Small-batch baking emphasizes quality and artisanal techniques, resulting in unique flavors and fresher products made with carefully selected ingredients. Mass production prioritizes efficiency and volume, enabling bakeries to supply large quantities consistently while often using standardized recipes and automated processes. Choosing between these methods depends on customer preferences for handcrafted authenticity or widespread availability.
Table of Comparison
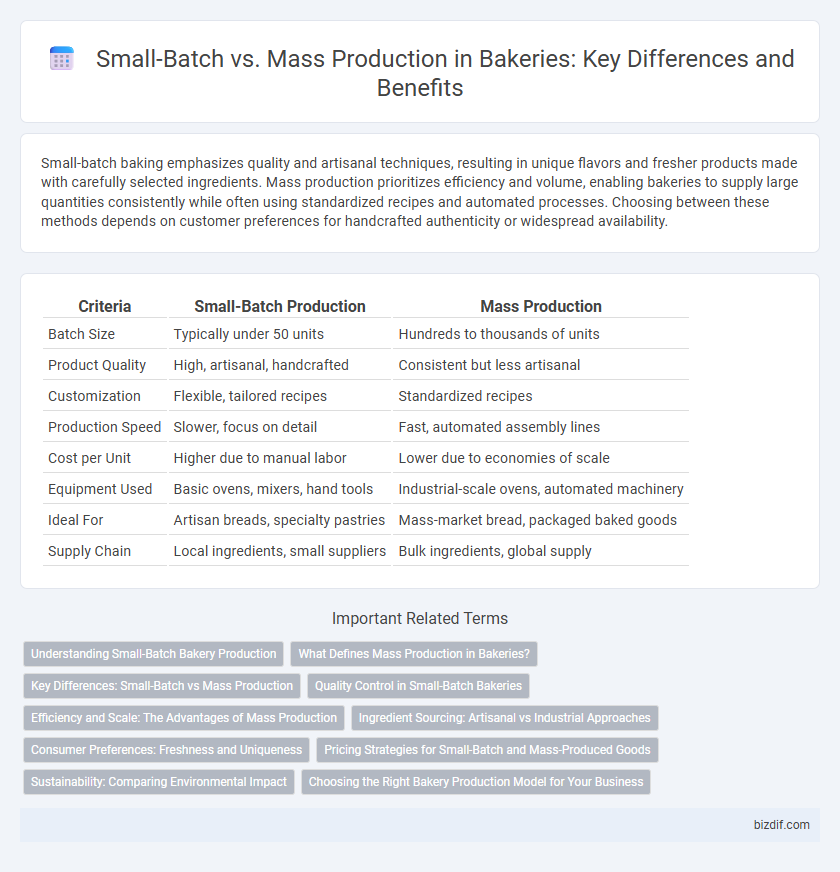
| Criteria | Small-Batch Production | Mass Production |
|---|---|---|
| Batch Size | Typically under 50 units | Hundreds to thousands of units |
| Product Quality | High, artisanal, handcrafted | Consistent but less artisanal |
| Customization | Flexible, tailored recipes | Standardized recipes |
| Production Speed | Slower, focus on detail | Fast, automated assembly lines |
| Cost per Unit | Higher due to manual labor | Lower due to economies of scale |
| Equipment Used | Basic ovens, mixers, hand tools | Industrial-scale ovens, automated machinery |
| Ideal For | Artisan breads, specialty pastries | Mass-market bread, packaged baked goods |
| Supply Chain | Local ingredients, small suppliers | Bulk ingredients, global supply |
Understanding Small-Batch Bakery Production
Small-batch bakery production emphasizes artisanal techniques, resulting in higher-quality, fresher baked goods with unique flavors and textures. This method uses limited ingredient quantities, allowing for precise control over dough fermentation and proofing times, which enhances product consistency and taste. Small-batch bakeries often prioritize local sourcing and handcrafted processes, distinguishing their products from mass-produced alternatives.
What Defines Mass Production in Bakeries?
Mass production in bakeries involves producing large quantities of baked goods using automated processes, standardized recipes, and industrial equipment to maximize efficiency and consistency. It is defined by high-volume output, continuous production lines, and minimal manual intervention, often serving supermarkets and large retail chains. This approach emphasizes uniformity and cost reduction while sacrificing the artisanal quality found in small-batch baking.
Key Differences: Small-Batch vs Mass Production
Small-batch bakery production emphasizes handcrafted techniques, limited quantities, and higher quality control, resulting in more unique and flavorful baked goods. Mass production utilizes automated processes, large-scale equipment, and standardized recipes to achieve consistent output and cost efficiency. Key differences include batch size, flexibility in recipe variation, production speed, and the level of artisanal craftsmanship involved.
Quality Control in Small-Batch Bakeries
Small-batch bakeries maintain rigorous quality control by closely monitoring each step of the baking process, ensuring consistent texture, flavor, and freshness in every product. Unlike mass production, which prioritizes volume, small-batch bakeries prioritize artisanal techniques and ingredient selection, resulting in superior taste and customer satisfaction. This meticulous attention to detail reduces waste and allows for quick adjustments based on real-time feedback, enhancing overall product quality.
Efficiency and Scale: The Advantages of Mass Production
Mass production in bakeries achieves unmatched efficiency by utilizing automated processes that reduce labor costs and increase output consistency. Large-scale operations benefit from economies of scale, lowering ingredient costs and streamlining supply chains. These advantages enable mass-produced baked goods to meet high consumer demand rapidly while maintaining uniform quality.
Ingredient Sourcing: Artisanal vs Industrial Approaches
Small-batch bakeries prioritize artisanal ingredient sourcing, often selecting organic, locally-sourced grains and natural leavening agents that enhance flavor complexity and nutritional value. Mass production relies on industrial suppliers to ensure consistency, cost-efficiency, and scalability by using standardized ingredients such as refined flours and preservatives. This difference impacts product quality, shelf life, and consumer perception of authenticity and freshness in bakery goods.
Consumer Preferences: Freshness and Uniqueness
Small-batch bakery products are preferred by consumers seeking superior freshness and unique flavors, as limited production ensures each item is crafted with attention to detail. Mass production often prioritizes quantity over quality, leading to longer shelf life and uniformity, which may compromise the artisanal appeal. Consumers increasingly value the distinctiveness and premium quality found in small-batch baked goods, driving demand for handcrafted, fresh offerings.
Pricing Strategies for Small-Batch and Mass-Produced Goods
Small-batch bakeries often adopt premium pricing strategies reflecting higher ingredient quality, artisanal techniques, and limited availability. Mass production enables economies of scale, allowing lower per-unit costs and competitive pricing in broader markets. Pricing strategies balance production volume with consumer perception of value and exclusivity in baked goods.
Sustainability: Comparing Environmental Impact
Small-batch bakeries typically generate less food waste and use locally sourced ingredients, reducing carbon footprints compared to mass production methods that rely on industrial-scale operations and extensive supply chains. The energy consumption per unit in small-batch baking is often lower due to manual processes and smaller equipment, whereas mass production demands significant electricity and fuel usage for large ovens and automated systems. Sustainable practices in small-batch production contribute to minimized packaging waste and offer better opportunities for ingredient traceability and organic certifications, enhancing the overall environmental benefits over mass-produced baked goods.
Choosing the Right Bakery Production Model for Your Business
Small-batch bakery production emphasizes artisanal quality, allowing for precise control over ingredient selection and freshness, which enhances flavor and customer satisfaction. Mass production offers high output efficiency and cost reduction through standardized processes and bulk ingredient purchasing, ideal for meeting large-scale demand. Evaluating factors such as target market size, product customization, and resource availability helps bakeries determine the optimal production model to balance quality, scalability, and profitability.
Small-batch vs Mass production Infographic
 bizdif.com
bizdif.com