with unexpected load increases. The event-driven nature of serverless computing enhances performance efficiency by optimizing resource utilization, whereas traditional hosting environments may incur higher operational costs and slower scalability due to fixed infrastructure constraints.
Security Considerations in Business Apps
Serverless architecture reduces the attack surface by abstracting server management but relies heavily on the security of third-party cloud providers and proper configuration of function permissions to prevent unauthorized access. Traditional hosting offers greater control over infrastructure, enabling tailored security policies and direct monitoring, but increases the risk of misconfigured servers and delayed patching. Business apps must evaluate compliance needs, data sensitivity, and incident response capabilities when choosing between serverless and traditional hosting for secure deployment.
Deployment Speed and Maintenance
Serverless architectures significantly reduce deployment speed by eliminating the need for server provisioning and configuration, enabling developers to deploy code updates almost instantly. Maintenance efforts are minimized as the cloud provider handles infrastructure management, scaling, and patching, freeing development teams from routine server upkeep. In contrast, traditional hosting requires manual server setup, ongoing maintenance, and scaling, which can delay release cycles and increase operational overhead.
Flexibility and Integration Capabilities
Serverless architecture offers unparalleled flexibility by automatically scaling resources based on demand, eliminating the need for manual server management prevalent in traditional hosting. Integration capabilities in serverless environments are enhanced through seamless connectivity with cloud-native services, enabling efficient deployment of microservices and APIs. Traditional hosting often requires complex configurations and lacks the dynamic adaptability necessary for rapid integration with modern development tools and platforms.
Use Cases: When to Choose Serverless or Traditional Hosting
Serverless hosting excels in event-driven applications, APIs with unpredictable traffic, and rapid development cycles due to its automatic scaling and pay-per-use model. Traditional hosting is preferable for legacy systems, applications requiring full control over server configurations, or consistent high-load environments where fixed resource allocation provides predictable performance. Developers should evaluate workload variability, control needs, and cost efficiency when deciding between serverless and traditional hosting models.
Impact on Development Workflow
Serverless architecture streamlines development workflows by abstracting server management, allowing developers to focus solely on code and functionality. Traditional hosting requires manual server configuration and maintenance, which can slow deployment cycles and increase operational overhead. Serverless platforms also enable automatic scaling and event-driven triggers, accelerating development speed and reducing infrastructure complexity.
Future Trends in Hosting for Business App Development
Serverless architecture is rapidly gaining traction in business app development due to its scalability, cost-effectiveness, and reduced infrastructure management compared to traditional hosting. Future trends indicate increased adoption of edge computing, AI-driven serverless platforms, and integration with container orchestration tools like Kubernetes to enhance performance and flexibility. Businesses investing in hybrid environments combining serverless and traditional hosting will optimize resource utilization and accelerate innovation.
Serverless vs Traditional Hosting Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com